Browsing: Bladder Cancer Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Bladder cancer
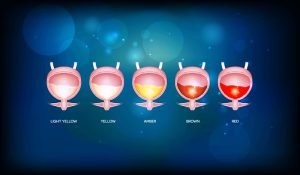
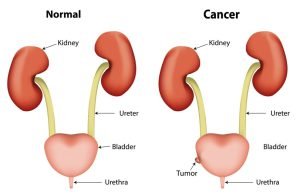
Bladder is a hollow, muscular organ in lower abdomen in the body that holds urine. Bladder cancer begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of bladder. During early stages of bladder cancer, no noticeable signs or symptoms of the disease are observed until the tumor has grown far enough into the bladder wall. Common symptoms for bladder cancer are back, pelvic or groin pain, painful urination, blood in urine (hematuria), etc. Hematuria is the most common sign in which the color of the urine changes from pale yellow-red to bright or rusty red due to the presence of blood or blood clots.
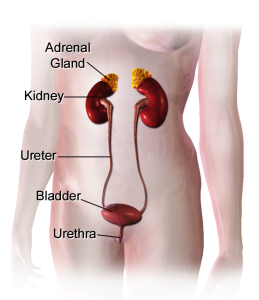
The urinary system in females is divided into upper and lower sections. The upper section comprises of the kidneys and a tube called the ureter. The lower section consists of the bladder and another tube called the urethra. The urinary system helps in the removal of waste products from the body, regulate water and salt balance, and stores and transports urine. The female urethra is much shorter than the male urethra. In females, the bladder lies in the front of the vagina and the uterus and anterior portion is fastened with the pubovesical ligament. Women are at a lower risk of bladder cancer than men, but are more prone to its advanced stages which results in unfavorable outcomes.
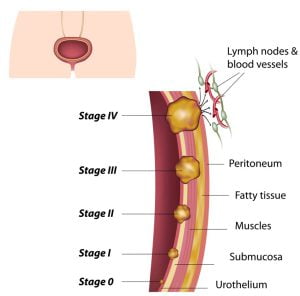
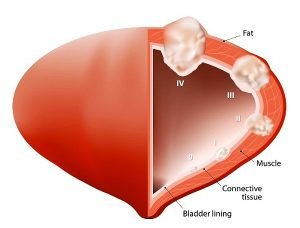
The type of a cancer tells you what type of cell it originally started in. The grade of a cancer tells how much the cancer cells look like normal cells. The stage of cancer defines the size of the cancer and whether it has spread beyond the original site. All this information helps your doctor decide the treatment you need.
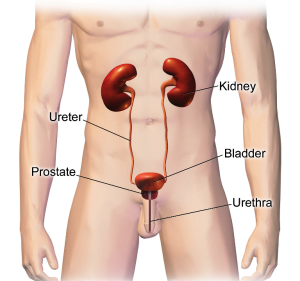
The urinary system is divided into upper and lower sections. The upper section comprises of the kidneys and a tube called the ureter. The lower section consists of the bladder and another tube called the urethra. The urinary system helps in the removal of waste products from the body, regulate water and salt balance, and stores and transports urine. In males, the urethra is a long tube that runs from the bottom of the bladder to the opening where urine exits the body. Bladder, in males, is located in front of the prostate gland (attached by puboprostatic ligament). Men have three times higher chances of getting bladder cancer than women.
Bladder cancer begins when cells in the urinary bladder start to grow uncontrollably. As more cancer cells develop, they can form a tumor and spread to other areas of the body. In the beginning, abnormal cells are found in tissues lining the inside of the bladder.
Bladder cancer staging specifies extent of the disease. Using degrees from 0 to 4, your doctor can identify your bladder cancer stage and develop a treatment plan for you. The early stages of bladder cancer generally cause bleeding but little or no pain or other symptoms. Blood in the urine (hematuria) does not always indicate that you have bladder cancer. Sometimes, it is caused by other conditions such as an infection, non-cancerous tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder.
Blood in the urine (hematuria) sometimes is a sign of bladder cancer. This cancer typically affects older adults. It’s usually diagnosed early, when it’s easier to treat it.
ADVERTISEMENT