Browsing: Migraine Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Migraine
Everyone has different migraine triggers, but there are a few common reasons that affect a large number of people living with migraine. Common migraine trigger factors include changes in routine, weekend headaches, stress, sleep, caffeine, hormonal changes and environmental factors. Fluctuations in estrogen seem to trigger headaches in many women. Not every migraine is associated with a trigger. But if your migrain is, one of the best ways to prevent them is to learn your triggers and try your best to avoid them.
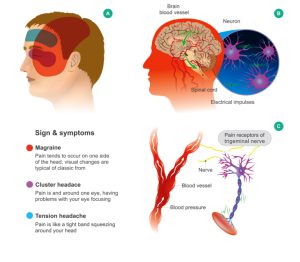
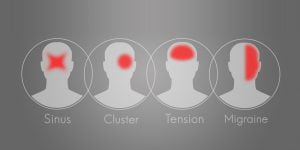
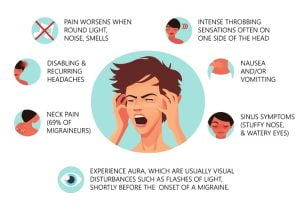
Migraines are severe headaches due to specific changes within the brain. Migraine pain can be throbbing or feel like a pulsing sensation. It generally occurs on just one side of the head for hours and may be for days in some cases. Migraine pain can be triggered due to headaches, such as allergies, light, and stress. Migraine can be felt like a normal headache, hemiplegic migraine (weakness on one side of the body, loss of sensation, or feeling of pins and needle in head), retinal migraine (resulting in temporary vision loss), cluster headache (excruciating pain around the eye), etc.
Migraine attack begins in the brain and involves nerve pathways and chemicals. The changes due to this affect the blood flow in the brain and surrounding tissues. Migraine begins due to waves of activity by groups of excitable brain cells which trigger chemicals, such as serotonin, to narrow blood vessels which results in pain. Alterations in structure and functions include the presence of sub-cortical white mater lesions, thickening of cortical areas involved in processing sensory information, and cortical neuroplastic changes induced by cortical spreading depression, which leads to migraine. Dopaminergic activation also plays a role in the headache phase, either by taking part in nociception mechanisms, or by regulating cerebral blood flow.
A migraine causes severe throbbing pain or a pulsing sensation, usually on one side of your head. It is accompanied with nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound. If you suffer with chronic migraine, the symptoms may occur 15 days or more every month. Medications can help prevent migraines and reduce their symptoms. Physical activity may intensify the pain.
Headache is an extremely common condition that causes pain and discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck region. It’s estimated that 7 in 10 people have at least one headache each year. Headache is the most common sign of migraine. Migraine headache is a result of certain changes within the brain. It causes severe head pain that is usually accompanied by sensitivity to light, sound, smells etc.
Migraines are recurring headaches due to abnormal brain activity, hormonal changes, stress, physical overexertion, etc. Some common symptoms of migraine are nausea or vomiting, about 1/3 of migraine patients suffer from neck pain, sinus symptoms, pain in eye, etc. The symptoms of migraine are specifically divided into 4 stages. Stage 1 is referred to as prodrome which includes mood swings, frequent yawning, neck stiffness, etc. Stage 2 is aura which leads to visual phenomena, such as bright spots or flashes of light, vision loss, speech or movement difficulty, etc. Stage 3 is attach which includes throbbing pain on one side or both sides of your head pain, sensitivity to light, sounds, and sometimes smells and touch, lightheadedness, etc. Stage 4 is post-drome which occurs after a migraine
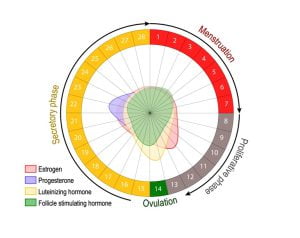
Some women experience migraine symptoms during menstruation, due to changing hormone levels (estrogen and progesterone). This is known as menstrual migraine. Menstrual migraine occurs due to declining levels of estrogen. The causes of menstrual migraine are overuse of birth control, hormone replacement therapy, menopause, pregnancy, etc. Lower hormone level triggers migraine pain during menstrual cycle. Over the counter medicines are preferred to reduce migraine pain and discomfort in such conditions.
ADVERTISEMENT