All You Need to Know About Meningitis
- Updated on: Jul 13, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
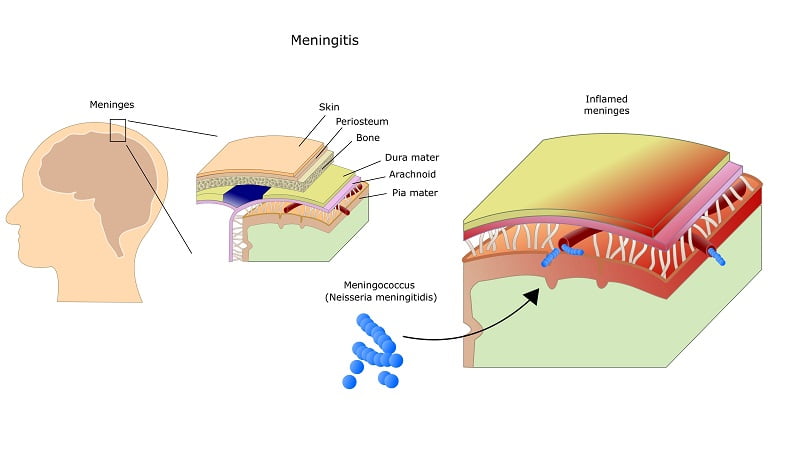
What is meningitis and meninges?
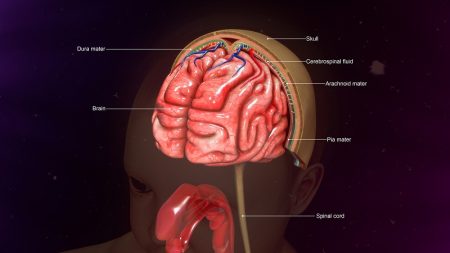
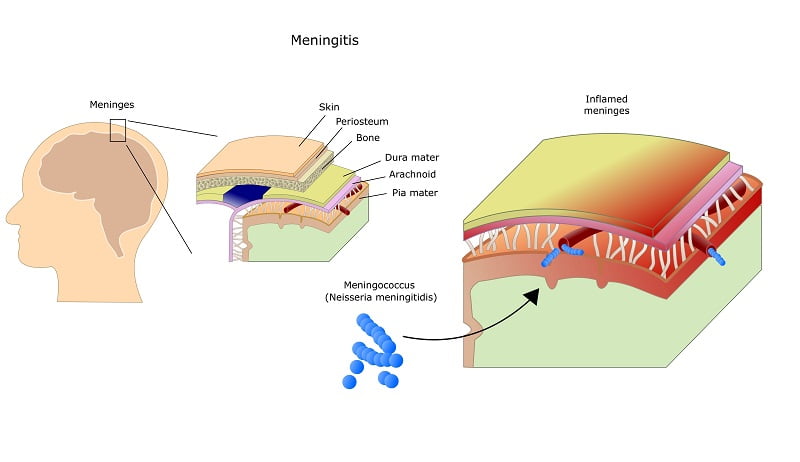
Brain and spinal cord are protected by a layer known as meninges. An inflammation or a swelling in meninges is termed as meningitis. Meningitis is a life-threatening infection and if left untreated, it can cause brain swelling, permanent disability and even death.
What are the causes and types of meningitis?
Meninges protect the brain and spinal cord from harmful agents and acts as a shock absorber. However, sometimes these protective layers get infected by some agents such as bacteria, viruses, etc and results in infection.
When such agents enter the membrane, they become isolated from the body’s immune system and starts spreading fast. By the time body fights back, the infection spreads and becomes worse. The blood vessels becomes leaky as the body fights the infection and the infection can even spread in the brain and spinal cord, causing life threatening consequences.
There are various agents responsible for causing meningitis. Meningitis is classified into different types on the basis of different causative agents. They are as follows-
What is bacterial meningitis?
There are certain bacteria that act as the main cause of meningitis. These bacteria can enter the bloodstream and reach the brain and spinal cord, thus infecting the meninges. This results in bacterial meningitis.
Bacterial meningitis can also occur when the bacteria directly invades the meninges. Many different strains are responsible of causing bacterial meningitis. Some of them are:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus)
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Group B Streptococcus
- Neisseria meningitides
- Haemophilus influenzae
Bacterial meningitis is a very serious form of meningitis and can even cause death in some cases if the condition worsens.
What is viral meningitis?
Viral meningitis is the most common type of meningitis but it is not as severe as bacterial meningitis. It usually takes a few weeks for a person to become well without any treatment but consulting a healthcare professional is important as some cases can be or become severe.
