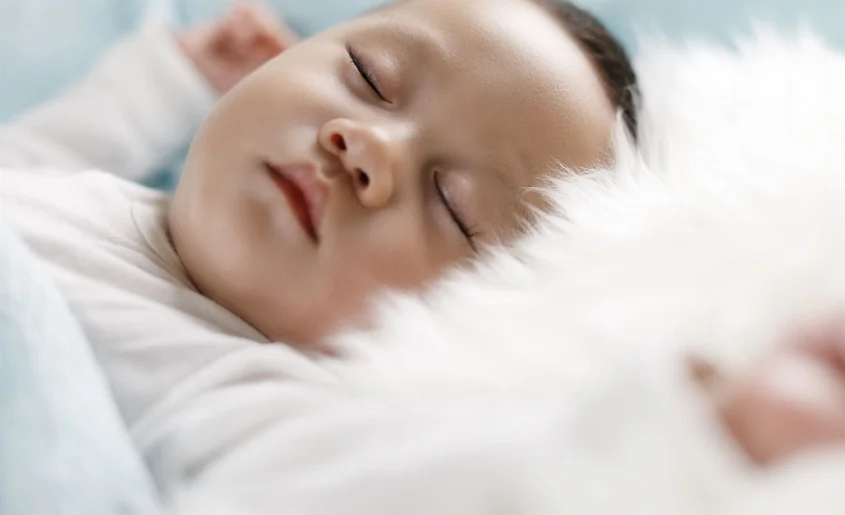
Lip tie is a condition that affects many infants, yet it often goes unnoticed or undiagnosed. It occurs when a baby’s upper lip is attached too tightly to their gums, which can cause a range of issues, including difficulty breastfeeding and problems with speech development.
Parents need to be aware of lip tie because it can have a significant impact on their child’s health and development. If left untreated, lip tie can cause breastfeeding problems, dental issues, and speech impediments. Identifying and treating lip tie early can help prevent these complications and ensure that your child reaches their full potential.
It’s also essential for parents to understand that lip tie is a common condition that can be easily treated with the right care and attention. By learning about the signs and symptoms of lip tie and the available treatment options, parents can take steps to address the issue and provide their child with the best possible care.
How Lip Tie Can Affect Infants
Lip tie can affect an infant’s ability to breastfeed or bottle-feed, as it can prevent the baby from creating a proper seal around the nipple or teat. This can lead to a poor latch, which can cause a range of breastfeeding problems such as:
- Difficulty latching or staying latched
- Low milk supply due to inadequate stimulation of the breasts
- Fussiness or colic due to swallowing air during feeding
- Weight loss or failure to thrive
Lip tie can also cause other issues in infants, such as:
- Difficulty with pacifier use
- Digestive issues such as reflux or gas
- Speech difficulties later in life
- Dental problems such as malocclusion or tooth decay
Common Signs and Symptoms of Lip Tie
Lip tie can be difficult to diagnose, especially in infants who cannot communicate their symptoms. However, there are some common signs and symptoms that parents can look out for, including:
- A gap between the upper front teeth
- A heart-shaped or notched appearance of the upper lip when the baby smiles or cries
- Difficulty flanging the upper lip outwards during breastfeeding
- Clicking sounds during breastfeeding
- Poor weight gain or slow growth
- Excessive gas, fussiness, or colic after feeding
If parents notice any of these symptoms or suspect their child has a lip tie, they should seek the advice of a healthcare provider, lactation consultant, or pediatric dentist for evaluation and treatment options.
Causes of Lip Tie
Lip tie is caused by a restriction in the frenulum, which is the thin band of tissue that connects the upper lip to the gums. This band of tissue is important for proper movement of the lip during breastfeeding, bottle feeding, and later on, speech development. When the frenulum is too tight or too thick, it can cause problems with feeding and speech development.
Risk factors for developing lip tie:
- There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing lip tie. These include:
- Family history: Lip tie tends to run in families, so if there is a history of lip tie in your family, your baby may be more likely to have it.
- Gender: Boys are more likely to develop lip tie than girls.
- Prematurity: Premature babies may have a higher risk of lip tie because the frenulum may not have had enough time to fully develop in the womb.
- Tongue tie: Infants with tongue tie, which is another condition caused by a restricted frenulum, may also be at a higher risk for lip tie.
Genetic factors that may contribute to lip tie
There is evidence to suggest that there may be a genetic component to lip tie. Researchers have identified certain genes that may be associated with the development of lip tie. These genes are involved in the formation and development of the frenulum during embryonic development.
In addition to genetic factors, there are also environmental factors that can contribute to the development of lip tie. For example, if the baby’s mouth is in an abnormal position in the womb, this can affect the development of the frenulum. Other factors that may contribute to lip tie include exposure to certain medications or environmental toxins during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of Lip Tie
How lip tie is diagnosed in infants
Lip tie can be diagnosed by a pediatrician, pediatric dentist, or lactation consultant during a routine physical examination of the newborn. The healthcare provider will examine the baby’s mouth, lips, and tongue to check for signs of lip tie. They may also ask questions about the baby’s feeding habits, such as how often the baby feeds, how long the feeding sessions last, and whether there are any difficulties in latching.
