What Is Transurethral Resection of the Prostate?
- Updated on: Jan 1, 2024
- 6 min Read
- Published on Jan 1, 2024
As men age, they often encounter health issues unique to their gender, with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) emerging as a prevalent concern. BPH, characterized by the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, can lead to a myriad of urinary symptoms, significantly impacting a man’s quality of life. Among the array of treatment options available, Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) stands out as a revolutionary and highly effective surgical procedure that merits in-depth exploration.
The Anatomy of the Prostate
Before delving into the intricacies of TURP, it is essential to understand the role of the prostate gland in male anatomy. The prostate, a walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder, surrounds the urethra. Its primary function is to produce seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. However, as men age, the prostate can undergo hyperplasia, leading to an enlargement that may impede the normal flow of urine.

The Conundrum of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, often referred to simply as an enlarged prostate, manifests in various symptoms that can significantly disrupt daily life. These symptoms include increased frequency of urination, urgency, a weakened urinary stream, and the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying. The impact on both physical and emotional well-being necessitates effective and sustainable solutions.
TURP: A Surgical Marvel Unveiled
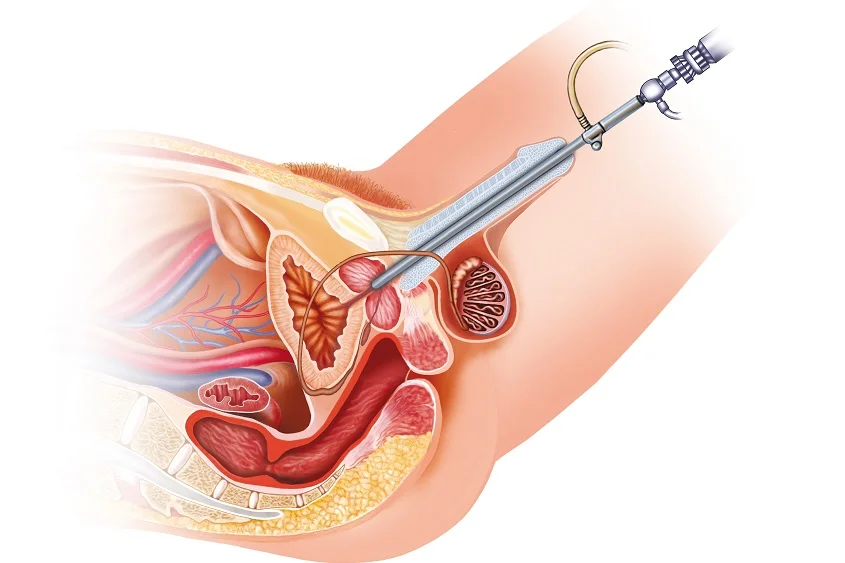
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) emerges as a transformative surgical intervention designed to address the root cause of BPH. This procedure is characterized by its minimally invasive approach, wherein a specialized instrument is inserted through the urethra to remove excess prostate tissue that obstructs the flow of urine.
The TURP Procedure: Step by Step
Patient Preparation: Before the procedure, patients undergo a thorough assessment to ensure they are suitable candidates for TURP. This assessment includes a medical history review, physical examination, and often diagnostic tests such as urodynamic studies.
Anesthesia: TURP is typically performed under spinal or general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort throughout the procedure.
Resection of Prostate Tissue: Using a resectoscope, a specialized surgical instrument with a camera and cutting loop, the surgeon carefully removes excess prostate tissue. This step is crucial for relieving the urethral obstruction and improving urinary flow.
Cauterization: After tissue removal, the surgeon cauterizes any bleeding to minimize postoperative complications.
Catheter Placement: A catheter is often inserted to facilitate urine drainage during the initial stages of recovery.
The Advantages of TURP
Minimally Invasive Nature: TURP is considered a minimally invasive procedure, as it is performed through the natural passageway of the urethra. This approach significantly reduces the risks associated with traditional open surgeries.
Efficacy in Symptom Relief: Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the high efficacy of TURP in alleviating the symptoms associated with BPH. Patients commonly experience improved urinary flow, reduced urgency, and a notable enhancement in overall quality of life.
Preservation of Sexual Function: Unlike some alternative treatments for BPH, TURP has a minimal impact on sexual function. Men can often maintain normal sexual activity after undergoing the procedure.
Long-Term Success: TURP has established itself as a long-term solution for BPH symptoms, providing enduring relief to patients. The sustainability of its effects makes it a preferable option for those seeking lasting improvements in urinary health.
Considerations and Potential Complications
While TURP is generally well-tolerated and associated with a low risk of complications, it is essential to acknowledge potential considerations and risks. These may include:
Temporary Incontinence: Some patients may experience temporary urinary incontinence following the procedure, but this often resolves as the body adjusts.
