Browsing: Prostate Cancer Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Prostate Cancer
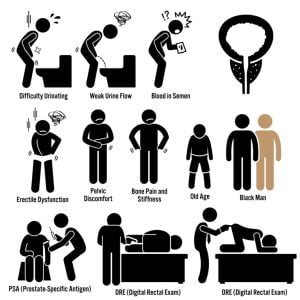
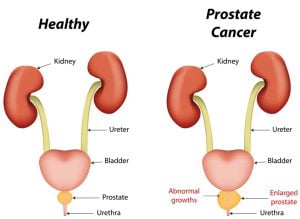
Prostate cancer begins when cells in the prostate gland start to grow uncontrollably. The prostate is a gland found only in males and is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. Some common symptoms are difficult or painful urination, blood in the urine, painful ejaculation, difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, discomfort in the pelvic area, etc. Risk factors associated with it are age, obesity, genetics or family history, etc. For treatment, the doctor may first keep the patient under surveillance and regular checkups. Surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy, etc are common treatment options for severe stages.
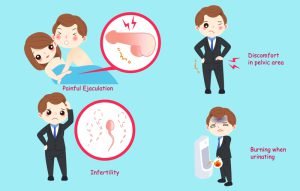
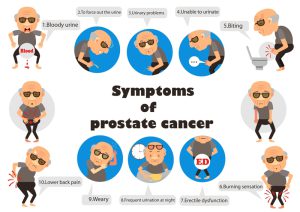
The picture shows some major problems that can occur in prostate cancer. It can lead to painful ejaculation and infertility in men. Some common symptoms of prostate cancer are burning or pain during urination, frequent urges to urinate at night, loss of bladder control, swelling in legs or pelvic area, blood in urine (hematuria), blood in semen, erectile dysfunction, etc. If the cancer has metastasized, fatigue, change in bowel habits, unexplained weight loss, pressure or pain in the rectum, numbness or pain in bone, etc are commonly observed symptoms.
The digital rectal examination (DRE) is a procedure in which a physician tries to feel the surface of the prostate with a gloved finger. The doctor is able to feel any lumps or hard areas on the prostate with this procedure. After DRE, PSA (prostate specific antigen) exams are conducted to check for levels of prostate-specific antigen in the blood, with higher levels signaling potential cancer. The level of these antigens is also higher in case of benign prostatic hyperplasia, or infection or inflammation of the prostate. To confirm the diagnosis after physical examination, a biopsy may be done.
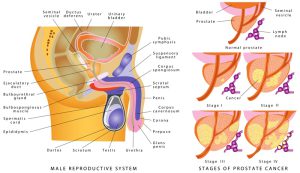
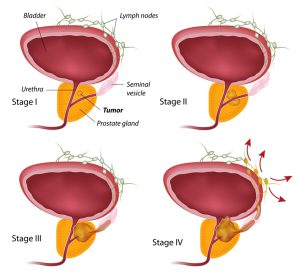
The graphics show a male genitourinary system, anatomy of the male reproductive system, and stages of prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men.
Prostate cancer is a cancer that occurs in the prostate gland — a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men worldwide.
Common symptoms of prostate cancer in men are – burning sensation, pain during urination, difficulty in urinating, trouble starting and stopping while urinating, frequent urge to urinate at night, incontinence, loss of bladder control, etc.
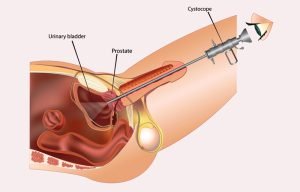
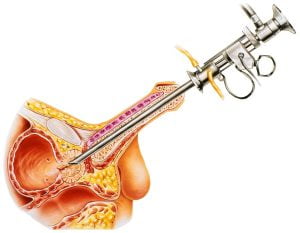
Transurethral Resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure to remove tissue from the prostate using a resectoscope. The device is inserted through the urethra in men via the tip of your penis.
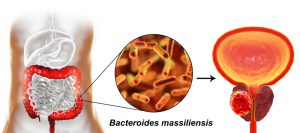
Research indicates that there might be an association between the gastrointestinal microbiome and prostate cancer risk.
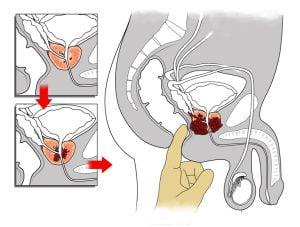
After the diagnosis of prostate cancer, doctors try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, to what extent. This process is called staging. The stage of a prostate cancer describes how much cancer is there in the body of a patient. It ihelps determine how serious the cancer is and what options should be considered to treat it.
ADVERTISEMENT