Browsing: Supernumerary Teeth Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Supernumerary Teeth
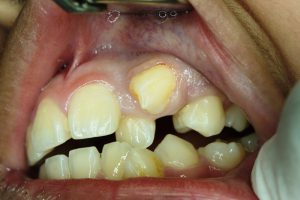
High canine position and tooth crowding in a patient because it has not enough space for tooth eruption in upper jaw. Crowding is the lack of sufficient space for all the teeth to fit normally within the jaws. The teeth may be rotated or displaced.
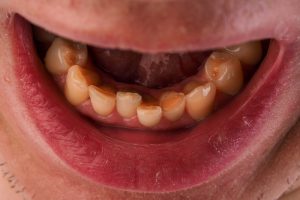
Dental crowding also called malocclusion is a hereditary condition that is characterized by an insufficient amount of space for all the teeth to properly fit within the mouth. Losing your primary teeth too early or an improper growth of teeth can also cause teeth crowding.
Common tooth disease: Sensitive teeth, caries, calculus, gingivitis, periodontitis and bad breath.
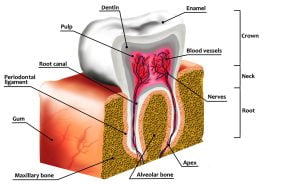
The image shows anatomy of human tooth decay and tooth loss. Tooth decay is the breakdown of teeth due to acids made by bacteria.
A malocclusion is the misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the two dental arches when they approach each other when the jaws are closed. Image shows crowding of the teeth of the lower jaw in a close-up view of a man mouth with crooked teeth.
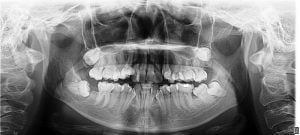
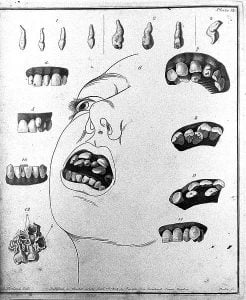
Hyperdontia is a condition in which too many extra teeth grow in the mouth. This condition is also referred to as supernumerary teeth. These teeth can grow anywhere in the curved areas or dental arches where the teeth attaches to the jaw. Development of supernumerary teeth might be due to several hereditary conditions such as Gardner’s syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, cleidocranial dysplasia, etc. Supernumerary teeth lead to delayed eruption of adjacent teeth and cause significant crowding. In some cases, this can lead to the development of cysts or tumors. [Image used under Creative Commons License from Wikimedia]
ADVERTISEMENT