Browsing: Thyroid Cancer Graphics
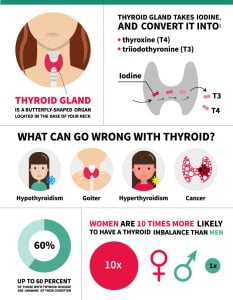
Thyroid cancer is uncommon as compared to other cancers. In the United States, it is estimated that approximately 65,000 new patients will be diagnosed with thyroid cancer in 2016, compared to about 250,000 patients with breast cancer.
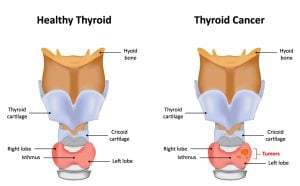
Thyroid cancer develops in the cells of the thyroid gland — a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck. Your thyroid produces hormones that regulate your heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature etc.
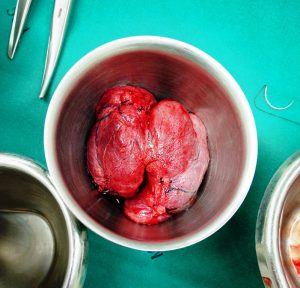
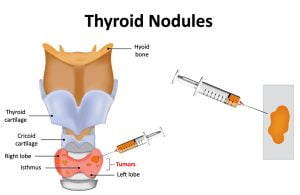
Thyroid nodule refers to an abnormal growth of thyroid cells which form lumps within the thyroid gland. In most of the cases, thyroid nodules are benign or noncancerous which can be detected with the help of fine needle biopsy. If the cells are found to be malignant, they indicate thyroid cancer. Thyroid nodules can be removed even at a very early stage to avoid the development of thyroid cancer for high risk patients. Thyroid nodules are removed during the surgical procedure to remove thyroid, known as a lobectomy or a total thyroidectomy.
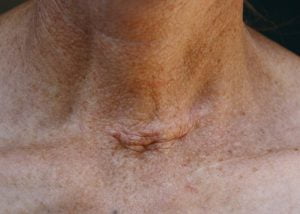
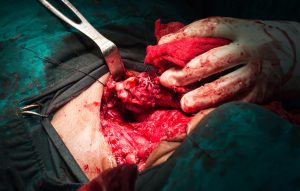
Surgical neck scar after removal of the thyroid gland due to thyroid cancer. Removal of a part or complete thyroid gland is known as thyroidectomy whereas removal of any one of the lobes of the thyroid is known as lobectomy. The incision created is of four to five inches in length (depending on the type of surgery) and on the lower portion of the patient’s neck. The scar might stay life-long in some cases.
Thyroidectomy is a surgery to treat thyroid disorders, such as cancer, noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid (goiter) and overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). It involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland.
Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) of the thyroid is a diagnostic procedure to detect cancer in a thyroid nodule or to treat thyroid cysts. A fine needle aspiration biopsy of a thyroid nodule is a simple and safe procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office. You may feel some pressure in the neck from the ultrasound device and the needle.
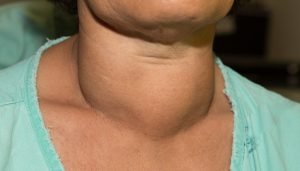
A closeup frontal view of enlarged multinodular thyroid goitre in a woman. The vast majority of thyroid goiters are benign (non-cancerous). But these symptoms are sometimes caused by thyroid cancer. Enlargement of the thyroid is due to the deficiency of iodine in diet. In multiple cases, goiter occurs due to the over or underproduction of thyroid hormones forming lumps. To detect whether goiter has resulted into thyroid cancer, a biopsy is
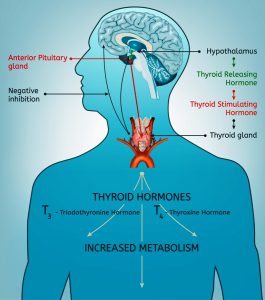
The thyroid system involves three glands to work together to produce thyroid hormones. These are thyroid gland, hypothalamus and the pituitary. The thyroid system maintains hormone balance. When an imbalance is created during the production of thyroid hormones, it may lead to the formation of lumps or tumor in the thyroid gland. These lumps can be cancerous and lead to thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer can be detected by performing biopsy of thyroid tissue.
ADVERTISEMENT