Browsing: Stargardt Disease Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Stargardt Disease
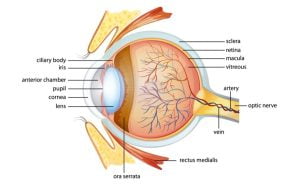
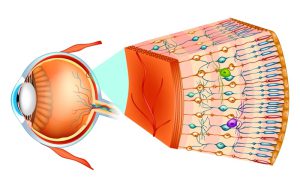
Eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe of about an inch in diameter. Parts of eye include iris, cornea, pupil, sclera, conjunctiva and retina. The retina is the sensory membrane which lines with the inner surface of the back of the eyeball. Light rays are focused onto the retina by the cornea and lens, where vision begins. The macula is a small and sensitive area of the retina which controls central vision and color vision. The death of photoreceptor cells in the central portion of the retina (called the macula- responsible for sharp central vision) leads to Stargardt disease. The function of photoreceptor cells in the retina (light sensitive tissue) of the eye is to provide vision by conveying information from the visual field to the brain.
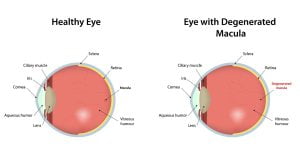
Stargardt disease is also called juvenile macular degeneration. It causes progressive damage or degeneration of the macula. Macula (as shown) is a small area in the center of the retina that is responsible for sharp, straight-ahead vision. Macula is the functional center of your retina in the eye. It is responsible to give an ability to see “20/20” vision and provides the best color vision.
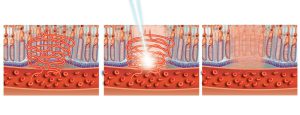
Sequence of three images shows the laser treatment of macula such as in macular degeneration or juvenile macular degeneration. Unfortunately, there is no known cure for Stargardt’s. Some patients may need laser treatment to seal leaking blood vessels in the retina. Laser treatment is performed to reduce lost vision from leaking vessels. But the treatment does not restore vision or stop the progression of the disease.
Stargardt disease is also called Stargardt macular dystrophy, juvenile macular degeneration, or fundus flavimaculatus. It is the most common form of inherited juvenile macular degeneration. It often has an autosomal recessive inheritance that is caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene. In only rare cases (about 1 in 20,000), macular degeneration is diagnosed in children and teenagers. Of those rare cases, the most common cause is Stargardt disease.
Photoreceptors are light-sensing cells present in the retina and are of two types: rods and cones. The function of rods and cones is to detect light and convert it into electrical signals sent to brain. Rods helps to see in dim and dark lighting and cones help us see fine visual details and colors. In Stargardt disease, these rods and cones die and cause impaired vision. Mutations in genes is one cause of Stargardt disease. It also leads to retinal dystrophy.
ADVERTISEMENT