Appendicitis Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatments, Surgery, and Complications
- Updated on: Jun 28, 2024
- 6 min Read
- Published on Apr 19, 2021

What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is the inflammation and welling of the appendix. The appendix is a small, pocket-type sac of tissue that is located in the first section of the colon in the lower-right side of the abdomen.
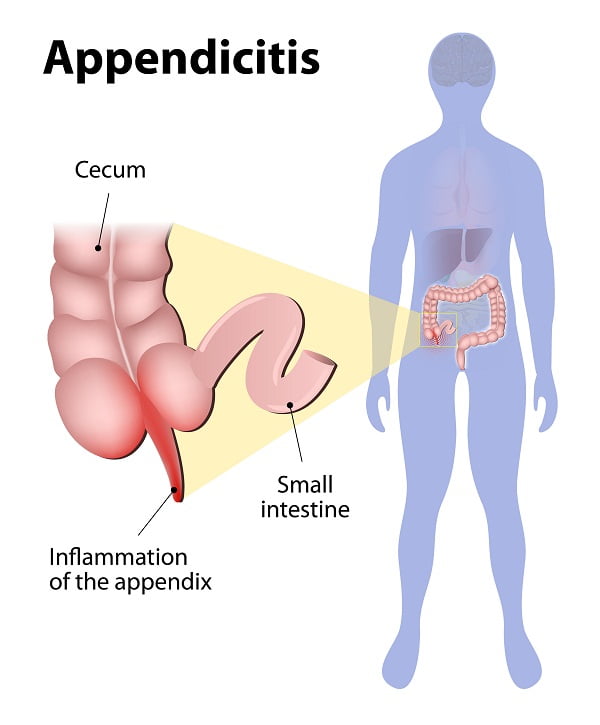
According to available statistics, appendicitis is the most common cause of abdominal pain in the United States. It is estimated that about 5 percent of all Americans experience appendicitis some time in their lives.
Who gets affected with appendicitis?
Almost anyone can get appendicitis, but it usually occurs in people between the age group of 10 and 30. It’s more common in males than in females.
If it is left untreated, the disease may cause the appendix to burst, which may lead to infection. This can be serious and sometimes dangerous.
What are the early signs and symptoms of appendicitis?
Early signs and symptoms of appendicitis are often mild. These may involve a loss of appetite and nausea and a sense of feeling unwell. Generally, people ignore them as some other less concerning condition.
As the disease progresses, appendicitis symptoms start appearing with a pain in the middle of abdomen that may come and go. The pain is not localized and may move from one spot to another. Most people are not able to pin point the exact location of the pain. It travels to the lower right-hand side (which is the location of the appendix) and becomes severe and constant after some time.
If the pain is due to appendicitis, you will experience other symptoms such as:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Feeling sick
- Poor appetite
- Diarrhoea
- High fever
- Abdominal swelling
- Constipation
- Pain around the belly
- Not able to pass gas
- Tenderness on your right side
What is the appendix pain location?
If the inflammation of your appendix increases, it may spread through the appendix to its outer surface and to the lining of the abdomen. When the lining and outer surface becomes inflamed, the nature of the pain changes and is then localized to one small spot. Generally, this location of pain is between the right hip bone and the belly.
If the disease causes complications and the appendix ruptures or becomes perforated, infection may spread throughout the abdomen. This may cause the pain to spread again as the entire lining of the abdomen becomes inflamed.
Is it appendicitis pain or gas?
Gas-related pain is a common symptom of appendicitis. If you have appendicitis, you may feel as if you’re unable to pass out the gas.
If you experience mild discomfort, you can take an over-the-counter heartburn medication. If the symptoms go away, it is likely due to gas (indigestion). If the symptoms persist more than a day or if the pain or discomfort is severe or if there is any other unusual symptom, you should contact a doctor. It may be due to appendicitis.
How is appendicitis diagnosed? Is there a test for the diagnosis of appendicitis?
Your doctor will start with a thorough history and physical examination to diagnose the condition. Patients generally have an increased temperature and tenderness in the right lower abdomen, which can be noted in the physical exam.
The doctor will look for tenderness in the lower right section of the abdomen. If you’re pregnant, the pain may be severe. If perforation occurs, your stomach may become hard and inflamed.
If inflammation has spread to the peritoneum, you will experience pain that becomes really bad when the doctor touches and quickly releases his or her hand after pressing over the tender area of the abdomen during a physical exam.