Ejaculatory Changes: TURP can lead to changes in ejaculatory function, including retrograde ejaculation. It is crucial for patients to discuss these potential effects with their healthcare providers before the procedure.
Patient Selection and Consultation
Patient selection plays a crucial role in the success of TURP. Candidates for the procedure are typically those with moderate to severe BPH symptoms that have not responded adequately to conservative treatments. Moreover, patients with certain medical conditions or anatomical considerations may require alternative approaches, emphasizing the importance of thorough consultation between the patient and their healthcare provider.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
In the realm of prostate health, the category of Emerging Technologies and Innovations plays a pivotal role, presenting alternative approaches to Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) and promising new dimensions in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Laser-Based Techniques
As a testament to the dynamic nature of medical innovation, laser-based techniques have emerged as noteworthy alternatives to traditional TURP. Two prominent methods, Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) and GreenLight laser therapy, showcase the integration of cutting-edge laser technology into prostate surgery.
Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP)
HoLEP involves the use of a holmium laser to remove obstructive prostate tissue precisely and efficiently. This technique is particularly effective for larger prostates and has been associated with reduced blood loss and shorter hospital stays compared to conventional TURP.
GreenLight Laser Therapy
Greenlight laser therapy employs a high-powered green laser to vaporize excess prostate tissue. This technique offers the advantage of being performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home on the same day as the procedure. GreenLight laser therapy has demonstrated efficacy in symptom relief comparable to traditional TURP.
Aquablation Therapy
In the quest for less invasive approaches, Aquablation therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation. This robotic-assisted procedure utilizes a high-velocity waterjet to precisely remove prostate tissue. The precision afforded by robotics enhances the surgeon’s ability to tailor the treatment to each patient’s unique anatomy, potentially reducing the risk of complications.
Precision and Control
Aquablation therapy integrates advanced robotics to provide surgeons with unparalleled precision and control during the procedure. This technology allows for a more targeted removal of prostate tissue, minimizing the impact on surrounding structures.
Reduced Sexual Side Effects
Early studies suggest that Aquablation therapy may have a lower impact on sexual function compared to traditional TURP, making it an appealing option for men concerned about potential changes in erectile and ejaculatory function.
Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE)
In the arena of non-surgical innovations, Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE) has garnered attention as a minimally invasive alternative to surgical interventions. This procedure involves the selective embolization of arteries that supply blood to the prostate, leading to a reduction in prostate size and alleviation of BPH symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Nature
PAE is performed through a tiny incision in the groin, allowing for a less invasive approach compared to traditional surgical interventions. Patients often experience shorter recovery times and reduced postoperative discomfort.
Preservation of Sexual Function
One notable advantage of PAE is its potential to preserve sexual function, as it does not involve the direct removal of prostate tissue. This aspect makes PAE an attractive option for men seeking a balance between symptom relief and maintaining normal sexual activity.
Personalized Medicine in Prostate Health
Advancements in genomics and personalized medicine are also making their mark in the field of prostate health. Understanding the genetic factors that contribute to BPH and tailoring treatment approaches based on individual patient profiles hold the promise of more precise and effective interventions.
Genomic Insights
Research is underway to identify genetic markers associated with BPH susceptibility and progression. The integration of genomic insights into clinical decision-making may pave the way for personalized treatment plans, optimizing outcomes for each patient.
Targeted Therapies
The development of targeted therapies based on the specific molecular characteristics of a patient’s prostate tissue represents a paradigm shift in the approach to BPH. By targeting the underlying mechanisms of prostate enlargement, these therapies aim to provide more effective and tailored solutions.
FAQs
How long does it take to recover from Transurethral Resection of the Prostate?
Recovery time varies, but most patients resume normal activities within a few weeks. Full recovery may take up to six weeks, depending on individual health and adherence to post-operative care.
Are there alternatives to Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for treating BPH?
Yes, alternatives include medications, lifestyle changes, and newer minimally invasive procedures. Your urologist will assess your condition and discuss the most suitable options based on your health and preferences.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with TURP?
While TURP is generally safe, potential risks include bleeding, infection, and sexual dysfunction. Serious complications are rare but can occur. Consult with your urologist to understand personalized risks and benefits.
Can TURP be performed on an outpatient basis?
Yes, TURP is often performed as an outpatient procedure. However, some patients may require a short hospital stay. Your urologist will determine the most appropriate setting based on your health and the extent of the procedure.
Is Transurethral Resection of the Prostate covered by insurance?
In most cases, insurance covers TURP, especially if deemed medically necessary. It's crucial to verify coverage with your insurance provider beforehand and discuss any potential out-of-pocket costs with your healthcare team.
Source
TURP: A Surgical Marvel Unveiled