Amazing Antomy & Physiology of Gallbladder
- Updated on: Jan 27, 2025
- 5 min Read
- Published on Oct 4, 2019

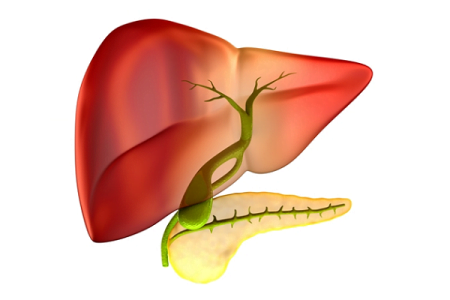
What is gallbladder? How much does a gallbladder weigh?
The gallbladder is a long pear-shaped membranous sac (hollow structure) that sits just under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced by the liver which is important in fat digestion.
It has a capacity of 30-50 ml, and is 2-3 cm wide and 7-10 cm long in humans and is dark green in colour. It weighs around 30 gm on average.
When food containing fat enters the digestive tract, the secretion of a hormone cholecystokinin is stimulated from the upper portions of the intestine which causes the gallbladder to release the bile into the small intestine through arrangement of tubes called ducts.
Gallbladder is not a vital organ and you can live without it, as it only stores the bile produced by the liver and do not produce the bile and is often removed by a surgical procedure known as cholecystectomy in case of gallbladder diseases and gallstones.
After removal of the gallbladder, bile continuously flows into the intestine from the liver which can cause diarrhoea in some people.
Parts of the gallbladder (gallbladder anatomy)
Gallbladder is a muscular sac and can be divided into 3 sections.
- The fundus
- The body
- The neck
- Cystic Duct: This duct connects the gallbladder neck to the common hepatic duct, forming the common bile duct. The bile stored in the gallbladder is released into this duct when needed.
- Hartmann’s Pouch: This is a small outpouching of the gallbladder neck. Sometimes, gallstones can get lodged in this pouch.
- Serosa: The outermost covering of the gallbladder, it’s a thin, protective layer.
- Mucosa: The inner lining of the gallbladder, which is characterized by its folds known as rugae. These allow the gallbladder to expand and contract as it fills and empties.The gallbladder’s primary function is to store bile produced by the liver. When you eat, especially foods that are fatty, the gallbladder contracts, pushing bile into the small intestine via the common bile duct, assisting in the emulsification and digestion of fats.The anatomy and function of the gallbladder are tightly linked with the liver and the overall biliary system. If gallstones form or if there’s inflammation (cholecystitis), it can hinder the gallbladder’s function and cause significant pain or other complications.
What is fundus of gallbladder?
The fundus is the bottom part of the gallbladder that protrudes from under the liver and is visible anteriorly. The main dilated portion of the gallbladder is the body part, which is located between the fundus and the cystic duct.
The narrower part of the gallbladder which is the neck tapers and connects to the biliary tree via the cystic duct – which joins the hepatic duct to become the common bile duct.

- Your gallbladder can hold about 30-50 milliliters of bile.
- The color of bile isn’t random! Its yellow-green tint comes from bile pigments, which are byproducts of red blood cell breakdown.
- The gallbladder is like a “storage tank” for bile, releasing it only when you eat fatty or greasy foods.
- Gallstones are more common than you think! Around 10-15% of adults in the U.S. have them, but many don’t even know it.
- Without a gallbladder, you can still digest food! The liver sends bile directly into the small intestine, although it may not be as efficient.
- Gallbladder problems can mimic heartburn. That’s why it’s important to consult a doctor if you experience persistent upper abdominal discomfort.
- Bile has a hidden superpower: It helps your body in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K!
- Your gallbladder isn’t a must-have organ. Many people live perfectly normal lives without it!
Histology of the gallbladder wall
There are several different layers of gallbladder wall; theses are (from inside out):
The mucosa
It is the innermost surface and consists of single layer of columnar epithelial cells which secrete mucus and absorb water followed by lamina propia, which is a connective tissue and supports epithelium.
Muscularis propia
It consists of smooth muscle fibre, which contracts to expel bile out of the gallbladder.
Subserosal layer
It mainly strengthens the gallbladder wall and is made up of connective tissue.
Serosa
It is the outermost layer and covers the gallbladder on its lower side. It contains epithelial cells that secrete a liquid which prevents friction between gallbladder and other nearby organs.
Blood and nerve supply to the gallbladder
Oxygenated blood is supplied to the gallbladder by the cystic artery, a branch of the right hepatic artery, while the deoxygenated blood is carried out by the cystic vein.
The cystic vein drains the blood into the portal vein. Lymph drains into the cystic lymph nodes which empty into the hepatic or celiac lymph nodes.