Different diagnostic techniques used to identify lip tie
There are several diagnostic techniques used to identify lip tie in infants. One of the most common methods is the “flip the lip” test, where the healthcare provider lifts the baby’s upper lip to check for a tight frenulum. Another technique is the “tongue lift” test, where the baby is asked to lift their tongue to check for restrictions in movement. The healthcare provider may also use a special instrument called a tongue depressor to evaluate the baby’s lip and tongue function.
When to seek medical attention for lip tie
It is important for parents to seek medical attention if they suspect their baby has lip tie. Some signs that may indicate lip tie include difficulty latching or feeding, poor weight gain, excessive drooling, and colic or reflux. If left untreated, lip tie can lead to long-term feeding problems, speech delays, and dental issues. Early intervention is key in preventing complications and improving outcomes for infants with lip tie.
If a healthcare provider suspects that a baby has lip tie, they may refer the baby to a pediatric dentist or a specialist in oral and maxillofacial surgery for further evaluation and treatment. Treatment for lip tie may involve a simple procedure to release the tight frenulum, such as a frenectomy or frenuloplasty. The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis and does not require general anesthesia.
Treatment Options for Lip Tie
There are several different treatment options available for lip tie, and the most appropriate option will depend on the severity of the lip tie and the age of the patient. Here are some common treatment options for lip tie:
Different treatment options for lip tie
- Frenotomy or Frenectomy: This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves snipping or cutting the frenulum, the small piece of tissue connecting the lip to the gums, using a pair of scissors or a laser. This is a quick and relatively painless procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office or a hospital setting.
- Myofunctional Therapy: This therapy involves exercises that help to strengthen the facial muscles and improve tongue and lip function. This can be a useful treatment option for infants with mild to moderate lip tie.
- Craniosacral Therapy: This therapy involves gentle manipulation of the skull and spine to improve the functioning of the central nervous system. It can be used in conjunction with other treatments to address lip tie.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors can provide gentle adjustments to the spine and skull to help address issues related to lip tie.
Pros and cons of each treatment method
Frenotomy or Frenectomy
Pros:
- Quick and relatively painless procedure
- Can be performed in a doctor’s office or a hospital setting
- Low risk of complications
- Immediate improvement in feeding and speech
Cons:
- May require local anesthesia or sedation for infants
- May cause some discomfort or bleeding for a short period after the procedure
Myofunctional Therapy
Pros:
- Non-invasive and painless
- Can be started at an early age
- Can be done at home with the guidance of a therapist
- Improves oral function and muscle strength
Cons:
- May require a longer period of therapy to see significant improvement
- May not be effective for severe cases of lip tie
- Requires active participation from the infant
Craniosacral Therapy
Pros:
- Non-invasive and gentle
- Can be used in conjunction with other treatments
- Can help address other issues related to lip tie, such as colic and sleep issues
Cons:
- May not be covered by insurance
- Requires multiple sessions to see significant improvement
- May not be effective for severe cases of lip tie
Chiropractic Care
Pros:
- Non-invasive and gentle
- Can be used in conjunction with other treatments
- Can help address other issues related to lip tie, such as colic and sleep issues
Cons:
- May not be covered by insurance
- Requires multiple sessions to see significant improvement
- May not be effective for severe cases of lip tie
What to expect during and after lip tie treatment
Frenotomy or Frenectomy
- The procedure typically takes just a few minutes and is done in a doctor’s office or hospital setting.
- For infants, local anesthesia or sedation may be used to help keep them calm and comfortable.
- After the procedure, the infant may experience some discomfort, swelling, and bleeding for a short period of time.
- The infant may be able to breastfeed immediately after the procedure.
- Follow-up care may include pain management, monitoring for signs of infection, and exercises to help improve oral function.
Myofunctional Therapy
- The therapist will work with the infant and parents to develop a customized treatment plan.
- The therapy involves exercises that can be done at home with the guidance of the therapist.
- Improvement may be gradual, and multiple sessions may be required to see significant improvement.
- Follow-up care may include ongoing exercises and monitoring of progress.
Breastfeeding and Lip Tie
Breastfeeding is an essential part of an infant’s growth and development. However, lip tie can cause problems for both the infant and mother when it comes to breastfeeding. In this section, we will discuss how lip tie can affect breastfeeding, common breastfeeding problems associated with lip tie, and tips and techniques for breastfeeding a baby with lip tie.
How lip tie can affect breastfeeding
Lip tie can make it difficult for the infant to latch onto the breast properly, resulting in an inefficient feeding process. When an infant has a lip tie, the frenulum (a band of tissue that connects the upper lip to the gums) is too short or too thick, preventing the baby from opening their mouth wide enough to latch onto the breast. This can cause discomfort for the infant, leading to frustration and an inability to get enough milk.
Common breastfeeding problems associated with lip tie
Some common breastfeeding problems that may arise as a result of lip tie include:
- Inefficient milk transfer: Due to the inability to latch properly, the infant may not be able to transfer milk effectively, leading to inadequate milk supply and poor weight gain.
- Sore nipples: The improper latch can cause the mother’s nipples to become sore, cracked, or even bleed, making breastfeeding a painful experience.
- Frustration and stress: The infant may become frustrated and stressed from not being able to feed properly, leading to a negative impact on the breastfeeding relationship.
Tips and techniques for breastfeeding a baby with lip tie
Fortunately, there are ways to manage lip tie and ensure that breastfeeding is a comfortable and successful experience. Here are some tips and techniques for breastfeeding a baby with lip tie:
- Seek professional help: Consult a lactation consultant or healthcare provider who is experienced in dealing with lip tie. They can provide guidance on how to position the baby for optimal latching and recommend tools such as nipple shields, breast pumps, or other aids to help with feeding.
- Use different feeding positions: Experiment with different breastfeeding positions such as the football hold or cross-cradle hold, which can help the baby latch onto the breast more easily.
- Take breaks: Frequent breaks during feeding can help relieve sore nipples and allow the baby to rest and regroup before continuing to feed.
- Consider alternative feeding methods: If breastfeeding becomes too difficult, consider using alternative feeding methods such as expressed breast milk or formula until the lip tie can be addressed through treatment.
Complications of Lip Tie
Lip tie is a condition that can lead to several complications if left untreated. Some of the potential complications of untreated lip tie include:
Potential complications of untreated lip tie
Difficulty with breastfeeding: Infants with lip tie may have difficulty latching on during breastfeeding. This can lead to poor weight gain, malnutrition, and dehydration, making it essential to monitor the child’s growth and development, which can be tracked using a BMI Calculator.
- Dental problems: Lip tie can cause spacing issues and gaps between teeth, leading to dental problems like cavities and gum disease.
- Speech delays: Children with lip tie may experience speech delays and difficulty with articulation.
- Swallowing problems: In some cases, lip tie can cause problems with swallowing, leading to choking and respiratory issues.
- Emotional distress: If lip tie goes untreated, it can lead to emotional distress in both the child and the parents.
Long-term effects of lip tie if left untreated
If lip tie goes untreated, it can have long-term effects on a child’s health and well-being. These long-term effects may include:
- Poor oral health: Untreated lip tie can lead to poor oral health, which can cause pain, infections, and tooth loss.
- Delayed speech development: If lip tie is not treated, it can cause speech delays and difficulty with articulation, which can impact a child’s academic and social development.
- Social and emotional issues: Children with untreated lip tie may struggle with self-esteem, socialization, and emotional well-being.
The importance of early intervention for lip tie
Early intervention is crucial for treating lip tie and preventing potential complications. In many cases, simple procedures like a frenectomy can effectively treat lip tie and prevent long-term complications. Seeking early treatment can also help infants and children avoid pain, discomfort, and potential emotional distress associated with untreated lip tie.
Lip Tie and Speech Development
How lip tie can affect speech development in children
Lip tie can have a significant impact on speech development in children. When a baby has lip tie, it can affect their ability to move their lips and tongue properly, which can lead to speech difficulties as they get older. The restriction caused by lip tie can affect a child’s ability to pronounce certain sounds correctly, such as “m,” “p,” and “b.” It can also lead to a speech impediment, making it difficult for them to communicate effectively.
The link between lip tie and speech impediments
The link between lip tie and speech impediments is well-established. When a child has lip tie, it can cause a gap or space between their teeth, which can impact their ability to speak clearly. Additionally, lip tie can limit the range of motion in the tongue, making it difficult to form certain sounds. As a result, children with lip tie may develop a lisp, have trouble articulating certain sounds, or have difficulty with fluency and rhythm when speaking.
Early intervention and speech therapy for lip tie
Early intervention is crucial for children with lip tie to prevent speech development issues from worsening. Speech therapy can be an effective treatment option for children with lip tie. A speech therapist can work with the child to strengthen the muscles in their mouth and improve their speech patterns. Additionally, a dentist or oral surgeon can perform a simple procedure to release the lip tie and alleviate any restrictions on movement that may be affecting speech development.
Parents should be aware of the potential impact of lip tie on speech development and take action as soon as possible if they suspect their child may be affected. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent speech impediments and ensure that their child has the best chance of developing clear and effective communication skills.
Can lip tie affect a child’s behavior or emotional development?
Answer: While there is no direct link between lip tie and behavioral or emotional development, some children with untreated lip tie may experience difficulty feeding and sleeping, which can lead to irritability and mood changes.