Browsing: Enlarged heart
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Enlarged heart
Human Heart: Anatomy, Function, Chambers, Location, Facts
The heart is a muscular organ that works as your body’s circulatory pump. It takes in deoxygenated blood through the veins and delivers it to the lungs for oxygenation and then pumps this oxygenated blood into the arteries. In coronary heart disease, the heart does not function properly. Learn more about your heart.
Sharp Pain in Chest: What It Means and When Should You See a Doctor?
Sharp pain in chest can be caused by anything from usual muscle pain to a severe heart disease. Enlarged or dilated heart can develop as a result of many heart diseases. Some of them can show signs such as pain in chest and breathlessness.
There are many diagnostic techniques used by doctors to perform diagnosis of an enlarged heart. You can identify certain early signs that indicate that it may possibly be due to enlarged heart or related complication. Doctors use several tests to confirm the diagnosis. ECG and imaging tests (MRI) are few examples.
What Does It Mean to Have an Enlarged Heart (cardiomegaly)? An enlarged heart (known as cardiomegaly in medical terms) isn’t…
An enlarged heart is generally treatable but can result in serious complications without treatment and even sudden death. It can increase the risk of deadly blood clots and cardiac arrest. Enlarged heart’s left ventricle can cause heart failure. The risk of sudden death increases during exercise or strenuous physical activity.
An enlarged heart is generally caused by some other condition or disease, which puts extra strains on your heart causing the heart muscles to damage and die. An enlarged heart can be caused by a variety of health conditions that cause your heart to work harder or that damage the muscles of your heart.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Enlarged Heart (Cardiomegaly)?
Symptoms of cardiomegaly depend on its underlying cause or disease. In some people, an enlarged heart causes no signs or symptoms at all. Others may have mild to severe signs such as breathing problems, palpitations, disturbed heart rhythm, fatigue, swelling etc. Heart failure may require you to seek emergency help.
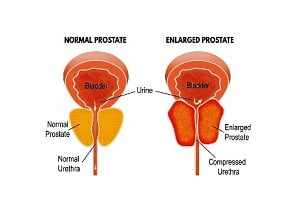
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostate Enlargement or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)?
The symptoms of Benign Prostate Enlargement (BPE) are often mild in the beginning, but they become serious if they aren’t treated early. If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can put pressure on the bladder and urethra causing urinary problems. Common symptoms are frequent urge of urine, waking up at night frequently for urination etc.
What is the Treatment of Enlarged Heart (Cardiomegaly)?
Can an enlarged heart be treated? An enlarged heart can be treated and, in some cases, it is possible over…
About 50 percent of men over the age of 60 have enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). By the age of 85, more than 95 percent of men have BPH. There is good news however for those living with enlarged prostate or who are at risk of developing the disease. Healthy habits such as exercising, eating certain foods, and limiting dietary fat may help with BPH.