Browsing: Rickets in Children
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Rickets in Children
First Treatment for Rare Form of Rickets Approved by FDA
Burosumab (KRN23) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that binds excess fibroblast growth factor 23. The FDA has approved it as the first treatment for a rare and inherited form of rickets called X linked hypophosphatemia.
Hypocalcaemia occurs when the total serum calcium concentration is less than 7.0 mg/dL and the ionized calcium is less than 3.5 mg/dL in your body. It is a commonly seen biochemical condition in which there are lower than average level of calcium in plasma. Calcium has many important functions in your body.
An Overview of Rickets Disease
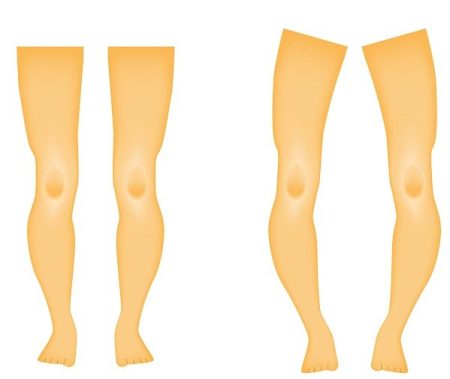
Rickets is a condition that affects the development of bones in children. It affects the skeleton causing the bones to become weak and soft. Weak and soft bones lead to skeleton deformities and poor growth. Rickets is caused by a severe and prolonged deficiency of vitamin D.
Rickets in the Twenty-First Century: Current State and Future Directions
What is rickets? Rickets is a bone deformity which occurs due to de-mineralization in a growing bone. Rickets mainly occur…
The increasing number of rickets cases is an alarm that children should be provided with proper nutrition to avoid such…