Browsing: Eczema Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Eczema
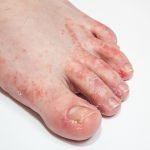
Dyshidrotic eczema, also known as dyshidrosis or pompholyx, is a type of eczema which leads to blistering rash on your hands or feet, especially on the fingers, palms, and soles. These blisters are small and often very itchy.
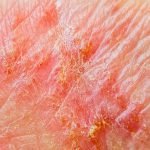
There is no permanent cure for eczema, but it is possible to manage the condition. To treat eczema, doctors aim to reduce the symptoms, heal the skin and prevent further skin damage, and prevent flare-ups. Multiple medical treatments such as anti-inflammatory medications, and steroid creams help in reducing the impact. Antibiotics are also recommended to clear the affected irritation and reduce allergies. Some home remedies are also beneficial in treating eczema and improving the health of skin.
Eczema on your hands can be uncomfortable and frustrating. It is generally job-related and can get worse by factors such as frequent hand washing and exposure to chemicals.
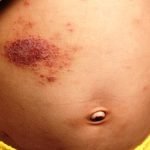
The picture shows a close-up eczema atopic dermatitis symptom with infected skin on a child’s body. Generally, eczema begins with redness, itchiness or rashes. Skin inside the elbows, behind the knees, and the front of the neck are very commonly affected by it. The symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary in all cases. Some of them are dry skin, red to brownish-gray patches, small and raised bumps, with leaking fluid and crust over when scratched, thickened, cracked, scaly, raw and swollen skin.
Eczema can cause your child’s skin red, raw, and painful. You can help prevent or manage eczema by keeping your child’s skin from becoming dry or itchy. Avoiding known triggers that cause the flare-ups in your child is importan.
Symptoms of eczema on hand, also known as hand dermatitis are redness, blistering, cracking, flaking, and itching of the palms or fingers. Dyshidrotic eczema (dyshidrosis) is a specific type of hand eczema, which is more common in women than in men.
The image shows an enlarged view of hand suffering with eczema disease.
ADVERTISEMENT