Can You Get Gallstones Without a Gallbladder?
- Updated on: Dec 13, 2024
- 7 min Read
- Published on Jul 12, 2022
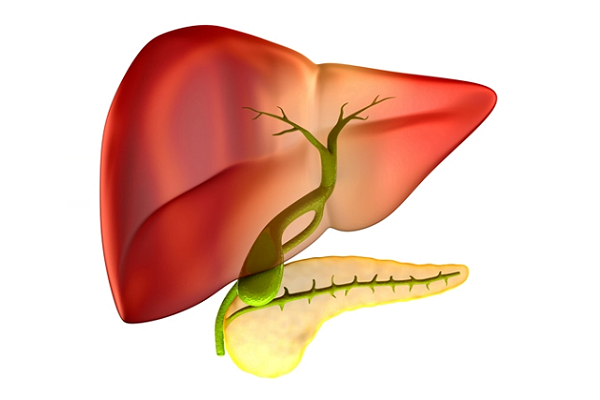
Gallbladder and Gallstones
Gallbladder is a small sac-like organ present below the liver. It helps in storage of bile produced in the liver. Bile juice helps in the digestion and breakdown of fats in small intestine.
Gallstones are hard, crystal-like particles which are formed due to deposition of bilirubin or cholesterol in the gallbladder. Gallstones may vary in size and number in different individuals. The condition has a high incidence rate, and about 25 million people experience gallstones at some point of time in their life. Imbalance in bile components, especially cholesterol, leads to gallstone formation.
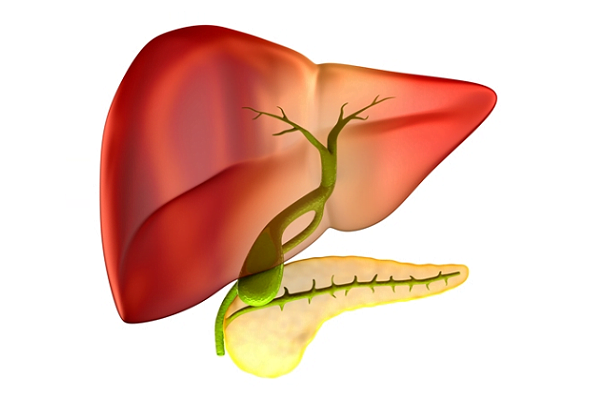
Common Bile Duct
The common bile duct is a small tube connecting the liver to the gallbladder. It also transports bile juice from the gallbladder to the small intestine. Gallbladder is a small sac-like organ present behind the liver.
Stones in the gallbladder are known as gallstones. The occurrence of gall stones is quite common. In some cases, these gallstones moves to the common bile duct along with bile juice and pass through the duct without getting stuck in it.
Can I get gallstones again after having gallbladder removed?
Yes, it is possible to get gallstones without a gallbladder. The presence of gallstones in the common bile duct is known as choledocholithiasis. They can also be found in cystic duct and common hepatic duct. They are also known as bile duct stones or gallstones in the bile duct. Bile duct stones are made up of bile pigments or calcium or cholesterol salts.
Incidence Rate of Gallstones in Bile Duct
According to the Medical Clinics of North America, about 15% of the people having gallstones will also have stones in their bile duct.
So, if you had gallstones before, then you are at a greater risk of getting them again. Bile duct stones recur in 4-24% of patients during the 15-year period after their first occurrence. The chances of their occurrence increase if any gallstones still remain in the body from the previous episodes.
See also: Gallbladder Removal Surgery (Gallstones Surgery or Cholecystectomy)
See also: What Happens When You Have Your Gallbladder Removed?
Symptoms of Choledocholithiasis
If gallstones are present in the bile duct, they may not cause any signs and symptoms for months or even years. You will experience certain symptoms only when the gallstones are stuck in the bile duct and obstruct it. You may experience the following symptoms in such cases:
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Clay-colored stool
- Dark or tea-colored urine
The pain may occur for irregular intervals for a long period of time. It may become constant and cramping. Pain may be mild at times, which then suddenly becomes quite severe. You may experience severe pain or heaviness after a meal. During severe pain, you should immediately consult a doctor for its treatment.
