Blood clots while you are pregnant
Clotting of blood can be a serious complication, especially if you are pregnant. Although such complications during pregnancy are rare as thromboembolism affects only 1 or 2 pregnant women out of every 1,000 cases but if it occurs, it can cause problems to both the developing baby and the mother. During pregnancy, blood clotting mainly occurs when the body sends signals (in the form of platelets) as a security to safeguard against excess blood loss during labor. This condition is mainly referred to as venous thromboembolism in pregnancy.
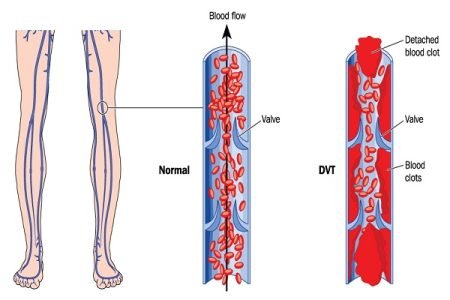
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a disorder that includes deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein. A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a clot breaks and travels to the lungs.
Understanding the causes of DVT in pregnancy
Deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy or pulmonary embolism during pregnancy can be fatal in severe cases. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is not a common condition during pregnancy but the risk of DVT in pregnancy is 5 to 10 times higher than in non-pregnant women. To prevent excess loss of blood during labor, formation of blood clots occurs (in the legs and pelvic region). This happens due to an increased level of blood-clotting proteins during pregnancy. Therefore, the main reason for the increased risk of VTE in pregnancy is hypercoagulability. Hypercoagulability is observed mainly in the first trimester of the pregnancy which is the body’s response to protect women from the bleeding challenges of miscarriage and childbirth.
Blood clots in deep veins of the legs or in the pelvic area can lead to pulmonary embolism (PE) in extreme conditions. This is of a greater risk as a blood clot can break off from its location and travel to the lungs. Pulmonary embolism in pregnancy is potentially a fatal condition for both the mother and the child. Sometimes, blood clots form inside the placenta and may cut off the blood flow to the fetus resulting in severe complications.
Other causes that increase risk of DVT in pregnancy are a history of thrombosis, inherited and acquired thrombophilia, and certain medical conditions such as compressed blood vessels or enlarged uterus (womb) results to an increased pressure on the veins in the pelvis or the lower body during pregnancy which returns blood back to the heart, etc.
Signs and Symptoms: How can you determine thrombosis in pregnancy?
DVT and PE are collectively known as venous thromboembolism. There are some clinical signs which might appear in pregnant women as an indication that there might be a possibility of formation of blood clots:
- During pregnancy, the legs become weak due to nerve pressure and poor circulation. But if the swelling or pain (especially in one leg) worsens, it should not be ignored. It is observed that more than 70 percent of pregnant women who suffer from venous thromboembolism have pain in the left leg.
- Lower abdominal pain due to extension of thrombus into the pelvic vessels or due to development of a collateral circulation
- The veins (in the pelvis) appear larger than normal due to a blood clot in leg (during pregnancy).
- Extreme tenderness is felt in one of the legs.
- During pulmonary embolism in pregnancy, shortness of breath or dyspnoea and excruciating chest pain are possible signs observed. Though, these signs generally appear during pregnancy but should not be ignored.
The symptoms of VTE in pregnancy are not very specific, therefore, a quick and appropriate diagnosis to rule out the possibility of such a severe condition is needed.
Diagnosing VTE and PE in pregnant women
Diagnosis of DVT or PE in pregnancy is not an easy task. Obstetricians study a patient’s history and general health to assess thromboembolism. Diagnostic imaging such as CT scan, MRI scan, or ultrasound) etc, blood tests, or other tests are commonly recommended to diagnose and confirm the presence of a blood clot.
Ultrasound during pregnancy
A doppler ultrasound helps to determine the speed of the blood flowing through a blood vessel. This can help the doctors establish whether blood flow is slowed or blocked which can indicate a clot. This test is mainly helpful in the diagnosis of DVT in pregnancy.
D-dimer test during pregnancy
A low D-dimer value results in eliminating the possibility of thromboembolism but an elevated or high D-dimer value can lead to risks. Although D-dimer values increase progressively during pregnancy, so other form of confirmatory testing is also required. VCUS (venous compression ultrasonography) and venography are then conducted as these are authentic tests for diagnosing DVT in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism in pregnancy through D-dimer test can result positive even in low D-dimer values. Therefore, multidetector-row (spiral) computed tomography is the confirmatory test conducted for diagnosing PE in pregnancy. Spiral computed tomography is a comparatively safer test compared to ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scanning as fetal exposure to radiation is lower with spiral CT. V/Q scanning is preferred only if spiral computed tomography is unavailable or embolism is not prominent in spiral CT. V/Q scanning is avoided in most cases as it leads to a risk of childhood cancer. Pulmonary angiography is also recommended in rare cases.
Treating blood clots while pregnant
Anticoagulation therapy in pregnancy is preferred in most cases. Anticoagulation includes use of low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs), unfractionated heparin (UFH), and warfarin, though warfarin in pregnancy is not recommended in all cases as it increases the risk of miscarriage, embryopathy, CNS abnormalities, maternal and fetal hemorrhage, etc.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that patients with higher risk of VTE should switch to intravenous heparin at the onset of labor. PE and DVT after delivery can be prevented through anticoagulants. Rivaroxaban is also a recommended medication by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) as a possible treatment for adults with DVT and to help prevent recurrent DVT and pulmonary embolism. Low-dose aspirin is safe and is sometimes recommended in pregnant women with an increased risk of thrombosis.
Several precautionary measures should be taken by pregnant women to avoid the risk of VTE such as staying active, wearing prescribed compression stockings, avoiding smoking, etc.