There are different types of viruses that can cause viral meningitis. Some of them are:
- Mumps virus
- Herpes viruses(Herpes simplex virus and varicella- zoster virus)
- Measles virus
- Influenza virus
- Arbovirus
What is fungal meningitis?
Fungal meningitis is a rare type of meningitis and is caused by the spreading of fungus in the meninges. The fungus can enter the layers through blood. People suffering from HIV infection or cancer are at a higher risk of developing fungal meningitis. People in Africa suffer mostly from fungal meningitis.
Different types of fungus responsible for causing fungal meningitis are as follows:
- Blastomyces
- Coccidioides
- Histoplasma
- Cryptococcus
Meningitis suffering by fungus can even spread to different organs such as lungs, etc.
What are the risk factors for meningitis?
Any person can suffer from meningitis. However, there are certain specific factors that can cause meningitis.
Some common risk factors are as follows:
Compromised Immunity
People with certain immune deficiency are more prone to suffer from meningitis. Some of the immunodeficiency diseases are as follows HIV AIDS, autoimmune disease, etc.
Community Living
Meningitis is a communicable disease and can even spread when people live in close quarters such as dormitories, boarding schools, etc.
Pregnancy
Pregnant women are at a higher risk of getting meningitis. It can even spread to her unborn child. Pregnancy increases the risk of listeriosis in women.
Age
People of all age are at a risk of developing meningitis. However, children below the age of 5 and young adults are at higher risk of suffering from the infection.
What are the symptoms of meningitis?
Meningitis shows its symptoms in a person soon after the infection develops. The most common symptoms of meningitis are fever and headache followed by stiff neck.
Some more symptoms associated with it are:
- Vomiting
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Extreme sensitivity to bright light (photophobia)
- Drowsiness
Symptoms of meningitis depend upon the cause of the infection.
Symptoms of viral meningitis
Symptoms of viral meningitis include:
- Decreased appetite
- Sleepiness
- Irritability
- Fever and pain
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Stiff neck, etc.
Symptoms of Bacterial meningitis
Symptoms of bacterial meningitis include:
- Irritability
- Headaches
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Altered mental status
A person should immediately consult a doctor if he or she experiences any of the above symptoms. Delay in treatment of meningitis can lead to severe consequences.
How is meningitis diagnosed?
As soon as the symptoms are noticed, the person should consult a doctor for accurate diagnosis. Diagnosis usually starts with a physical examination in which your doctor will check for the signs of infection near head, ear, throat and skin and near the spinal cord.
After physical examination, the doctor will advise you for certain diagnostic tests which may further help him to understand the nature of meningitis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnostic tests and methods for meningitis
Common diagnostic tests for meningitis are as follows:
Blood Tests
Blood samples are collected from patients and are tested for the presence of microorganisms, especially bacteria.
Gram stain may also be performed to understand the physiology of bacteria under the microscope.
Imaging
Magnetic resonance (MR) and Computerized tomography (CT) scans are used to observe the swelling and inflammation in the head.
Spinal tap (Lumbar puncture)
For proper diagnosis, a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is taken with the help of spinal tap. People with meningitis have low sugar level in CSF. This test also helps the doctor to identify the exact bacteria that has caused meningitis in that patient.
What are the complications of meningitis?
Generally, people recover fully from meningitis. However, in some cases, a case can become very severe and it can lead to various complications such as:
- Partial or full loss of hearing
- Epilepsy (recurrent seizures)
- Problem with memory and concentration
- Partial or full loss of vision
- Loss of limbs due to spreading of infection in the body
- Bone and joint problems like arthritis
- Kidney problems, etc.
What are the treatment options for meningitis?
Treatment for meningitis depends upon its cause.
Treatment of viral meningitis
Viral meningitis cannot be cured by antibiotics and can improve on their own in some weeks. The most common treatment for viral meningitis is:
- Complete bed rest
- Intake of fluids
- Over-the-counter medicines for fever and body aches.
Some doctors can even prescribe corticosteroids that can help in reducing brain swelling and anticonvulsant medicine to control seizures.
Treatment of bacterial meningitis
Bacterial meningitis is the most severe form of meningitis and should be immediately treated after diagnosis.
Medications such as intravenous antibiotics, corticosteroids, etc are prescribed which can help in reducing and controlling the symptoms of the infection such as swelling and seizures.
How is meningitis prevented?
Meningitis is a serious infection and can lead to severe consequences. It is therefore important to follow certain basic things to maintain a healthy lifestyle such as:
- Taking proper rest
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking
- Avoiding contact with sick people
- Taking medications at proper time interval
Apart from the above points, the most important preventive measure for meningitis is vaccination. There are some vaccines that can protect a child from developing meningitis such as:
- Meningococcal vaccine
- Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
- Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine