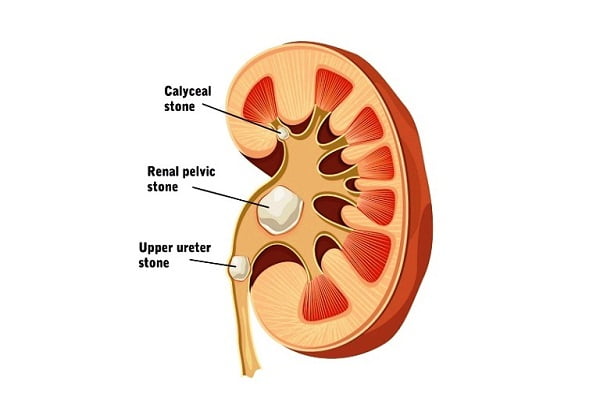
What are the types of kidney stones?
Four different kinds of kidney stones are found. They are as follows:
Calcium stones– They are the most common type of kidney stones. Calcium stones are made up of calcium and oxalate and in rare cases, they are even made up of calcium and phosphate.
Uric acid stones- They are formed when your urine becomes highly acidic. Uric acid stones are either made up of uric acid or a combination of uric acid and calcium.
Struvite stones – They occur due to a urinary tract infection, as the amount of ammonia increases in the urine by the infectious bacterial organism. Struvite stones consist of ammonium, magnesium, and phosphate.
Cystine stones– They are made up of cystine, an amino acid found in the human system. Cystine stones are extremely rare. They are formed due to a genetic disorder that causes leakage of cystine into the urine.
What can I drink to dissolve kidney stones? How do you dissolve kidney stones naturally?
By drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day, you can dissolve your kidney stones and allow them to easily pass through the urinary tract. It also prevents the formation of new stones. By increasing the fluid intake, toxins can also be flushed out of your body.
You can try the following fluids to dissolve your kidney stones:
- Water- By increasing your water intake, kidney stones can be removed faster. It is advised to drink a minimum of 12 glasses of water daily. Dehydration is one of the major behind the development of kidney stones.
- Lemon juice- Lemons are rich in citrate, which prevents the formation of calcium stones. It also helps in breaking large stones and allows them to pass easily through the ureter.
- Basil juice- Basil contains acetic acid, which helps in breaking down large size stones into small particles and reduces pain. You can add basil leaves to your tea or smoothie or drink its juice.
- Apple cider vinegar- Apple cider vinegar also contains acetic acid, which helps in dissolving kidney stones. It also helps in easing kidney stone pain.
- Celery juice- Celery juice helps remove toxins that are responsible for the formation of kidney stones. It also helps in flushing your body to allow effortless removal of stones.
- Pomegranate juice- Pomegranate flushes stones and other toxins from your excretory system. It is full of antioxidants and also lowers your urine’s acidity level, which indeed prevents the formation of new stones.
- Kidney bean broth- The broth from cooked kidney beans improves overall urinary and kidney function. It also helps in dissolving and flushing out stones from the kidneys.
- Dandelion root juice- Dandelion root is considered a kidney tonic that stimulates the production of bile. It helps in eliminating waste; increases urine output and improves your digestion.
- Wheatgrass juice- Wheatgrass increases your urine flow to help pass stones easily. It also contains certain vital nutrients which help in cleansing your kidneys.
- Horsetail juice- Horsetail increases urine flow and helps in flushing out kidney stones. They also soothe swelling and inflammation. It also has antibacterial and antioxidant properties which aid in overall urinary health.
How long does it take to pass a kidney stone?
Small size stones (less than 5 or 6 mm) generally pass on their own, without any medical intervention. It usually takes a few days to a few weeks to pass through your kidneys. Whereas large-size stones rarely pass through the kidneys without any medical intervention. If they pass on their own, it may take months and can be extremely painful.
How do I know if I have kidney stones? What are the first signs of kidney stones?
If you observe any of these signs and symptoms, then you may have kidney stones.
