What is Lymphoma?
Lymphoma is the cancer of lymphocytes, infection-fighting cells of the immune system. Lymphocytes are present in the lymph nodes, thymus, bone-marrow, and various other parts of the body. In lymphoma, lymphocytes change and grow out of control. Lymphoma cancer starts in the white blood cells, or lymphocytes and can spread, or metastasize, to different parts of the body because it is present in the blood stream.
Lymphoma is not age-specific and therefore can occur at any age. It is one of the most common causes of cancer in children and young adults usually in between 15 to 24 years of age.
More than 70 types of cancers have been classified as lymphomas. Lymphomas can affect any part of the lymphatic system, especially:
- tonsils
- bone marrow
- thymus
- lymph nodes
- spleen
Types of lymphoma
Lymphomas fall into two major categories:
- Hodgkin lymphoma or HL or Hodgkin’s disease.
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma or NHL.
Both these types of lymphoma cancers have somewhat similar symptoms but they can be distinguished on examination of blood or tissue samples under a microscope. Hodgkin’s lymphoma arises from abnormal B lymphocytes which produce proteins that attach to abnormal or infected cells and alert the immune system to destroy them. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma on the other hand arise from either abnormal B cells or T cells, which destroy infected cells and therefore helps to regulate immunity.
Read more: Lymphoma Survival Rate
Types of non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
NHL is of following types:
B-cell lymphoma
Also called as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and is the most aggressive type of NHL.
T-cell lymphoma
Unlike T-cell lymphoma, B-cell lymphoma is not very common and approximately 15 percent of all NHL cases belong to this type.
Burkitt’s lymphoma
Burkitt’s lymphoma is a very rare, aggressive type of NHL and most commonly found in people with weak immune systems.
Follicular lymphoma
This type of NHL usually starts in the white blood cells and is the most common in old people. This type of NHL lymphoma is very slow-growing.
Mantle cell lymphoma
This is an aggressive and rare form of NHL and only 6 percent of NHL cases are usually of this type. Mantle cell lymphoma is commonly diagnosed at a very late stage.
Primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma
This is a subtype of B-cell lymphoma and primarily affects women at the age of 20 and 30.
Small lymphocytic lymphoma
Small lymphatic lymphoma (SLL) is a type of slowly growing lymphoma and the cancer cells of SLL are mostly found in the lymph nodes.
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma)
This is a rare type of cancer characterized by the formation of abnormal antibodies and accounts for only 1 to 2% of all lymphomas.
Types of Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma can be of the following types:
Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin’s disease
This is a rare, aggressive type of lymphoma that occurs in about 1 percent of lymphoma cases and is commonly diagnosed at the age of 30. In diagnostic tests, normal lymphocytes reveal an abundant number of Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells. Immunocompromised individuals such as HIV patients are mostly diagnosed with this type of lymphoma.
Lymphocyte-rich Hodgkin’s disease
This type of lymphoma is usually found in men and accounts for about 5% of all Hodgkin’s lymphoma cases.
Mixed cellularity Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Both lymphocytes and RS cells are found in this type of lymphoma and is very common type of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s disease
This type of Hodgkin’s lymphoma occurs in almost 5% of lymphoma patients and is characterized by an absence of RS cells.
Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin’s lymphoma
This is a common type of lymphoma and usually occurs in 70% of Hodgkin’s cases.
Read more: Types of lymphoma
Symptoms of lymphoma
Common symptoms of lymphoma usually include the following:
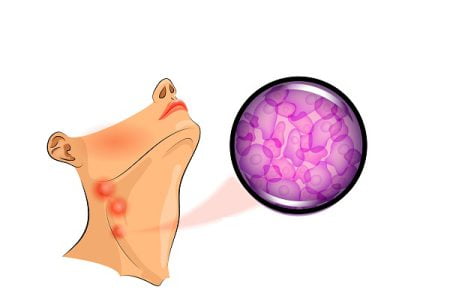
- Swollen lymph nodes especially in the armpits, neck, groin
- Sweating
- Weakness and fatigue
- Difficulty in breathing
- Chest pain
- Itchy skin
- Weight loss
Causes of lymphoma
The exact cause of lymphoma is not known, however, the following factors have been found to increase the risk of developing the disease:
- Older age
- Autoimmune diseases
- High fat diets
- HIV or AIDS
- Exposure to certain pesticides
Facts about lymphoma
Some key points about lymphoma are:
- Lymphoma is a type of cancer found in lymph nodes and lymphatic system
- Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin are two main types of lymphoma
- Non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is the most common of all types pf lymphoma
- The main symptom is enlarged lymph nodes that do not go away as in case of normal infection.
- Lymphoma cannot be prevented but after treatment the survival rates are quite good.
Classification of Lymphomas
Lymphomas can be classified as low, intermediate and high grade based on the type of lymphoma cells present and their effect on lymph nodes and chromosomes.
Low-Grade Lymphoma
Lymphomas belonging to this class grow very slowly due to which patients can live for many years mostly without any symptoms except that some may experience pain due to an enlarged lymph gland. Low-grade disorders begin to progress rapidly after 5 to 10 years and become aggressive or high-grade thereby producing more severe symptoms.
Intermediate-Grade Lymphoma
This class of lymphomas progress fairly rapidly in absence of treatment but under proper treatment, remission can occur in 50 to 75% of cases. Initial treatment has been found to be so successful that people who are in remission for almost three years after diagnosis can be considered as cured.
High-Grade Lymphoma
If not treated properly, this class of lymphoma can progress rapidly despite of the stage and therefore need an aggressive treatment. After treatment, 50 to 75% of patients enter remission. Patients who stay in remission for one year can live a life free from recurrence.
Stages of lymphoma
Both types of lymphoma (hodgkins and non-hodgkins) have been classified into four stages based on the location of cancer i.e, where the cancer is and how far it has or has not spread.
Stage 1 lymphoma
In this stage, cancer is either in one lymph node or one organ site.
Stage 2 lymphoma
In this stage, cancer is present in two lymph nodes close to one another on the same side of the body or cancer is in one organ and neighboring lymph nodes.
Stage 3 lymphoma
In this stage, cancer is present in lymph nodes present on both sides of the body involving multiple lymph nodes.
Stage 4 lymphoma
In this stage, cancer is in an organ and can spread beyond nearby lymph nodes and with the progression; it may begin to spread to other sites. The most common sites for advanced lymphoma include the liver, bone marrow, and lungs.
Screening for lymphoma
As such there is no routine screening or blood tests for lymphoma but if any family member (parent, brother or sister) has/ had Hodgkin lymphoma or non-Hodgkin lymphoma, the chances slightly increase for a person to develop it. However, the family link is not very common and most people with any one type of lymphoma do not share any family history.
Prognosis of lymphoma
Prognosis in individuals usually depends on their type and stage of cancer, as well as their age and general health during diagnosis.
Treatment for lymphoma
Treatment for lymphoma is usually based on the type of lymphoma, the stage of the disease and the rate of growth of the cancer (how fast it is likely to grow).
Types of treatment for lymphoma
Following treatment options are currently available for lymphoma:
- Chemotherapy
- radiotherapy
- monoclonal antibodies
- stem cell transplant.
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Early Hodgkin disease is usually treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma can be managed with localized radiotherapy alone or by a combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Palliative care
In some cases of lymphoma, palliative care (palliative care aims to improve quality of life by alleviating symptoms of cancer, without aiming to cure it) is recommended. Palliative treatment helps to relieve pain besides managing the symptoms.