Browsing: Calcium Deficiency (Hypocalcemia) Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Calcium Deficiency (Hypocalcemia)
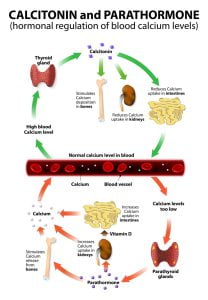
The parathyroid hormone (PTH), secreted by the parathyroid glands, is responsible for regulating blood calcium levels in our body. The hormone is released when blood calcium levels becomes low. PTH increases blood calcium levels by stimulating osteoclasts, which help in breaking down of bones to release calcium into the blood stream.
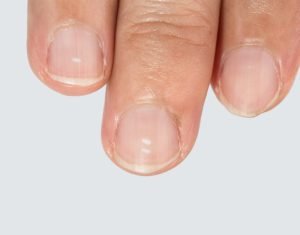
The image shows white spots on fingernails that are caused by a calcium deficiency. Common signs of hypocalcemia are numbness and/or tingling of the hands, feet, or lips, muscle cramps, muscle spasms, seizures, facial twitching, muscle weakness, lightheadedness, and slow heartbeat. Acute hypocalcemia can result in severe symptoms and may require hospitalization.

One main cause of hypocalcemia is low levels of vitamin D. Vitamin D is necessary as it helps the body to absorb calcium from the diet. Foods such as fatty fish, like tuna, mackerel, and salmon, some dairy products like soy milk cheese, etc, orange juice, soy milk, and cereals, mushrooms, beef liver, egg yolks, etc are rich in Vitamin D. Sunlight is the best and natural source of Vitamin D.

The main foods rich in calcium are dairy products such as milk, cheese and yogurt. However, there are several non-dairy sources of calcium also such as seafood, leafy greens, legumes, dried fruit, tofu and various other foods that are fortified with calcium.
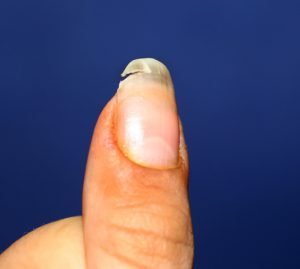
Broken nails could be a sign of lack of enough vitamins and calcium in the body.
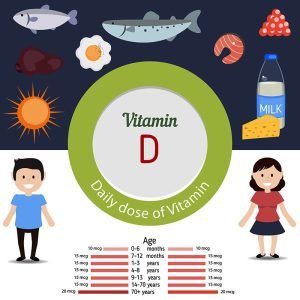
Calcium deficiency occurs due to low calcium levels in the blood. Deficiency of calcium leads to dental changes, cataracts, etc. In severe cases, it also leads to increased risk of disorders like osteoporosis, osteopenia, calcium deficiency disease (hypocalcemia), etc. Hypocalcemia is a common calcium deficiency disease. Complications of hypocalcemia can be life-threatening if it is left untreated. Causes of calcium deficiency can be overuse of medications that decrease calcium absorption, dietary intolerance to foods rich in calcium, hormonal changes, genetic factors, etc. Calcium deficiency can be treated by taking in more calcium and getting enough vitamin D. Vitamin D helps the body to effectively absorb calcium. The image shows daily dosage of vitamin D required by men and women at a certain age.
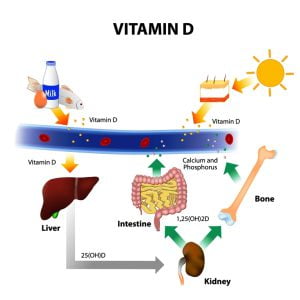
Calcium and vitamin D are two essential components necessary to build strong and dense bones. Calcium helps in blood clotting, muscles contractions, pumping of heart, etc. Our bones and teeth are made up of calcium (upto 99%). The function of Vitamin D is to absorb maximum amount of calcium. Calcium deficiency or hypocalcemia leads to bone fractures, tooth loss, osteoporosis, etc. Food sources of calcium and vitamin D are some dairy products, fish, spinach, beef liver, etc. About 75% of calcium absorption takes place in the intestinal tract (lower segment of the small intestine). The presence of Vitamin D helps calcium to enter the blood stream via the gut. Calcium is absorbed by the liver, kidney, small intestine, bones, etc.
ADVERTISEMENT



