Browsing: Eye Health
The page provides quick access to a list of common eye diseases, syndromes, health conditions, and other topics of health importance. The list is organized alphabetically. Links are provided to respective diseases sections that serve as a comprehensive and ultimate guide about the disease or health condition.
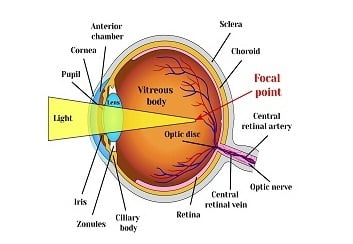
Eyes are the most complex and essential sensory organ of our body. Several parts of the eye work together to produce a clear vision. Most people suffer from various types of eye disorders such as age-related macular degeneration, cataract, diabetic eye disease, glaucoma, low vision and dry eye.
Visual impairment is a national and global health concern which creates a negative impact on the physical and mental health of an individual. These visually impaired people are at a high risk for chronic health conditions, accidents, social withdrawal, depression, and mortality.
Most people may experience an eye problem at some point in their life. Some of them may be minor conditions, which can be cured easily whereas others may require a specialist’s care. Eye disorders mostly occur in elderly people due to weakness of eye muscles or due to another medical condition such as diabetes, infections and brain or neuronal disorders.
It is ideal to undergo regular eye checkups, as many eye diseases do not show obvious symptoms. Early detection and treatment of eye problems could easily prevent vision loss.
Certain eye diseases which are quite prevalent worldwide include cataract, glaucoma, nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, diabetic retinopathy, dry eye syndrome, color blindness and conjunctivitis.
What is Myopia or Nearsightedness?
Nearsightedness also known as myopia is a common condition of eye in which distant objects unclear or blurred. A personal is unable to see them clearly. It can be mild, moderate or severe. It is in fact not a disease but a variation from the normal caused by a change in the shape of the eyeball.
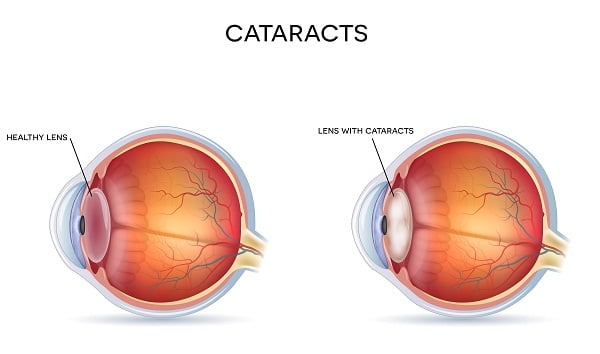
What Is a Cataract?
A cataract is defined as clouding of your eye’s natural lens. Cataracts are the most common cause of vision loss in people over the age of 40. It is the most common cause of blindness in the world. There are as many as 22 million Americans aged 40 and older with cataract.
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back wall of the eye. It is responsible for absorbing light and converting it into a signal sent to the brain. A retinal detachment is serious eye condition which involves separation of the retina from its attachments to the underlying tissues.
What Is Myopia (Nearsightedness)?
