Browsing: Prostate Cancer
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Prostate Cancer
Cancer detection is an important process that helps identify the presence of cancerous cells early enough to improve treatment outcomes.…
Introduction: A Cancer Screening Conundrum Prostate cancer screening is a hot-button issue in the medical community. With the potential to…
There are more than 100 known types of cancer, a disease that involves abnormal cell growth in one or more…
Cancer treatments can cause several changes to your body. There are some side effects of each type of cancer treatment, which different people experience differently. As you prepare yourself for cancer treatment, you may benefit from these coping strategies.
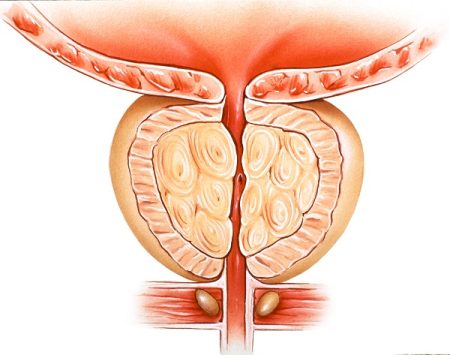
Prostate gland is a chestnut-shaped male reproductive organ that contains not just one but about 30-50 glands. It is located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate secretes a milky fluid that is discharged into the urethra at the time of the ejaculation of semen.
Women have small glands on the front side of the vagina. These are called “Skene’s glands” or “Skene’s ducts. Skene’s glands are considered analogous to male prostate because of similarities with the prostate. One similarity is the presence of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and PSA phosphatase (PSAP) in both the male prostate and the Skene’s glands.
There is no ‘one size fits all’ treatment for prostate cancer. Your physician will evaluate your condition and make a decision about what is best for you. The decision-making process for treatment may include a combination of clinical and psychological factors such as the following. You should discuss all of them with your doctors before drafting a plan of treatment.
What are the early warning signs of prostate cancer? Usually, there aren’t any. Often, prostate cancer does not cause any signs and symptoms in the beginning. Signs begin to appear only after the cancer has spread large enough to influence functioning of the urethra. At this stage, the cancer is much advanced and can cause troubles particularly of urination.
According to the Urology Care Foundation, prostate cancer is the second most common cause of all cancer-related deaths among American…
Prostate cancer grows slowly and is initially limited to the prostate gland only. Therefore, it does not show any symptoms…