- Pain in your back, belly, or side
- Pain may radiate to your lower abdomen and groin
- You may experience pain in short waves whose intensity may fluctuate
- You may experience pain or a burning sensation while passing urine
- If you experience any urgent need to visit a toilet
- If you observe blood in your urine
- You may experience cloudy or smelly urine
- You may visit the washroom to pass a small amount of urine
- If you experience nausea and vomiting
- You may experience fever and chills due to an infection
Can kidney stones kill you?
In rare cases, kidney stones can even kill you. If they are left untreated, they can cause severe kidney infection, thereby leading to sepsis. Untreated kidney stones can even lead to kidney damage and create risks to your life. Therefore it is important to get a diagnosis done if you observe any signs of kidney stones. Smaller stones can be treated with simple home remedies and larger ones can be treated with short medical procedures.
What foods cause kidney stones? What foods do I need to avoid if I have kidney stones?
You should avoid the following foods if you have kidney stones:
Take an adequate amount of calcium– If you reduce your intake of calcium in your diet, oxalate levels will rise in your body and lead to kidney stone formation. To prevent this, you should consume an appropriate amount of calcium as per your age. You can consume calcium from low-oxalate, plant-based foods such as calcium-fortified juices, bread, cereals, some kinds of vegetables, and beans.
Reduce oxalate- A high amount of oxalate, increases the risk of calcium oxalate stone development. You can reduce intake of certain oxalate-rich foods such as nuts and nut products, peanuts, rhubarb, spinach, and wheat bran.
Reduce sodium– A high-sodium diet can also increase calcium levels in your body, thereby triggering kidney stone formation. Doctors recommend a low-sodium diet to inhibit stone formation. You should consume 2,300 mg of sodium in a day and if you have suffered from stones before, try reducing your daily intake to 1,500 mg.
Limit intake of animal protein– Consumption of excessive animal protein can boost the level of uric acid in the body, leading to kidney stone formation. A high-protein diet can also reduce the level of citrate, which helps in preventing stone formation. You should avoid the following foods, such as red meat, poultry, eggs, and seafood.
Avoid consumption of certain stone-forming foods– Beets, chocolate, spinach, rhubarb, tea, and most nuts are rich in oxalate, and colas are rich in phosphate, all these foods contribute to kidney stone formation.
Can I pee out kidney stones?
Kidney stones can be peed out along with urine. Their size and location are important factors that determine the time required to pass stones on their own. It also determines whether they require certain medical intervention for its removal.
Small-sized stones that are present close to the ureter can pass on their own within a few days. Whereas large-sized stones that are located near the bladder may require medical intervention for their removal.
How to get rid of kidney stones? Can kidney stones be cured?
You can get rid of kidney stones by different methods, such as home remedies, medication, or surgery. The best method to remove stones depends upon their size location and severity of your symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
- The most significant lifestyle change that helps in preventing stones is to drink more liquids. Try to drink a sufficient amount of water throughout the day. You can also take water with certain fluids such as fruit juices or some homemade drinks.
- People at risk of developing calcium stones should avoid dairy products and foods rich in calcium.
- To prevent the formation of acidic urine, which leads to the development of uric acid stones, you should limit the consumption of meat, fish, and poultry.
Medical Therapy
Doctors prescribe certain medications to help prevent the formation of different kinds of stones. These medications inhibit the accumulation of crystal-forming units in the body. Doctors prescribe the following medication to avoid the risk of a particular type of stone:
- To prevent the occurrence of calcium stones, you can take certain diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide and sodium cellulose phosphate.
- To prevent cystine stone formation, you should drink more fluids or take thiola and cuprimine, which reduces the amount of cystine in your urine.
- To prevent struvite stone formation, you can take acetohydroxamic acid (AHA), which helps in preventing infection.
