Browsing: Celiac Disease Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Celiac Disease
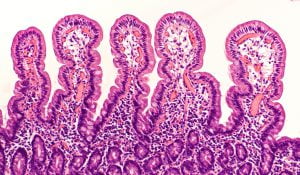
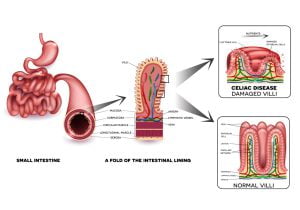
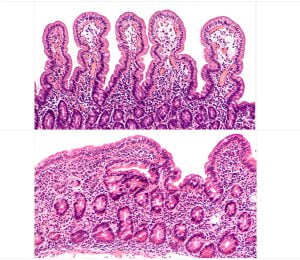
The picture shows a microscopic view of small intestine with normal elongated villi. The elongated villi increases the surface area for absorption of nutrients. If you have celiac disease, the villi are flat, which causes diarrhea.
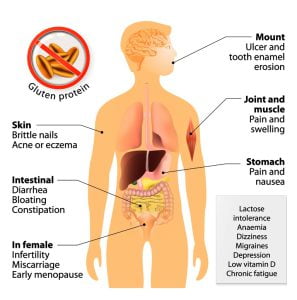
The most common symptoms of celiac disease are diarrhea, bloating, gas (flatulence, farting), swollen ankles, anemia, fatigue, vitamin K deficiency, bruising and bleeding. In celiac disease, consuming gluten triggers an immune response in the body which causes inflammation and damage to the small intestine. Celiac disease is not an allergic reaction to something; therefore, the symptoms vary in this case. Other associated signs are bone or joint pain, arthritis, osteoporosis or osteopenia (bone loss), liver and biliary tract disorders, missed menstrual periods, infertility or recurrent miscarriage, dermatitis herpetiformis (itchy skin rash), etc.
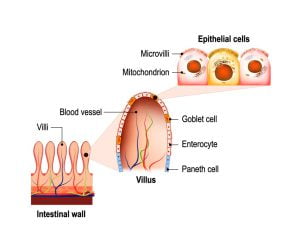
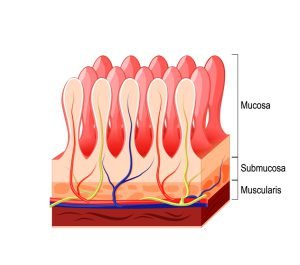
Digested food is able to pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the small intestine through a process called diffusion. The inner wall (called mucosa) of the small intestine is covered with folds called plicae circulares that project finger-like projections of tissue called villi. Celiac disease damages these villi.
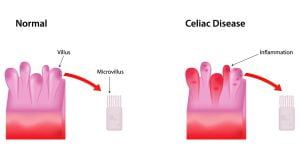
Celiac disease is a problem that results in the damage of the lining of the small intestine when foods with gluten are eaten. The tiny, finger-like projections which line the bowel (villi) become inflamed when food with gluten is eaten.
A horrible truth of celiac disease is that though the damage affects the gut, only 40% of children and 60% of adults report digestion-related symptoms. During celiac disease, when a person eats something with gluten, their body overreacts to the protein and damages their villi. When the villi are injured, the small intestine is unable absorb the nutrients from food properly. This in-turn leads to vomiting, chronic diarrhea, swollen belly, delayed puberty, etc
Villi are small, finger-like projections in the small intestines that help absorb the nutrients. The blunting or flattening of the villi can be caused by the damage done by the immune system due to celiac disease after ingesting gluten-containing foods.
For people with celiac disease, gluten disrupt the lining of the small intestine and triggers an immune response that attracts inflammatory cells and causes inflammation. Such people must avoid gluten-containing foods. Gluten intolerance is also known as gluten sensitivity. There are several gluten free foods which can be taken during celiac disease to avoid any discomfort. Some of them are fruits, vegetables, eggs, low-fat dairy products, etc. Processed foods, bakery products, some grains such as (wheat, barley, rye, etc) are not gluten free. Therefore, they should be avoided. There is no treatment of celiac disease except a strict gluten-free diet.
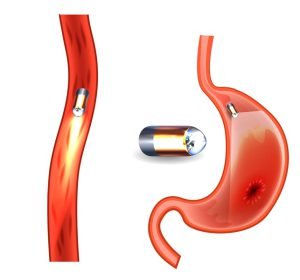
Capsule endoscopy is a procedure that uses a tiny wireless camera to take pictures of your digestive tract. This helps in diagnpsis of GI problems such as esophageal cancer.
ADVERTISEMENT