Shingles: Causes, Pain, Duration & Complications
- Updated on: Jul 13, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
Causes of Shingles
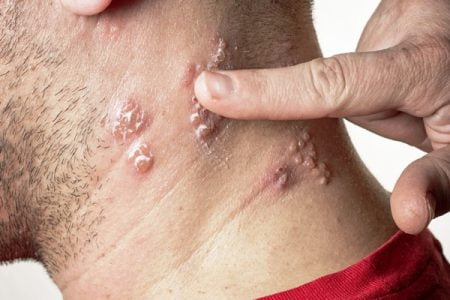
Shingles is a viral infection. It occurs due to reactivation of varicella zoster virus which stays in inactive form in your nerves. The first encounter with the virus, leads to development of chicken pox. After recovering from chicken pox, its symptoms may vanish, but the virus will still persist in your body in dormant stage.
In later stages, the virus may get activated due to stress or weak immune system and may develop shingles. It causes itchy, burning sensation on the affected skin, which may develop into fluid-filled blisters.
Shingles is quite common. It affects one in every three individuals.
Stages of Virus Growth
When the virus gets reactivated from its dormant stage, it causes severe discomfort such as tingling sensation or a twinge under your skin. Such sensations are experienced at a particular point on any one side of your body. These sensations can make the skin sensitive to touch and you may experience numbness, itching or a burning sensation on the affected region.
This sensation may appear anywhere on your body, such as on:
- Waist
- Back
- Thigh
- Chest
- Face
- Ear
- Eye
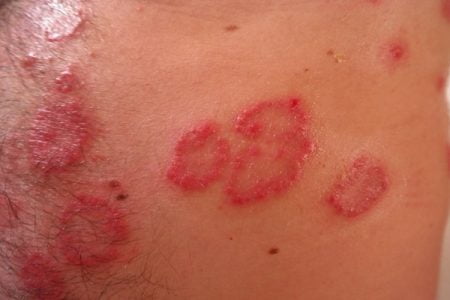
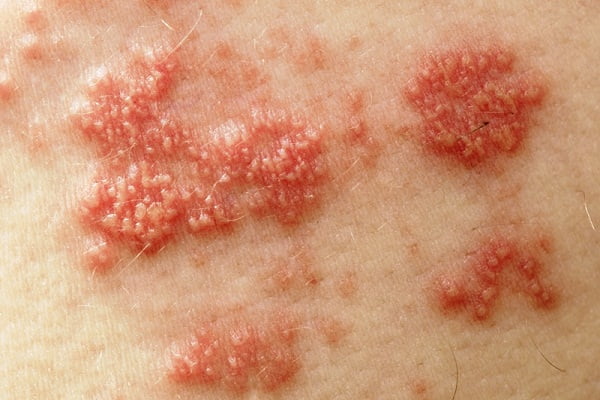
The affected skin will develop rashes within five days, which will grow further and form blister. These blisters are fluid-filled initially and with time they may ooze and dry out completely. Blisters require about one to two weeks to completely dry off and crust over to form scrubs on the affected skin surface.
Along with these blisters, people may experience certain flu-like symptoms, such as:
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Light sensitivity
- You may feel unwell and lethargic
Duration: How long does shingles last?
In most cases, shingles may last for three to five weeks. The duration of shingles is as follows:
- The initial signs of shingles involve pain, numbness and tingling sensation on the affected skin surface, on one side of the body.
- After 1-5 days after the tingling sensation has initiated, the skin may become red and rashes may develop on the affected surface.
- After 3-5 days, rashes get converted to fluid-filled blisters.
- It may take about a week to 10 days for the blisters to ooze out and dry off completely from your skin.
- Then, about a couple of weeks later, these scabs may also clear off.
With the clearance of scabs, shingles may also end. But, you may experience pain for a few days after the blisters may crust over.
In most cases, the duration of shingles depend upon the health and age of the affected individual and the severity of the viral infection.
In some cases, chances of recurrence of shingles persist or people may experience some complications, in severe cases.
How long is shingles contagious?
When shingles rashes get converted to blisters, they become contagious. These blisters contain fluid, which contain high concentration of infectious zoster virus. If an unaffected individual comes in contact with these fluid-filled blisters, the virus can be transmitted to the individual. It can cause chicken pox or directly result in shingles, if he/she had chicken pox before.
Slowly with time, these blisters may ooze out and then crust off from your skin. Once they ooze off, they are no longer contagious. The blisters may take about 1 week to 10 days to ooze and crust over completely. In severe cases, this period may prolong further.
This period is termed as the incubation period for shingles. During this period, you should avoid contact with people such as pregnant women, infants and children, elderly people and immune-compromised individuals.
You should cover the blisters to avoid transmission of the virus. You should also take antiviral drugs to heal the blisters faster and provide comfort from shingle symptoms.
How long does shingles pain last?
Pain during shingles, is one of the initial symptoms and may last even after the blisters have crust over. Shingle pain may last for about eight to 12 weeks. It may occur for months to even years in severe cases. Pain during shingles is extremely severe and creates huge discomfort in individuals.
If a patient suffers from postherpatic neuropathy, then pain may last for years which would be quite severe and distressful for the patient.
Complication of shingles
The most common complication of shingles involves postherpetic neuropathy (PHN). It occurs due to injury in the nerve where shingle rashes were formed. Postherpetic neuropathy leads to severe pain, even after the blisters have been cleared off from your skin.
It is quite difficult to treat a patient suffering from PHN. It is a lingering condition which lasts for several months to years. PHN causes sensitivity to touch and change in temperature and wind. In some cases, it can also lead to depression, anxiety, weight loss, and sleeplessness.
People above 60, who suffer from shingles, have a high risk of PHN occurrence. The risk of PHN development also increases in the following cases:
- If you are above 50
- If you have a weak immune system
- If you suffer from severe shingles, which has spread on your major part of the body
The incidence of PHN development further increases by 50%, if you belong to more than one category.
Certain Complications which can occur due to shingles are as follows:
- Bacterial infection, mainly due to Staphylococcus aureus, which lead to development of skin rashes.
- It can lead to severe vision problems, if you suffer from Ophthalmic Shingles
- If one of your cranial nerve is affected by shingles virus, it can lead to hearing loss, loss of taste, facial paralysis, vertigo and may experience ringing sound in your ears.
- If your internal organs are damaged by the zoster virus, it can cause pneumonia, hepatitis, and other infections.
- Blisters may get infected with other microorganism.
- Blisters may leave a scar, once they ooze out completely, in rare cases.
How can you get rid of shingles faster?
Your doctor may prescribe certain antiviral drugs to kill the number of zoster virus residing in your body. He/she may also prescribe some pain killers to provide relief from discomforting symptoms. Researchers have developed a shingle vaccine, which is effective in treating shingle, especially in older adults.
You can even try some simple home remedies to provide comfort from shingle symptoms, such as healing bath, cold compress, soothing lotion or creams and certain dietary recommendations.