Surgical Treatment
You may require surgery to remove kidney stones, if
- They do not pass after a reasonable period and cause constant pain in your back and side
- The stone is too large to pass on its own or is located in a difficult or deep position
- It blocks the flow of urine
- It leads to an ongoing urinary tract infection
- It damages your kidney tissue or causes constant bleeding
- It has grown in size
Doctors may advise one of these surgical procedures to remove your kidney stones:
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy
- Ureteroscopic stone removal
Should I go to the ER for kidney stones?
If your kidney stones cause severe or unbearable symptoms, then you should go to the emergency room (ER). You can visit the emergency room, if you have:
- Fever and suffer from severe kidney stone pain. These are usually signs of a serious infection in your kidneys
- Pain that is not curable by over-the-counter medications
- Severe nausea or vomiting which has significantly reduced your intake of fluids
- Previous difficult stone episodes
Does lemon juice help dissolve kidney stones?
The latest research states that lemonade is highly effective for treating kidney stones. Lemon juice increases the amount of citrate in your urine, which indeed inhibits kidney stone formation. Research also indicates that the rate of kidney stone formation decreases significantly in people with a risk for stone development.
Is cranberry juice good for kidney stones?
Cranberry juice is not good for kidney stones, as it contains a large amount of oxalate which can form calcium oxalate stones. Thereby, you should not drink cranberry juice or take its supplements, if you have kidney stones.
Cranberry juice is effective in preventing urinary tract infections, as it solidifies your urine and prevents the growth of infectious organisms in your kidneys.
Do bananas help with kidney stones?
The latest study proves that banana stalk acts as an alternative herbal remedy for treating kidney stones. Banana decreases the tendency of kidney stone formation in patients and also improve overall kidney function.
Bananas are rich in magnesium and potassium, which act as stone-inhibiting substances. Magnesium combines with oxalates in your food and inhibits the growth of calcium oxalate crystals. Potassium helps in balancing the acidity of your urine; thereby it also prevents the development of calcium oxalate crystals.
Is kidney stone surgery serious?
Kidney stone surgery helps remove kidney stones in severe cases. But it also has several side effects. The side effects are as follows:
- Your kidney may internally start bleeding
- You may observe blood in your urine
- This can lead to urinary tract infection
- Kidney can be damaged
- Your ureter may get injured leading to urethral perforation and avulsion
- You may need a urethral stent
- In rare cases, it can lead to sepsis
How painful are kidney stones?
Kidney stones cause severe pain in your abdomen, flank, or groin. People may describe this pain as the worst pain of their lives, even worse than the pain of childbirth or pain due to broken bones. Kidney stone pain is felt in waves and its severity may change from time to time. This pain is usually referred to as renal colic. Some people experience cramping pain in their lower back or side, groin, or abdomen.
People may experience painless kidney stones until they start traveling from their kidney, down to the ureter, and into the bladder. The size of the stone and movement of the stone through the urinary tract are major factors that cause severe pain.
Can kidney stones cause cancer?
A scientific study has reported that people who have stones in their kidneys have an increased risk of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and transitional cell carcinoma (TCC). This risk of RCC was higher in male patients rather than female patients. These findings could help in clinical management and cancer surveillance in the human population.
FAQs
What are the common symptoms of kidney stones?
Common symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain in the back or side, pain radiating to the lower abdomen or groin, blood in the urine, nausea, and vomiting. Seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
Can kidney stones be passed naturally without medical intervention?
In some cases, small kidney stones can pass through the urinary tract without medical intervention. However, larger stones may require medical treatment to facilitate passage and alleviate symptoms.
Are there any dietary changes that can help prevent kidney stones?
Yes, adopting a diet low in sodium and oxalates while staying hydrated can help prevent the formation of kidney stones. Additionally, consuming adequate calcium and limiting animal protein intake may also be beneficial.
What are the risk factors for developing kidney stones?
Risk factors for kidney stones include dehydration, a diet high in sodium or oxalates, family history of kidney stones, certain medical conditions like urinary tract infections or metabolic disorders, and certain medications.
How are kidney stones diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds. Treatment options vary depending on the size and location of the stone but may include pain management, hydration, medications, or surgical intervention.