Passing a Kidney Stone With Urine
- Updated on: Jul 13, 2024
- 6 min Read
- Published on Jun 12, 2019
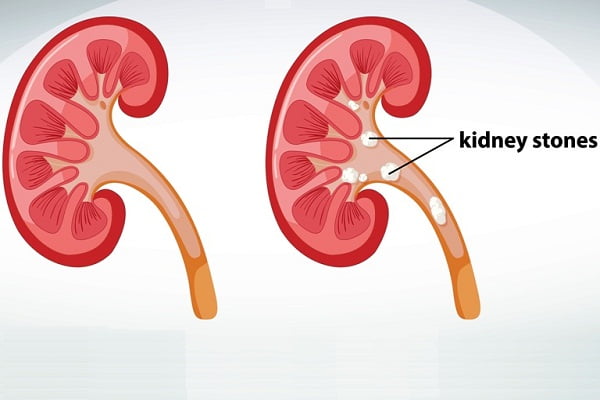
What are kidney stones?
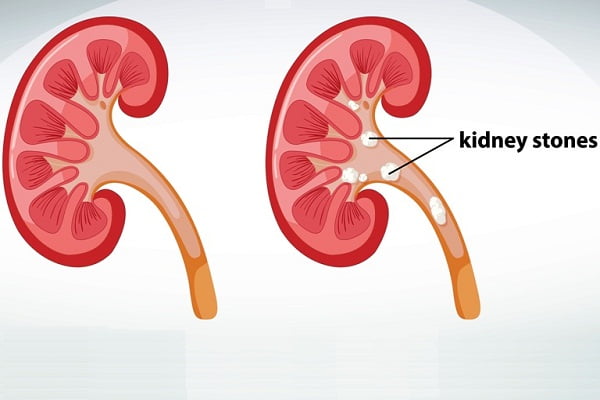
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis, nephrolithiasis) are hard deposits that are formed in kidneys and could be extremely painful for an individual. Kidney stones form when there is a decrease in urine volume and/or an excess of stone-forming substances in the urine. Deyhydration is also considered a major culprit. Read more about kidney stones overview.
Passing kidney stones in urine
Most kidney stones ultimately pass from the kidney through the ureter and bladder and then through the urethra on their own. However, treatment is usually need to control pain from kidney stones as they pass because the pain can be unbearable. The passage of kidney stones can sometimes occur easily with the urine but it could be a dreadful event in some cases if the stones get stuck in the urinary tract. In such cases, it causes severe and unbearable pain.
See also: Kidney Stone Pain: How Does It Feel When You Have A Kidney Stone?
What helps pass kidney stones easily?
The following steps help in passing a kidney stone:
- Increased fluid intake
- Higher intake of water and lemon juice
- Certain medications help to increase the passage of kidney stones from the urinary tract. These medications are usually recommended by doctors when kidney stones do not pass on their own.
Medicines and procedures to help pass kidney stones
Calcium channel blockers
This category of drugs is usually recommended for high blood pressure patients, but they also help prevent the ureter from spasming which indeed helps in relieving pain. They also widen the ureter to allow passage of stones more comfortably. Calcium channel blockers for example include nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia, Afeditab, and Nifediac).
Alpha blockers
Alpha blockers help relax muscles of the ureter and facilitate the passage of stones from kidney. They also relive pain by reducing the spasms in the ureter. Example of these medicines include tamsulosin (flomax).
Lithotripsy
Lithotripsy is a non-surgical procedure which involves use of shock waves (high energy sound waves) that are directed at the site of the kidney stone to break the stones into smaller pieces. Once the stones are broken by shock waves, the smaller pieces can then easily pass through the ureter.
See also: Tips To Dissolve Kidney Stones Naturally: What Helps Pass Kidney Stones?
What are the factors that affect passing of a kidney stone from the kidneys?
There are several factors which influence the ability to pass a kidney stone, which are as follows:
Size of the stone
Size of the kidney stone is one of the major factors which determine whether the stone can be passed easily on its own without any medical intervention or not. A stone of size 4mm has 80% chances of its passage from the kidneys, in about a month whereas a stone of size 5mm has 20% chance of passage in about 45 days.
Stone of size > 6mm, if passed naturally, can take a longer time such as about a year. Stones having a size > 9-10mm cannot pass on their own. They will require specific medical treatment to help pass them through the urinary tract.
Location of a kidney stone
The location of the kidney stone also affects its normal passage from the kidneys. If kidney stones are present in the ureter closer to the bladder rather than the end portion close to the kidneys, there are about 79% chances of them to pass on their own. If the stones are present in the ureter section closer to the bladder, then there are about 48% chances that stones will pass from the kidney without any medical intervention.
