Browsing: Brain Cancer Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Brain cancer
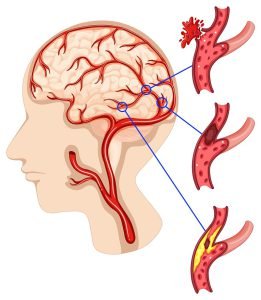
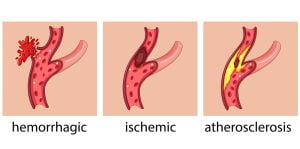
This picture represents changes in the blood vessels due to brain cancer. These changes lead to the development of several brain cancer symptoms.
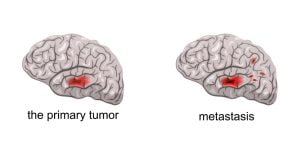
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in the brain. A primary brain tumor is a tumor which starts in the brain tissue. If a cancerous tumor starts elsewhere in the body, which spreads cancerous cells in the brain, the type of tumors are known as secondary or metastatic brain tumors.
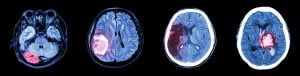
This image represents a collection of CT scan of brain and images of various brain diseases (Left to Right : Normal brain, Brain tumor, Cerebral infarction, Intracerebral hemorrhage)
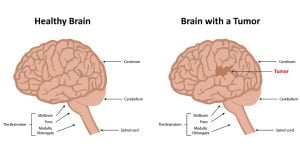
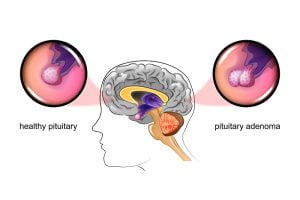
The image shows differences between a healthy brain and a brain containing tumor. Imaging tests such as MRI and CT scans are used to show an abnormal area that is likely to be a brain tumor. But often these scans can’t exactly tell what type of tumor it is.
Pituitary adenomas are slow-growing and benign cells. With their growth, they start creating pressure on the nearby structures, such as the nerves that connect the eyes to the brain, and cause various symptoms. About 8 out of 100 (8%) of brain tumours are in the pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small gland found inside the skull just below the brain and above the nasal passages.
Brain metastases occurs when cancerous cells from the brain start spreading to other parts of the body. Any cancer can spread to the brain, but the types which lead to brain metastases are mainly cancer of lung, breast, colon, kidney and melanoma. Brain metastases, or secondary brain tumors, occur in 10-30% of adults suffering from cancer.
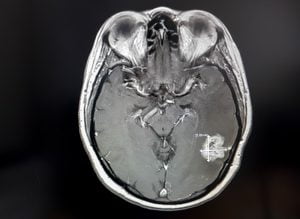
The image represents an MRI scan of brain tumor. An MRI scan is used to diagnose a brain tumour. Specialised MRI scans called magnetic resonance angiography (MRA scans) show blood vessels in your brain. Another type of MRI scan, known as functional MRI (fMRI) helps in planning a surgery.
Brain cancer can cause symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke. The symptoms of a stroke caused by an intracerebral hemorrhage due to cancer or tumor are different from typical stroke symptoms. This is because most strokes happen due to a sudden blockage of blood flow to a region of the brain, which causes stroke symptoms to develop suddenly.
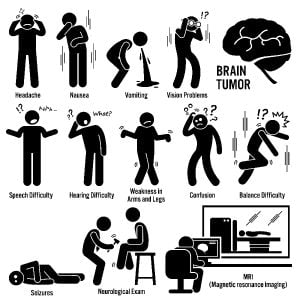
Brain cancer shows several symptoms such as those depicted in the image. It requires several diagnostic techniques to identify presence of cancerous cells in a person’s brain.
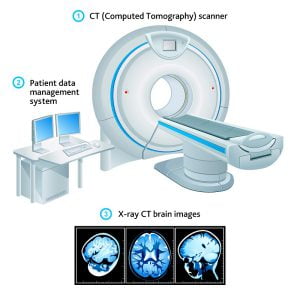
A CT scan uses x-rays to make detailed cross-sectional images of your brain and spinal cord. They are not used as often as MRI scans are used for the diagnosis of brain cancer. But they are also useful in some cases.
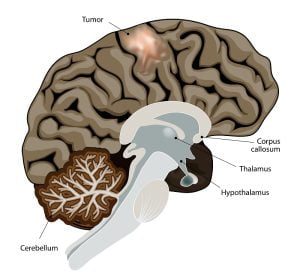
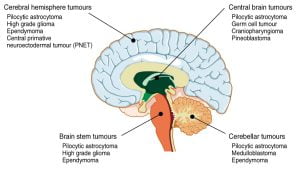
The image illustrates brain tumours of the cerebral hemisphere, brain stem, cerebrum and brain centre. These are common brain tumor locations. The brain stem, located under the cerebrum and in front of the cerebellum, joins our brain to the spinal cord. The brain stem itself controls many bodily functions required for life, such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure and alertness.
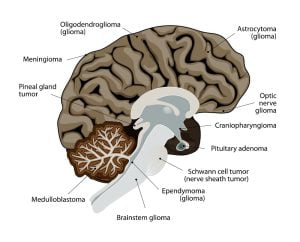
Different types of brain tumors exist. They are categorized on the basis of the type of cell where the tumor intiates. The most common types of primary brain cancer are gliomas, meningiomas, schwannomas, craniopharyngiomas, germinoma and pineal gland tumor.
ADVERTISEMENT