There isn’t any one test to diagnosis appendicitis. Your doctor will use a combination of tests to arrive at a conclusion. H or she will order a complete blood count test to determine if there’s a bacterial infection. He or she will recommend other tests such as:
- Pelvic exams to ensure that you aren’t experiencing any reproductive or sexual problems.
- Pregnancy tests to rule out a suspected complication of pregnancy
- Imaging tests of the abdomen (such as X-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan) to determine if you have an abscess or cyst or other complications.
- Chest X-ray to rule out right lower lobe pneumonia, which sometimes has similar symptoms.
- Urine test: Your doctor may want you to have urinalysis to rule out a urinary tract infection or kidney stone
What are the causes of appendicitis? What complications can occur due to the appendicitis?
In many cases, the exact cause for appendicitis is not known. Sometimes, there can be multiple causes for it.
Doctors believe that a blockage in the lining of the appendix is the cause of appendicitis. The blockage may result in infection which causes the disease appendicitis. The bacteria grow fast, causing the appendix to become inflamed. This causes the accumulation of pus inside therein. If it is not treated promptly, the appendix can also burst due to the swelling. If the appendix ruptures, fecal matter can enter the abdomen, which becomes a medical emergency and requires urgent treatment.
The bursting of the appendix can also compress the blood vessels. This may cause a lack of blood flow to the appendix leading to another complication called gangrene.
The obstruction occurs generally due to accumulation of fecal matter. It can also result due to:
- enlarged lymphoid follicles
- worms
- tumors
- trauma
Peritonitis is another possible complication due that may develop to a ruptured appendix. It’s the inflammation of the tissue that lines your abdominal wall. If the appendix bursts, it can also cause other nearby organs to inflame. Others organs that may be affected are bladder, cecum, and sigmoid colon etc.
If the infected appendix leaks but does not rupture, an abscess can form. This limits the infection to a small area. However, the abscess can also be dangerous and needs prompt treatment.
What is the treatment for appendicitis? What is appendicitis surgery?
Appendicitis treatment involves surgery in most cases. Surgery is used to remove the inflamed portion of the appendix. Your doctor may give antibiotics to prevent occurrence of infection before the appendix operation is performed.
The following surgical options can be recommended by your doctor based on your condition and the complications associated with the appendicitis:
Surgery to remove the appendix (known as appendectomy performed for appendix removal)
Appendectomy is a procedure that can be performed as open surgery using one abdominal incision about 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 centimeters) long. The surgery can be done through a few small abdominal incisions in a laparoscopic procedure. If a laparoscopic appendectomy is performed, your surgeon will insert a surgical tools and a video camera into your abdomen through the small incisions to remove your inflamed appendix.
Laparoscopy is less invasive, and the recovery time is shorter. But, sometimes an open surgery is required if you have an abscess or peritonitis.
Draining an abscess before appendix surgery
If the appendix has burst and an abscess has formed, the abscess may be drained through this procedure. The surgeon will place a small sized tube into the abscess through the skin. Appendectomy can then be performed several weeks later after the skin has been controlled.
What’s the recovery time for appendicitis?
If you undergo a laparoscopy surgery, you will leave the hospital within a few days after the procedure is performed. Laparoscopic procedure is less invasive and the recovery time is shorter.
If the treatment involves an open surgery or surgery for additional complications, such as peritonitis, you have to remain at the hospital for about a week’s time. The recovery time will be even longer if the abdominal muscles are cut during the procedure.
How will you feel after the surgery?
You may experience tenderness and bruising after the operation. This will go away over time. Your doctor may prescribe medicines such as pain killers (acetaminophen and ibuprofen).
You may also experience constipation for a few days. It is important to remain hydrated, drink plenty of water, and eat fiber-rich foods to help in the bowel movements.
Can appendicitis be treated without a surgery?
Only in rare cases, appendicitis may be treated without a surgery. This is considered if the pain is not severe and the diagnostic tests are also normal. Your doctor in such cases may prescribe antibiotics and a liquid diet until your symptoms resolve.
How can I prevent appendicitis?
You can’t prevent appendicitis, but you can take certain steps to lower the risk of getting it. It’s less common in people who consume lots of fiber in the diet such as fresh vegetables and fruits.
Who is at risk for appendicitis? What are the risk factors of appendicitis?
Appendicitis rarely happens in children below the age of two. It mostly occurs in people between the age group of 15 and 30 years. It is more common in males than females. People who consume lesser amounts of fiber are found to be at higher risk of getting it than those who have plenty of fibers in their diet.