Browsing: Gallstones
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Gallstones
Understanding Laparoscopy: A Best Guide to Normal Without Pain Operation
Introduction Laparoscopy, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery (MIS), is a modern surgical technique that has revolutionized the field…
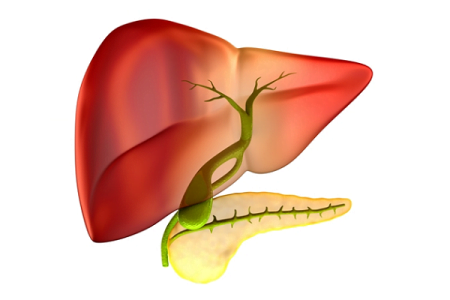
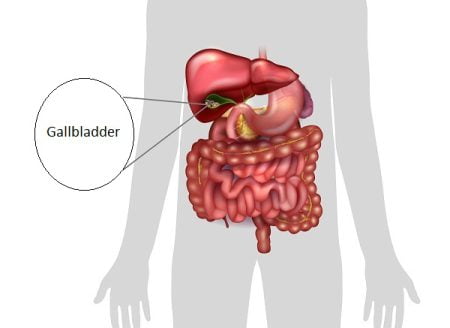
Gallstones are small, solid masses that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located just below the liver. The gallbladder…
It is possible to develop gallstones without you having a gallbladder. The presence of gallstones in the common bile duct is known as choledocholithiasis. These types of stones can also be found in cystic duct and common hepatic duct. They are commonly known as bile duct stones or gallstones in the bile duct.
Weight Loss After Gallbladder Removal: Do You Put on Weight After Gallbladder Removal?
After cholecystectomy, you may experience trouble in digesting fatty foods until your body adjusts. For this reason, your doctor or dietician may instruct you to avoid high fats and fried foods until your body is not ready to tolerate them. In fact, gallbladder problems and your weight changes go hand in hand.
It is not difficult to live without a gall bladder if the patient follows some dietary recommendations. No gall bladder diet is the best diet for patients without a gall bladder, especially after the surgery. The no gallbladder diet helps the body adjust the way it releases bile juice into the small intestine.
Gall stones are the hardened deposits made up of digestive fluids that are formed in your gall bladder. Non-surgical removal of gall stones is usually done in patients who are unfit for surgery or have some complications. Non-surgical treatment of gall stones is usually preferred when there are chances to save the organ (gall bladder).
Know About Cholecystectomy (Gallstones) Surgery, Its Procedure & Related Complications
Treatment of gallstones is not needed when they are asymptomatic. But if it has started causing symptoms, then it is likely that symptoms may get worse in the future paving the way for serious complications such as jaundice and pancreatitis. Your doctor may recommend for removal of the gallbladder surgically.
What Is Gallbladder Pain Like?
Gallbladder pain (often misspelled gall bladder) is a term used to describe any pain that occurs due to a disease or a medical condition of the gallbladder. The majority of gall bladder pain is caused by gallbladder problems such as biliary colic, cholecystitis, gallstones, pancreatitis and ascending cholangitis.
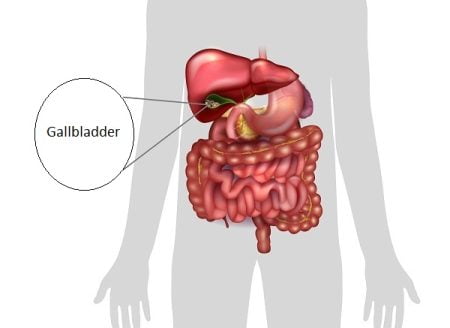
What is gallbladder? How much does a gallbladder weigh? The gallbladder is a long pear-shaped membranous sac (hollow structure)…
The gallbladder is a pear shaped hollow sac that sits right below the liver and stores and concentrates the bile produced by the liver. Because it only stores the bile produced by the liver and do not produce any digestive enzyme or chemical of its own, you can live without a gallbladder.