What causes Myopia? Short-sightedness or myopia is a refractive error in which the light rays coming from the object…
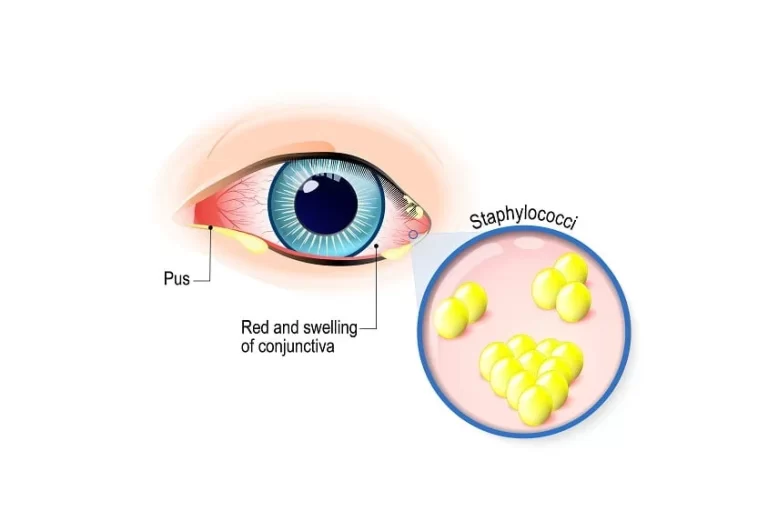
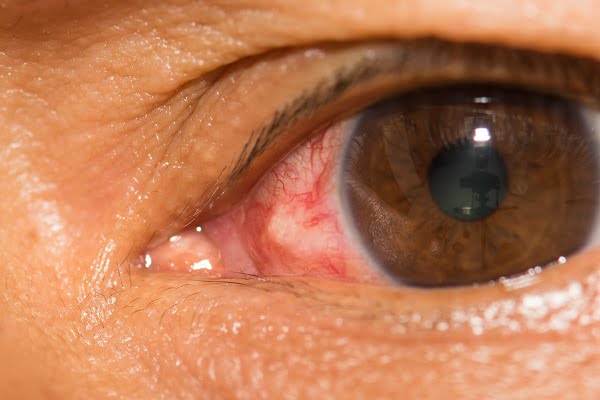
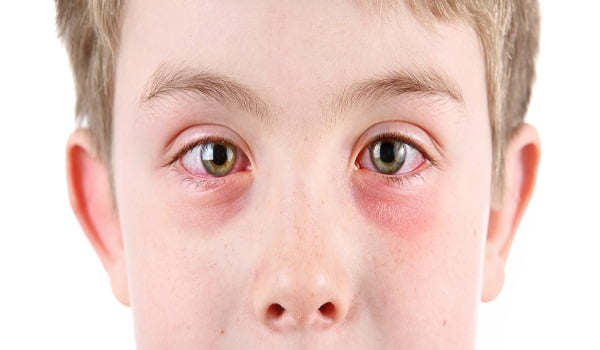
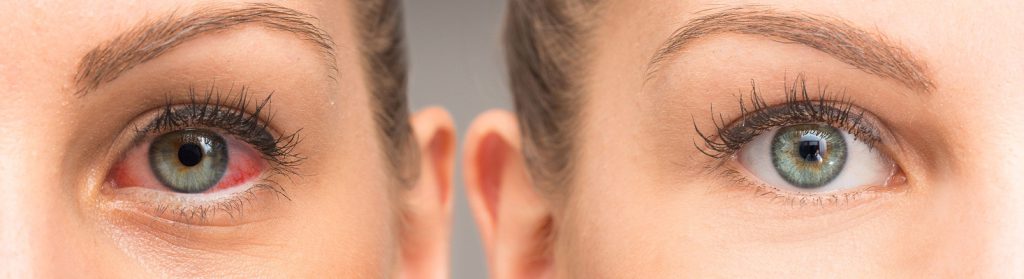
Conjunctivitis (pink eye infection) is a contagious disease that can spread in the environment widely. There are many causes of conjunctivitis such as bacteria, viruses, chemicals, pollutants from environment, use of contact lenses for a long time, Chlamydia, parasite, etc. Bacterial conjunctivitis is the most common of all forms of conjunctivitis.
Diabetic retinopathy is a chronic condition of the eye caused as a complication of diabetes. It leads to damage of the retina, which is a light sensitive tissue at the back of the eyes. In severe cases you may lose your sight. It occurs in more than half of the people who develop diabetes.
Symptoms Leading to Complications in Conjunctivitis Patients
There are a variety of signs and symptoms of conjunctivitis. Many people usually think of them as normal eye irritation and ignore them. This sometimes results in adverse complications which can lead to eye damage. Redness in the white portion of the eye is the most common symptom of conjunctivitis.
What Is Conjunctivitis?
Our Eyes and Conjuntivitis Our eyes are one of the most sensitive sense organs in the body. They are always…
Cataract: Causes and Risk Factors
You develop cataract when protein builds up in the lens of your eye and makes it cloudy. There are different types of cataracts which may be caused by different factors. Common causes are genetics, trauma, age, certain medical conditions such as diabetes, use of certain medicines, and exposure to radiations.
Color blindness is a condition in which a person is unable to differentiate between colors. Color blindness is not a form of complete blindness instead it is a deficiency which doesn’t allow a person to see certain specific colors such as yellow and blue or red and green.