Browsing: Erectile Dysfunction
Comprehensive Information, Resources, and Support on Erectile Dysfunction
Generic Viagra, Cialis & Levitra: Do They Work Like the Brand?
If you have ever had any sexual health issue, you must have come across the names of these medications—Viagra, Cialis,…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is an incredibly common issue that impacts men of all ages globally. Statistics show that around 322…
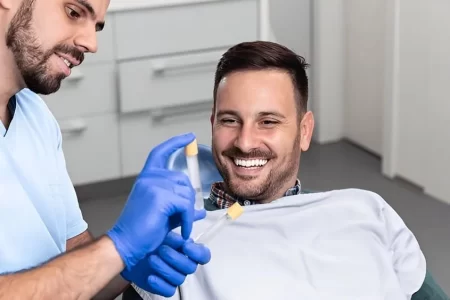
Understanding Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Its Role in the P-Shot Procedure
Erectile Dysfunction is faced by many men all over the world. It not only impacts one sexual libido and performance…
In today’s world, living a healthier lifestyle is not so easy. People are developing many health disorders due to an…
Erectile dysfunction is found to play some role in the development of erectile dysfunction, according to a new research. Researchers say that they have found an area of the genome which is responsible to increase the risk of impotence due to erectile dysfunction.
Peripheral Vascular Disease and Erectile Dysfunction
Both erectile dysfunction (ED) and peripheral vascular disease (ED) are two different conditions. Erectile dysfunction is found in men making them unable to get and maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) on the other hand is a circulatory problem in which the arteries become narrow and therefore reduce the flow of blood to lower limbs.
Early Signs and Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition found in men which makes them unable to get or keep an erection firm enough to go for sexual intercourse. Uncommonly, this condition is also referred to impotence. Age can be a risk factor for erectile dysfunction in men but it doesn’t cause ED. Some early warning signs of ED are discussed in this article.
There are some ways to identify if your erectile dysfunction (ED) has occurred due to a physical or psychological cause. It involves a simple test which can be performed at home using stamp rolls. It is based upon the process of nocturnal penile tumescence. The cause of ED helps us analyze the most suitable treatment option for curing impotence.
Drugs that Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Several studies have indicated that specific classes of drugs which are used for treating certain disorders or diseases have eventually produced side-effects. One common side-effect is erectile dysfunction (ED). These drugs influence the hormonal levels, nerve activity or blood circulation in the body, leading to an increased risk of impotence.
Researchers reported that men have a higher risk of erectile dysfunction, if they had suffered from hemorrhoids before. The study was conducted in Taiwan using the Longitudinal Health Insurance Database 2000, a nationwide population-based dataset in Taiwan.