Browsing: Urinary Incontinence Graphics
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Urinary Incontinence
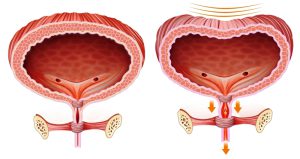
Urinary bladder is a pear shaped muscular sac in the pelvis, that rests just above and posterior to the pubic bone. Urine, made in the kidneys, passes down to ureters to the bladder which holds it. Several disorders associated with bladder include cystitis, urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, bladder cancer, etc. Urinary retention is a condition in which the bladder doesn’t empty completely even after being full. Normal bladder is reservoir that holds 1.5 to 2 cups of urine. This occurs due to any obstruction (bladder or kidney stones). Poor stream and difficulty in passing urine leads to urine incontinency or involuntary loss of urine.
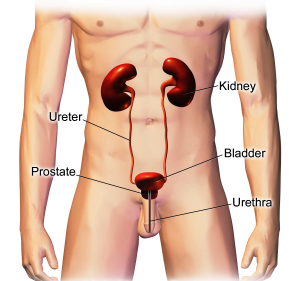
The main organs which build the urinary system in men are kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra and prostate. Kidneys make urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood and urine is then brought down to be stored in the bladder before excretion. Urinary incontinence occurs either because the signal to the brain gets scrambled, or there is some problem or obstruction somewhere in the urinary tract. Men suffer from incontinence due to several causes such as benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) or benign prostatic enlargement (BPE), prostate cancer, phimosis, etc.
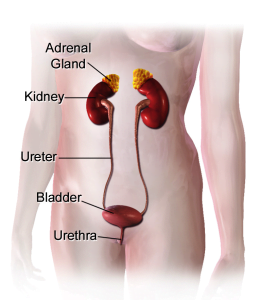
The only difference between a male and a female urinary system is the length of the urethra due to which women are more prone to urine infections. Bladder problems in women are common because of pregnancy and childbirth, trauma or injury, such as sexual assault, menopause, etc which weakens the bladder muscles. Urinary incontinency is a more common problem in women than in men and the structure of the female urinary tract is one reason for it.
ADVERTISEMENT