Browsing: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
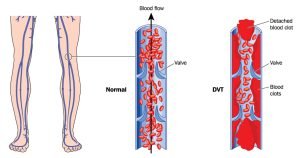
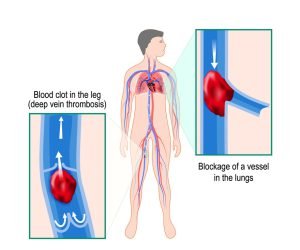
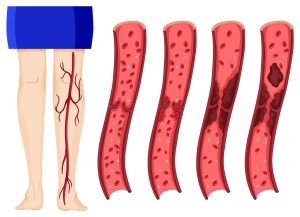
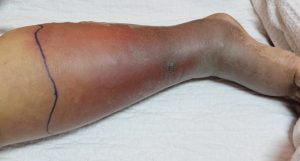
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (called thrombus) forms in the deep veins in your body, usually in the legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling but can occur without any symptoms too. People with family history of increased clotting are at a higher risk. If DVT is left untreated, the blood clots can separate from vein walls and travel through the heart which leads to pulmonary embolism that can be life threatening.
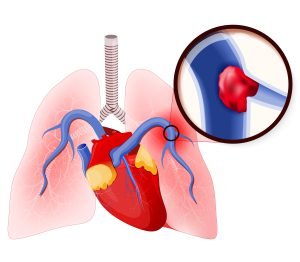
A pulmonary embolism (PE) may happen when a blood clot called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in your leg travels to the lungs and blocks one or more blood vessels. This can cause low oxygen levels in the blood, which can damage the lung and other organs. It can be life-threatening as well and cause heart failure, too.
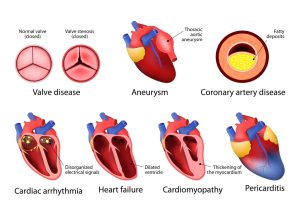
Heart disease is a term that covers a range of disorders that affect the heart. Coronary artery disease is the most common type of heart disease.
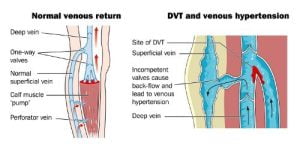
Chronic venous hypertension may also develop due to obstruction in the veins because of many reasons such as obesity, previous venous thrombosis (VTE, clotting), or compression of abdominal or pelvic veins. Symptoms of chronic venous hypertension may include swelling, pain, tenderness, venous leg ulcers etc.
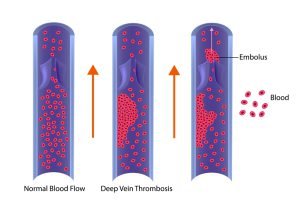
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance (such as a clot) that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream. It can be a result of injury or damage, inactive lifestyle, etc. In some cases, a surgery or therapy can also cause pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulants are used during treatment to inhibit blood clotting and also prevent formation of new clots.
About 50% of DVT cases have no symptoms. Complications may include pulmonary embolism, as a result of detachment of a clot which
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a condition in which blood clots form generally in the deep veins of the leg (called deep vein thrombosis, DVT), which can travel in the blood circulation and lodge in the lungs (known as pulmonary embolism, PE). Together, DVT and PE are known as VTE. VTE is a potentially deadly condition and can lead to heart problems such as a heart attack.
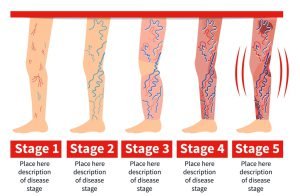
Each person is affected by vein disease differently. Some people feel only mild symptoms and only a few visible veins, and others may show signs and symptoms of much more advanced stages of venous diseases with large, bulging veins and noticeable swelling of the legs.
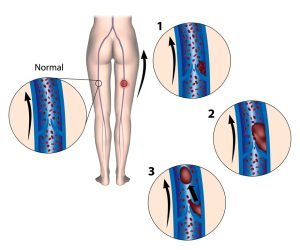
A blood clot is a clump of blood that is in a solid state. Deep vein blood clots generally form in thighs or lower legs, but they can also develop in other areas of the body.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) generally affects the lower limb, with clot formation beginning in a deep calf vein and extending proximally. Lower extremity deep vein thrombosis can be a life threatening medical condition as it can result in death or major disability due to pulmonary embolism or post-thrombotic syndrome. Lower extremity DVT can be infectious, neoplastic, traumatic, inflammatory, vascular, etc. Endovascular treatment is recommended as a standard method for removal of thrombus at an early stage.
ADVERTISEMENT