Browsing: Gallbladder Cancer Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Gallbladder Cancer
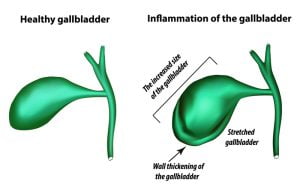
Gallbladder inflammation is commonly found in gallbladder cancer cases. For example, if someone has gallstones, the gallbladder may release bile more slowly. This indicates that gallbladder cells are exposed to the chemicals in bile for longer than usual. Scientists believe that inflammation of the gallbladder may have some role in the development of the cancer of gallbladder.
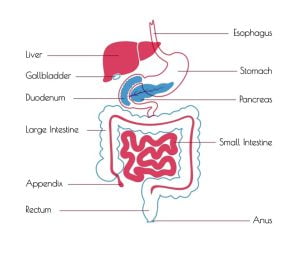
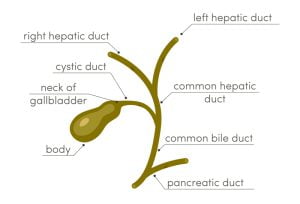
Human digestive system converts food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth and cell repair. The digestive tract is made up of gastrointestinal tract (mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus), liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small storage organ as it holds bile juice (needed for digesting fatty foods in the duodenum of the small intestine) produced in the liver. Cancers can develop in the gallbladder though they are rare and diagnosed in later stages. Gallbladder cancer starts in the glandular cells which line the inner surface of the gallbladder.
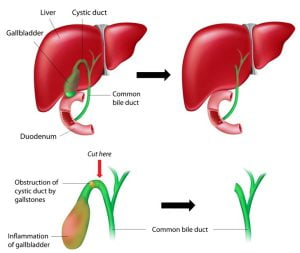
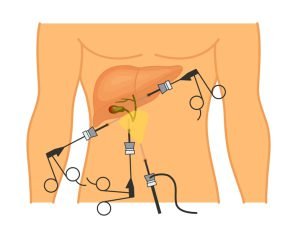
The operation to remove the gallbladder is called Cholecystectomy. It is done in conditions involving gallbladder such as gallstones, gallbladder cancer, etc.
Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped, hollow structure located under the liver and on your right side of the abdomen. The primary function of your gallbladder is to store and concentrate bile, which is a yellow-brown enzyme produced by the liver to help in digestion. It is part of your biliary tract. Cancerous tumors may somtime develop in the gallbladder, though this is rare. Gallbladder cancer is generally not detected at an early stage because the gallbladder is located deep inside the body.
Bile ducts carry bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to the duodenum (a part of small intestine). Bile is a dark-green or yellowish-brown fluid that is produced by the liver to digest fats. Cancer of the gallbladder can spread to the nearby tissues including bile ducts.
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. The operation is done to remove the gallbladder in conditions such as gallstones causing pain or infection or gallbladder cancer etc. Clinical trials and meta-analyses show that incidental gallbladder cancer occurs in 0.19%–2.8% of patients after cholecystectomy. Depending on the stage and spread of the cancer, your doctor and cancer team may recommend a cholecystectomy.
ADVERTISEMENT