The gallbladder is supplied by nerves of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which arise from the celiac plexus located in the abdomen, vagus nerve and right phrenic nerve.
Gallbladder Function: What are the functions of the gallbladder? What does a gallbladder do in your body?
Gallbladder is a part of biliary system and primary function of the gallbladder is to aid in the digestion. Mainly, gallbladder functions are to:
- store and concentrate the bile produces by the liver.
- secrete this bile by muscular contractions of its wall in response to both neuronal and hormonal factors stimulated by foods, especially fatty foods, in the duodenum- the first part of small intestine.
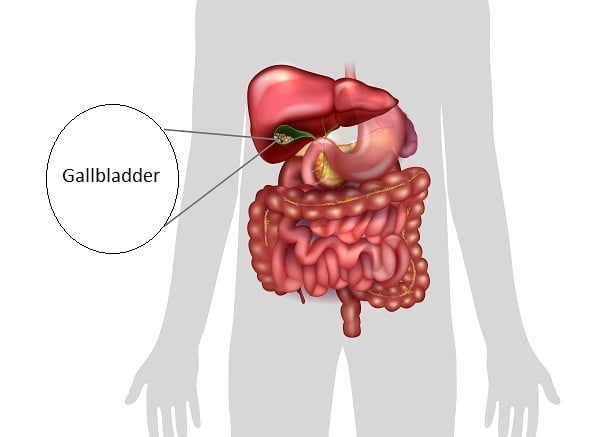
Gallbladder location: Where is your gallbladder located?
The gallbladder is situated in the shallow gallbladder fossa (a depression on the under-face of the liver, between the quadrate and the right lobes on the visceral surface of the liver. The capsule surrounding the liver is connected by connective tissue with the hepatic surface of the gallbladder.
Gallbladder is located in the right upper abdominal quadrant, around the 9th cost cartilage. The fundus of the gallbladder protrudes anteriorly from the inferior border of the liver. Various organs which come in contact with the gallbladder are the liver, the abdominal wall, the transverse colon and the duodenum.
How much does a gallbladder weigh with and without stones?
A normal gallbladder average weight without stones ranges between 300-400 gm. If there is an evidence of gallstones in your gallbladder, the weight will depend on the number and size of the gallstones.
Since a gallstone can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball, weight of the gallbladder with stones will vary accordingly.
- Gallstones only happen to older adults.
- You can’t eat fatty foods after gallbladder removal.
- They can develop at any age but are more common after 40.
- With some adjustments, most people can digest fats normally post-surgery.
Gallbladder Health: Diseases of gallbladder/gallbladder problems:
Though it is a small non-vital organ, yet gallbladder health is important. Some common gallbladder diseases and problems are:
- Gallstones/Cholelithiasis – deposition of solid masses of cholesterol in the gallbladder.
- Common bile duct stones/Choledocholithiasis – formation of gallstones in bile duct.
- Gallbladder inflammation/cholecystitis – irritation of gallbladder leading to swelling and infection.
- Perforated gallbladder – untreated deposition of gallstones can cause a hole in the wall of the organ and infection.
- Bile duct infection – blockage of bile duct can lead to severe infection.
- Dysfunctional gallbladder – repeated gallstone attacks may damage gallbladder permanently.
- Gallstone ileus – migration of gallstones to the intestine, it is rare but can be fatal.
- Gallbladder abscess – development of pus along with gallstones, can produce severe pain in the abdomen.
- Porcelain gallbladder – calcium deposition over a time can stiffen the gallbladder walls making them rigid. It is a risk factor for developing gallbladder cancer.
- Gallbladder polyps – these are noncancerous growth that develops in the gallbladder. A larger polyp needs to be surgically removed before it poses any threat.
- Gallbladder cancer – it is rare, but if left undetected and treated, can spread beyond the gallbladder quickly.
Diagnostic tests of gallbladder
Various gallbladder tests to diagnose problems and diseases of gallbladder are as follows:
Abdominal ultrasound
It is a non-invasive test in which high-frequency sound waves are used to check the gallbladder wall.
HIDA scan (cholescintigraphy)
It is a nuclear medicine-based test. A radioactive dye is injected intravenously and is secreted into the bile.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
A flexible tube is inserted through the mouth, stomach, and into the small intestine in this test. A doctor can visualize through the tube and inject dye into the bile system ducts. This test can be used to treat gallstone conditions during ERCP procedure.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
In this test, an MRI scanner is used to generate high-resolution images of the bile ducts, pancreas, and gallbladder. These images help in developing a treatment plan.
Endoscopic ultrasound
A tiny ultrasound probe attached on one end of a flexible tube is inserted through the mouth to the intestines. The device helps detect gallstone pancreatitis.
Abdominal X-ray
These X-rays are used to detect gallstones