Browsing: Epilepsy Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Epilepsy
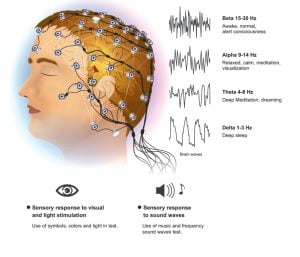
The image shows a representation of EEG or electroencephalogram. It is a test to record the electrical signals of the brain. Doctors generally use it to help diagnose epilepsy and sleep problems. Other tests such as CT scan, MRI scan, MRS scan, blood test, etc can also help in the diagnosis of epilepsy. EEG is the most common test to record electrical activity in the brain and is the most commonly used method for epilepsy. High-density EEG helps in determining areas of the brain which are affected by seizures.
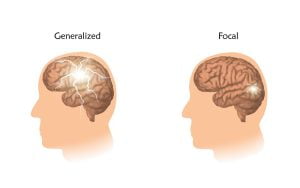
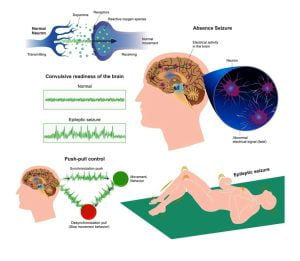
There are different types of seizures. Most seizures are categorized as focal or generalized. Focal seizures occur when seizure activity is limited to a part of a brain hemisphere. Generalized seizures occur when there is widespread seizure activity in the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
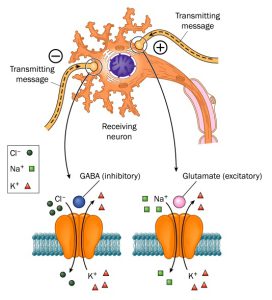
One of the most important neurotransmitters that plays a role in epilepsy is GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Researchers have identified drugs which alter the amount of GABA in the brain or change how the brain responds to its activity.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder in which the brain activity becomes abnormal and results in seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes leads to loss of awareness. Epileptic seizures occur when electrical impulses in the brain escape their normal limits and spread to neighboring areas. This creates an uncontrolled storm of electrical activity. This results in twitches or convulsions. Epileptic seizures are of two types i.e. focal seizures (or partial seizure) and generalized seizures. Seizures may occur after a stroke, a closed head injury, infection such as meningitis or another illness, etc.
ADVERTISEMENT