Browsing: Ovarian Cyst
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Ovarian Cyst
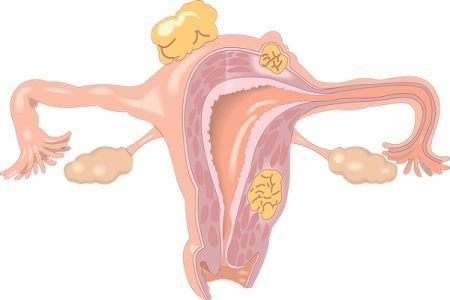
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Cysts usually refer to fluid-filled sacs that are not a normal part of the tissue where they are found. Ovarian cysts are the cysts that are found within or on the surface of an ovary. Most ovarian cysts are small and harmless. They occur most frequently during the reproductive years, but can affect women of any age.
Ovarian Cyst During Pregnancy
Women with cysts caused by endometriosis and due to polycystic ovaries syndrome are infertile and cannot conceive naturally as their ovaries are not working right and they are most probably not ovulating too. These women also suffer from an ovulation disorder which prevents the ovaries from releasing a mature egg for fertilisation.
Pain associated with an ovarian cyst is an unpleasant symptom and fairly common. The pain can be dull or sharp and either constant or intermittent and may come and go. Ovarian cyst pain is usually felt in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst.
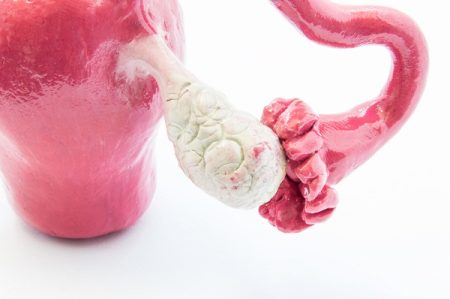
Ovarian cysts which are not part of a normal menstrual cycle are also known as ovarian tumours. Some tumours are filled with fluid and some are solid. Most ovarian cysts resolve spontaneously and are harmless. But if your cyst is causing you pain or discomfort you may need surgery for it.
Most cysts never get noticed and resolve without the woman even noticing that they had cysts. Most ovarian cysts dissolve and disappear on their own after several menstrual cycles. It is logical to think that when you stop having periods, chronic conditions of your female reproductive organs will also go away.
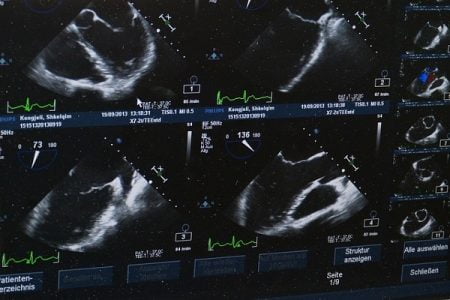
Ovarian Cyst Ultrasound
The first step in the diagnosis of a ruptured ovarian cyst is an ultrasound also called ultrasonography that allows your doctor to see inside of your abdomen. In case of a ruptured ovarian cyst, the ultrasound usually will show some fluid around the ovary, and may even show the empty sac.
Ovarian cyst rupture is a medical complication in which the cyst ruptures causing intense pain and internal bleeding in the pelvic region. Ovarian cysts rupture when there is too much fluid accumulation inside the sac and the sac cannot withstand the resulting pressure. The sac then simply tears, hence the rupture or burst.