Other factors that can influence passing of a kidney stone in urine are:
- Size of the person
- Previous stone passage path
- Prostate enlargement
- Pregnancy
Symptoms: How do you experience while passing kidney stones? Is it too painful?
The movement of kidney stones within the kidney and their passing into the ureter leads to the following symptoms:
- A person would experience severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs region
- Pain is experienced in lower abdomen and groin region which travels through the back of the body
- The pain may have a wave-like movement and its intensity would vary
- The person can experience pain during urination
- The color of urine might change from yellow to pink or red or brown
- The urine may have a cloudy or foul-like smell
- The person may nausea or vomiting
- There might be a continuous urge to urinate
- The frequency of urination might increase
- The person may urinate small amounts of urine in short intervals of time
- If an infection occurs, then the person may get fever and chills
How long does it take to pass a kidney stone?
Usually, very small particles of kidney stones are passed through the urinary tract within 48 hours on their own, with consumption of large amount of fluids. Small stones of about 5-6mm can be passed from the kidney by medical expulsive therapy in about few days to a few weeks.
Passing kidney stones at home: How can you pass kidney stones faster?
If you have been diagnosed with a kidney stone of small size (<5mm), there are certain things you can do to help pass them and prevent their growth. You can try these simple methods. However, you should speak to your doctor to seek medical advice in case the passing of stones creates problem or causes pain or the stones do not pass on their own. You might need medical or surgical intervention.
- Increase fluid intake and large consumption of water and citrus juices such as grape and orange juices. You should consume at least 2-3 quarts of water per day. By increasing the water intake, the stones keep on moving and are not allowed to grow. This slowly leads to smooth passage of kidney stones through urine.
- Stones can be prevented from growing by consuming low salt, protein and calcium diet. But these elements are important for the growth and survival of the body, therefore these dietary changes must be considered only as instructed by a medical practitioner.
- In certain cases, passing a kidney stone might be painful. You can take ibuprofen or other painkillers as suggested by your doctor to reduce the pain and also speed up the process of passing the stone.
- A heating pad can also be used to reduce pain.
Passing of kidney stones in males VS females
The chances of occurrences of kidney stones in males are higher as compared to females, but presently this scenario has started changing and a higher incidence rate is observed in middle aged women and pregnant ladies. This increased risk is possibly due to high salt intake, increased sugar consumption, diabetes and obesity.
The symptoms indicating the presence of kidney stones in males and females may also vary. In some cases, no sign of passing a stone is observed in males. But in some cases, they may experience pain in the back and testicular region. But the pain is usually not as severe as experienced by females. Females also commonly experience nausea, vomiting and change in color and smell of urine.
The symptoms experienced by females include severe pain in the back that travels to the abdomen and pelvic region, presence of blood in urine, urine urgency and infection.
How to know if you passed a kidney stone?
The passage of kidney stone through the urinary tract leads to movement of pain in different regions of the lower body. When the kidney stone is present near the kidneys, a person may experience pain in the back. As the stone travels down in the tract, the pain may be experienced in the back and the abdomen region. When the stone further moves down the ureter, the pain moves to the front region of the abdomen.
As soon as the stone enters the bladder, the pain is experienced in the groin area, whose intensity is decreased. At this stage, the urgency to urinate may increase. Some people might observe other specific signs also during the passing of kidney stones. You should consult a physician from time to time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can drinking more water help in passing a kidney stone naturally?
Yes, increasing water intake can aid in passing a kidney stone naturally. Adequate hydration helps dilute the urine, making it easier for the stone to pass through the urinary tract without causing significant pain or obstruction.
What are the signs that a kidney stone is moving or passing?
Common signs that a kidney stone is moving or passing include intense pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen, frequent urination, blood in the urine, and relief from pain as the stone moves closer to exiting the urinary tract.
Is there any dietary advice to follow while passing a kidney stone?
Yes, individuals passing a kidney stone should follow a low-sodium diet, avoid foods high in oxalate, such as spinach and chocolate, limit intake of animal proteins, and maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables to support kidney health.
How long does it typically take to pass a kidney stone?
The time it takes to pass a kidney stone varies depending on its size and location within the urinary tract. Small stones may pass within a few days to a few weeks, while larger stones may require medical intervention for removal.
Can physical activity help in passing a kidney stone?
Light physical activity, such as walking or gentle stretching, may help promote movement of a kidney stone within the urinary tract. However, vigorous exercise is not recommended, as it can exacerbate pain and discomfort associated with passing the stone.