Sometimes, people get confused with severe symptoms of choledocholithiasis to cardiac event like a heart attack. In such a situation, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Types of gallstones found in bile duct
Different types of gallstones are found depending upon their composition. These are as follows:
Cholesterol Gallstones
Cholesterol gallstones are the most common type of gallbladder stones. These stones are formed in the gallbladder and then travel to the bile duct. They are formed due to buildup of cholesterol in gallbladder and are yellow in color. Cholesterol gallstones are formed due the following reasons:
- Excessive cholesterol in bile juice
- Large amount of bilirubin
- Reduced concentration of bile salts
- If the gallbladder does not empty out the bile juice completely
- Bile juice is not released frequently from the gallbladder
Pigment Gallstones
Pigment stones are brown in color and formed due to the deposition of bilirubin and calcium in the common bile duct. The cause of pigment stone formation is not clearly known, but these gallstones are commonly found in people suffering from:
- cirrhosis of liver
- biliary tract infection
- hereditary blood disorders in which the liver produces excessive bilirubin
Mixed Gallstones
Mixed gallstones are formed due to accumulation of two or more substances such as calcium, phosphate, protein and cystine.
There exist different types of gallstones depending upon how they are formed. These include:
Residual Gallstones
In some cases, stones are still left behind after the removal of gallbladder. These stones are usually found after 3 years from cholecystectomy.
Recurrent Gallstones
Recurrent gallstones develop in the bile duct even after the removal of gallbladder.
| Type of Stone | Primary Composition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol Stones | Cholesterol | Most common type. Yellow-green in color. Formed when there's an imbalance in the substances that make up bile. |
| Pigment Stones | Bilirubin | Darker and smaller than cholesterol stones. They arise from conditions that cause an increase in the production of bilirubin, such as certain types of anemia. |
| Black Pigment Stones | Bilirubin and Calcium Salts | Formed in the gallbladder and are the more common type of pigment stone. They can be associated with cirrhosis and certain other conditions. |
| Brown Pigment Stones | Cholesterol, Fatty Acids, Bilirubin, and Calcium Salts | Often form in the bile ducts rather than the gallbladder. They can be associated with bile infections and certain conditions where the bile remains in the gallbladder for an extended time. |
| Mixed Stones | Mix of the above components | Contain varying amounts of cholesterol, calcium bilirubinate and calcium carbonate. They are typically in between the characteristics of pure cholesterol and pigment stones. |
More: Gallbladder Pain (Causes, Symptoms): What Is Gallbladder Pain Like?
More: Weight Loss After Gallbladder Removal: Do You Put on Weight After Gallbladder Removal?
Who is at risk of having gallstones without a gallbladder?
Gallstones in bile duct can occur in those individuals who have a history of gallstones or a gallbladder disease. Gallstones can also occur even after the removal of gallbladder in an individual.
There are several factors which increase the chances of gallstone formation in bile duct. These risk factors include:
Age:
Elder people (above 40 years) are at greater risk of developing gallstones without a gallbladder.
Gender:
Women are at higher risk than men due to large amount of estrogen in them.
Ethnicity:
Asians, American Indians and Mexican Americans have higher chances of gallstones in bile duct than other people.
Family History:
The chances of gallstones to develop increase if someone in your family have suffered from it before. People who had gallstones earlier in their gallbladder or bile duct and even got their gallbladder removed are also at a higher risk for choledoclithiasis.
People, who have a history of any gastrointestinal condition such as Crohn’s disease, are also at a higher risk.
Other factors which also increase the risk of bile duct stones include:
- Obesity
- People who consume low-fiber, high calorie and high-fat diet
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged fasting
- Rapid weight loss
- Lack of physical activity
- People who undergo hormone replacement therapy or take birth control pills
- People who suffer from any metabolic syndrome such as diabetes or insulin resistance
- People who have cirrhosis or any bile duct infection
- People who suffer from hemolytic anemia, such as sickle cell disease.
Several of these risk factors can be improved by simple lifestyle and dietary changes.
Diagnosis of Choledocholithiasis
If you notice any symptoms of choledocholithiasis, seek medical advice or head to a hospital. The doctor may examine your abdomen and ask about the symptoms you may experience. The doctor may carry out one of the following blood tests to check for the presence of an infection or inflammation in the liver and biliary system and also examine functions of liver and pancreas:
- Complete blood count
- Bilirubin
- Pancreatic enzymes
- Liver function tests (LFT)
For further verification, the doctor will carry out certain imaging tests. The different imaging tests for diagnosis of gallstones include:
Transabdominal Ultrasound (TUS)
Transabdominal ultrasound involves examination of liver, spleen, kidneys and pancreas using high-frequency sound waves.
