How Are Kidney Stones Formed?
- Updated on: Jun 28, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Oct 7, 2019
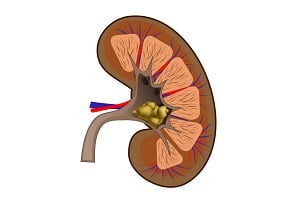
The hard crystalline deposits formed inside the urinary tract, mostly in kidneys, are known as kidney stones. They may be very small or large in size and exist in various shapes and colors. They do not usually show any symptoms when they are not moving along the urinary tract. But when they start moving with the urine, they cause severe pain in the sides and back side and may also cause difficulty while urination.
In most cases, kidney stones are removed on their own without any medical intervention. The stones may easily pass along with urine. If these stones get stuck in the urinary tract, they cause extreme pain. Blood may also be observed in the urine. In such cases, certain medical procedures are required to remove the blocked stones from the kidneys.
Formation of Kidney Stones
Kidneys are the major tissue system which helps in the formation of urine. Urine is formed after purification of blood to remove toxic and waste substances from the body. Urine contains certain substances which can form crystals upon their accumulation. They are known as stone promoting substances, such as calcium, sodium, oxalate, phosphorous and uric acid.
The stone promoting substances enter the kidneys through blood. Kidneys regulate the absorption and re-absorption of these substances from the blood. Our kidneys decide what amount of these substances will remain in the body (dissolved in blood) and what amount will be eliminated through the urine.
Kidneys also contain certain proteins and compounds which inhibit stone formation in the kidneys. The stone inhibiting molecules are known as urinary macromolecules, and may include magnesium, citrate, Tamm-Horsfall protein and nephrocalcin protein, phytate, pyrophosphate and alkaline pH. All these urinary macromolecules are derived from normal body metabolism.
The total urine volume also acts as one of the major stone inhibiting factor. More the amount of urine produced, less concentrated it will be and lesser will be the chances of it being super-saturated. If the amount of water increases in the urine, the concentration of stone forming substances decreases in the kidneys, thereby reducing the risk of kidney stone formation.
Why are Kidney Stones Formed?
As the concentration of stone forming substances increases in the kidneys, they start acclimating and gathering together. With their accumulation, tiny crystals are formed. This process is known as precipitation. With time, these crystals grow and form large hard insoluble substances, known as kidney stones.
There are various reasons which lead to conversion of tiny crystals into large kidney stones. Most common of them are as follows:
- If the total urine volume decreases
- If the concentration of stone forming substances increases tremendously
- If the concentration of stone inhibiting substances decreases tremendously
- If the pH of the urine changes
Any one or a combination of these causes can lead to kidney stone formation. Under normal conditions, a balance is maintained in the level of stone forming and inhibiting substances. If tiny crystals are formed, then they may be removed and no kidney stones will be formed.
An imbalance in the level of stone promoting and inhibiting substances in the kidneys can lead to kidney stone formation. This process is known as nucleation. It also indicates presence of an abnormality in the body or improper regulation of certain body metabolisms.
If tiny crystals are formed in the kidneys, they can be further prevented to develop into kidney stones by diluting the urine. Urine dilution will lead to removal of these crystals through the bladder and ureter along with urine. The stone removal may not create any problem and may not be noticed by the individual.
Several factors help in maintaining a balance in the level of stone forming and inhibiting substances in the kidneys. These include:
- Genetic factors
- Lifestyle choices
- Diet
- Certain diseases
There are certain sites in the kidneys which also increase the risk of kidney stone formation. One such site is Randall’s plaques which is a small calcification. These binding sites act as anchor and allow formation of stones easily. Initially, a small seed is formed at the Randall’s plaque where nucleation occurs and a small visible stone is then formed.
Risk Factors
There are several factors which increases the risk of kidney stone formation in the urinary tract. These are as follows:
Super-saturation
Super-saturation indicates an increase in the level of dissolvable salts and minerals in the urine. One of the major reasons of super-saturation is dehydration. If you decrease the intake of fluid or water, the amount of solutes and salts increases in the urine, leading to its super-saturation.
Stone Inhibitor Substances
If the stone inhibitory substance decreases in the kidneys, the chances of kidney stone formation increases. These substances have the capability to slow down the formation and growth of crystals in the kidneys and also have the power to eliminate them from the urinary system.
Health
The health status of an individual also contributes to kidney stone formation. Obesity or certain medical conditions such as gout, hypercalciuria, inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal bypass or ostomy surgery increases the risk of kidney stone formation. Certain medications also increase the risk for stone development.
Diet
Certain dietary factors such as intake of diet rich in animal protein or a decrease in water or fluid intake significantly increase the risk of kidney stone formation.
How are Different Kinds of Kidney Stones Formed?
Kidney stones exist in various chemical compositions. They are made of different kinds of materials. These include such as:
Calcium Stones
Calcium stones are mostly made of calcium oxalate. In some cases, they are formed due to accumulation of calcium phosphate or calcium maleate. They are the most common type of kidney stones. By reducing intake of calcium and oxalate rich foods in your diet, such as peanuts, chocolate, beets, milk, cheese, etc, the occurrence of calcium stones can be reduced.
Uric Acid Stones
Uric acid stones are formed due to accumulation of uric acid or due to the presence of acidic urine. An increase in intake of purine also increases the risk of uric acid stone formation. You should avoid foods such as fish, shellfish and meats, which are rich in purine.
Struvite Stones
Struvite stones are formed due to accumulation of struvite in the kidneys. They mainly occur due to urinary tract infection. They are large stones which block urine passage in the ureter.
Cystine Stones
Cystine stones are formed due to accumulation of cystine amino acid in the kidneys. It occurs due to a rare genetic disorder known as cystinuria.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are kidney stones made of, and how do they form?
Kidney stones are typically composed of minerals and salts, such as calcium, oxalate, uric acid, and cystine, which crystallize and accumulate in the kidneys. Various factors, including dehydration, diet, genetics, and certain medical conditions, contribute to their formation.
Can certain medications or supplements increase the risk of kidney stone formation?
Yes, certain medications and supplements, such as diuretics, calcium supplements, antacids containing calcium, and certain antibiotics, can increase the risk of kidney stone formation by altering urine composition or increasing the excretion of stone-forming substances.
Are there different types of kidney stones, and do they form differently?
Yes, there are different types of kidney stones, including calcium stones, uric acid stones, struvite stones, and cystine stones, each forming through different mechanisms. For example, calcium stones may form due to excess calcium or oxalate in the urine.
Can recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) contribute to kidney stone formation?
Yes, recurrent UTIs, especially those caused by certain bacteria like Proteus or Klebsiella, can contribute to the formation of struvite stones, which can grow rapidly and form large stone deposits in the kidneys or urinary tract.
Is there a genetic predisposition to developing kidney stones?
Yes, genetics play a role in kidney stone formation, and individuals with a family history of kidney stones are at higher risk of developing them. Certain genetic disorders, such as cystinuria or hypercalciuria, can also increase the likelihood of stone formation.