Browsing: Urological Conditions
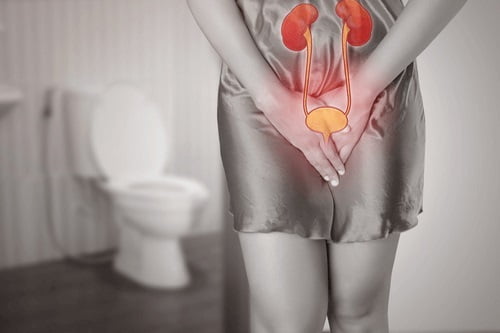
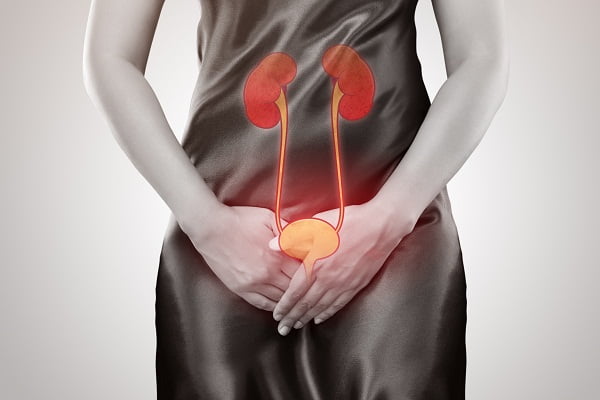
Urological conditions refer to a wide range of medical conditions that affect the urinary tract and reproductive system in both males and females. These conditions may involve the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, prostate gland, and genitals, and can cause a variety of symptoms that may affect a person’s quality of life.
Some common urological conditions include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, bladder infections, urinary incontinence, prostate disorders (such as benign prostatic hyperplasia or prostate cancer), erectile dysfunction, and urinary tract obstructions. These conditions may result from various factors such as infections, inflammation, hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, or other underlying health conditions.
It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you may have a urological condition, as early diagnosis and appropriate management can help prevent potential complications and promote better health outcomes. Your healthcare provider, such as a urologist, can provide accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Why Is My Pee Burning? 5 Reasons Urination Can Be Painful
Urinary issues have serious consequences for our daily lives. A burning sensation after urination is one of the most common…
Phenazopyridine (Azo) for Urinary Infections: Usage and Side Effects
Azo is a medicine that is used to relieve symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI) such as irritation in the urinary tract, pain, burning, and the feeling to urinate frequently. The generic name for this medicine is phenazopyridine. Azo is the brand name for phenazopyridine hydrochloride.
The main difference between a circumcised and uncircumcised penis is the presence of foreskin around the head of the penis. Several recent studies confirm that uncircumcised boys are at higher risk of urinary tract infection (UTI). Baby boys who have an uncircumcised penis have an increased risk of urinary tract infection irrespective of whether their foreskin is tight or loose.
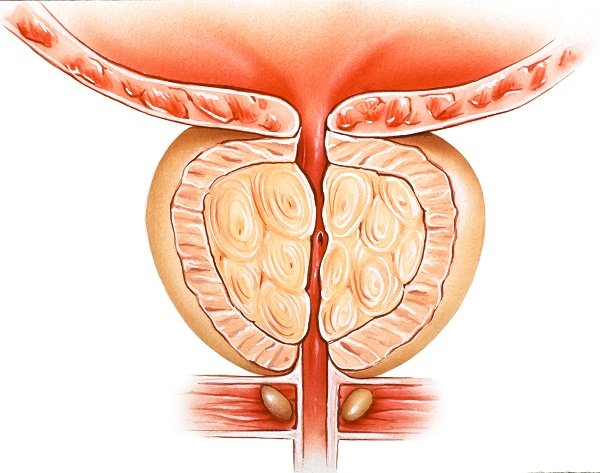
Enlarged Prostate Diet: What to Eat if You Have Enlarged Prostate?
About 50 percent of men over the age of 60 have enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). By the age of 85, more than 95 percent of men have BPH. There is good news however for those living with enlarged prostate or who are at risk of developing the disease. Healthy habits such as exercising, eating certain foods, and limiting dietary fat may help with BPH.
What is prostate gland? The prostate gland is a chestnut-shaped male reproductive organ. The prostate is not one but many…
Urethritis is generally transmitted through sexual contact, but it can also occur due to other reasons. It can develop as a result of a complication of brachytherapy. If it is transmitted through a sexual activity, it is generally caused by one of the two types of sexually transmitted infections.
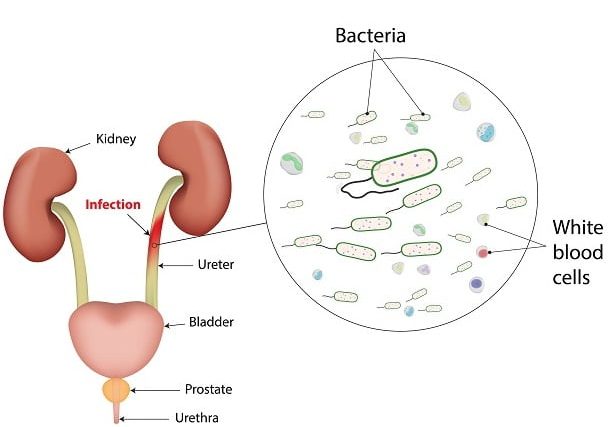
Doctors often advise to clean from front to back after using the bathroom. Urinary Tract infection (UTI) is the reason for this advice. Our urethra which transports urine from the bladder to outside of the body is located close to the anus. Bacteria can escape the intestines through anus and attack the urethra.
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) can be easily treated. Your doctor will likely start with antibiotics as these are usually the…
If you’re a woman, the chances of you getting a urinary tract infection (UTI) are much higher than in men. People of any age and sex can develop UTI. The symptoms of a urinary tract infection can vary based on your age, gender, and whether you had used any external device like catheter.
As the name suggests, urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is responsible for removing waste and excess water from our body. It consists of the bladder, the kidneys and the urethra. These are the structures that urine passes through before being eliminated from our body.