Browsing: Tuberculosis
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Tuberculosis
What Is Tuberculosis?
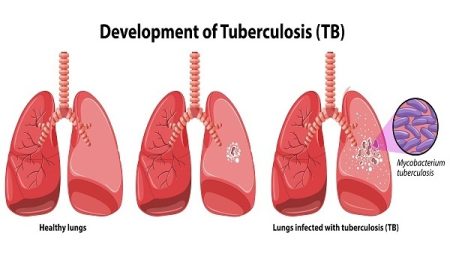
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The infection is generally hidden i.e. it does not cause any visible symptom. About 10% of such infections of this disease advance into an active condition. If the disease is left untreated, it can become fatal.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Tuberculosis (TB)?
The diagnosis of tuberculosis is based on the detection of the presence of M.tuberculosis in the clinical specimen taken from the patient. The healthcare professional may evaluate the medical history of the patient along with physical examination and X-ray. No single test is used for the diagnosis in all circumstances.
Prevention of Tuberculosis (TB)
The main focus in tuberculosis prevention strategy is to stop the transmission of infection from one person to another. This is done by identifying the person with active tuberculosis and curing him/her with drugs. With proper treatment, the patient becomes non-infectious and is no longer able to transmit the disease.
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria. If the disease is left untreated, it can be fatal. The bacteria can live in the body of the host without making him/her sick. The person may or may not feel any obvious symptoms of the condition in the beginning. When the bacteria actively multiply, symptoms become visible.
What Causes Tuberculosis (TB) and What are the Risk Factors for Tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent of tuberculosis infection in humans. These bacteria are slow growing and oxygen utilizing and can grow in our body cells. The bacterium has a cell wall that helps to protect it from the body’s immune system and defense mechanism. It is an intracellular parasite.
What is the Treatment of Tuberculosis?
The objective of the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) is not only to cure the patient but also to prevent the outspread of the infection. The treatment is directed towards inhibition of bacteria causing latent infection, which can further develop into an active one if not treated well.
Treatment of tuberculosis is a challenging task because of heterogeneous sites of infection. Even with proper treatment, tuberculosis (TB) can cause major health complications. Lungs are the primary site of infection by M.tuberculosis. If it is left untreated, the disease can cause many fatal complications.