Abdominal CT Scan
Abdominal CT scan involves cross-sectional X-rays of abdomen.
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
Endoscopic ultrasound involves insertion of an ultrasound probe on a flexible endoscopic tube. It is inserted through the mouth to examine the digestive tract.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiography (ERCP)
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography is a technique to identity presence of stones, tumors and any narrowing in the bile duct. It involves passing a lighted tube with a camera on one end to examine the pancreatic and bile ducts. A dye is also injected into the duct and X-ray scan is carried out.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography involves MRI examination of gallbladder, bile ducts and pancreatic ducts.
Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiogram (PTCA)
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram involves X-rays of bile duct.
Cholescintigraphy
Cholescintigraphy is a type of nuclear medicine scan which is used to evaluate the gallbladder and biliary system. It is also known as hydroxyl iminodiacetic acid scan (HIDA scan).
Treatment of Bile Duct Stones
The treatment of gallstones which are formed without a gallbladder mainly focuses on reliving the obstruction caused by gallstones in the bile duct. Medication has not been effective for the treatment of gallstones.
The treatments for gallstones in bile duct include:
Biliary Endoscopic Sphincterotomy (BES)
Biliary endoscopic sphincterotomy is a common technique for treatment of gallstones present in the bile duct. About 85% of bile duct stones can be successfully removed using this method. It involves insertion of a balloon or basket-type device into the bile duct to extract out the stones.
Shock Wave Lithotripsy
Shock wave Lithotripsy involves fragmentation of gallstones present in the bile duct. Breaking the stones into smaller pieces allow them to easily pass through the duct or get captured. Stones which cannot pass on their own or which cannot be removed by BES are removed by lithotripsy. This method has a limitation as it increases the chances of gallstones formation in future.
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystestomy involves removal of gallbladder and stones through surgery. Those individuals who have gallstones in their gallbladder and bile duct undergo this method for removal of gallstones.
During the surgery, the doctor may examine your bile duct for any remaining stones present in it.
Sphincterotomy
Sphincterotomy involves making a cut into the common bile duct during the surgery after identifying the location of gallstones using ERCP technique. This leads to either removal or passing of stones from the bile duct.
Biliary stenting
Biliary stenting involves placing of biliary stents (tiny tubes) in the bile duct. These stents will provide adequate drainage of bile juice and will also prevent formation of gallstones in bile duct in future.
Biliary stents also prevent from spreading infection in the body. This technique is carried out by those patients whose gallstones cannot be removed completely or have a history of gallbladder stones or do not want removal of their gallbladder.
Complication of bile duct stones
If the bile duct stones are not detected and treated in early stages, it may lead to a life threatening condition. The following complication may occur due to blockage of gallstones which are formed without a gallbladder:
- Due to obstruction of gallstones, the bile juice gets infected. The bacteria may spread into the liver, leading to a severe bacterial infection.
- Damage to gallbladder, bile ducts or liver
- Cholecystitis involves inflammation of gallbladder due to blockage of bile flow in cystic duct (channel through which bile juice flows from gallbladder to small intestine). This blockage occurs due to the presence of a gallstone in the cystic duct.
- Inflammation of pancreas known as gallstone pancreatitis can occur. It occurs due to blockage of digestive juices into the small intestine by a gallstone.
- Cirrhosis
- Cholangitis involves blockage of bile duct by a gallstone. It disrupts the flow of bile juice and leads to jaundice, fever and severe pain.
- Death, in rare cases
How can gallstone formation be prevented?
If you had gallstones in the past, you may likely experience them again. Gallstones can be formed even without a gallbladder. If the gallstones are produced once, there is always a risk of their occurrence in future as well.
Simple lifestyle and dietary changes can help prevent the development of gallstones in future. These changes include:
- moderate physical activity
- increasing fiber content in your diet
- decreasing fat consumption











1 Comment
4 Almost 70 of all deaths in the world from cancer occur in the low and middle income countries