Bruxism (Teeth Grinding or Jaw Clinching)
- Updated on: Nov 22, 2024
- 7 min Read
By
- Published on Sep 26, 2019
What is bruxism?
Bruxism is a medical term used broadly for a number of behaviors that may include the following:
- Gnashing of teeth
- Grinding of teeth
- Clenching of teeth
- Gritting of teeth
- Jaw clenching
A person suffering from the condition does not have any idea about his condition because it usually happens during the night time and is called nocturnal bruxism or sleep-related bruxism. But it can also happen when the person is awake often during situations that make them feel tense or anxious such as while lifting heavy objects, driving, reading and writing.
How many people have bruxism? Is bruxism common?
Bruxism is a very common condition. One in three people suffers from the condition. The condition can range from normal to severe. 10 percent patients grind their teeth so hard that teeth are reduced to nubs, and the only treatment left is reconstructive surgery.
What are the symptoms of bruxism?
Bruxism symptoms may include any one or more of the following:
- Rhythmic contractions of the jaw muscles
- A grinding sound at night, loud enough to disturb the sleep of sleeping partner
- A morning headache
- Tight and painful jaw muscles (painful to open your mouth wide after waking up)
- Long-lasting pain in the face
- Damaged teeth (flattened, fractured or loose), broken dental fillings and injured gums
- Damaged tooth enamel, severe enough to expose deep layers of tooth
- Tooth pain and increased sensitivity
- Swelling on the side of your lower jaw
- Neck or face pain or soreness
- Damage to inner cheek because of chewing
- Sleep disruption
What are the causes of bruxism? What causes bruxism when sleeping?
The cause of teeth grinding can be any of the following:
Stress and anxiety
Teeth grinding is most often caused by stress or anxiety and most people aren’t aware of it. It often happens during sleep.
Medication
Certain medications have some side effects and teeth grinding is one of them. Teeth grinding is also linked to an antidepressant known as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Examples of SSRIs include paroxetine, fluoxetine, and sertraline.
Sleep disorders
Certain sleep disorders such as snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) also cause bruxism. These disorders interrupt the breathing process while sleeping. Some other sleep disorders that can cause bruxism are:
- Talk while asleep
- Violent actions while asleep, such as kicking out or punching
- Sleep paralysis (an inability to move or speak while waking up or falling asleep)
- Hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t real) while half-sleep
Lifestyle
Certain lifestyle factors that can make a person susceptible to teeth grinding may include:
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Using recreational drugs, such as ecstasy and cocaine
- Having excess (more than 6 cups a day) of caffeinated drinks, such as tea or coffee
What are the risk factors for bruxism?
The factors that may increase the risk of bruxism are:
Stress, anger and frustration
All these strong emotions have a negative impact on the brain and body and can lead to teeth grinding.
Age
Bruxism is very common in young children, but it usually goes away by adulthood.
Personality type
A person who is aggressive, competitive, or hyperactive has a high chance of getting this disorder.
Medications and other substances
Taking certain psychiatric medications, such as certain antidepressants increases the risk of bruxism. Other factors such as smoking tobacco, and drinking caffeinated beverages and alcohol also increase the risk of bruxism.
Family history
Sleep bruxism tends to occur in families. A person having bruxism indicates that other members of the family also may have bruxism or a history of it.
Other disorders
Certain mental health problems and medical disorders increase the chances of bruxism. Such disorders include:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Dementia
- Gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD)
- Epilepsy
- Night terrors
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
How is bruxism diagnosed? How do you know if you have bruxism?
A dentist diagnoses bruxism in the following ways:
Evaluation
In an evaluation, the dentist looks for the signs and symptoms of changes in the teeth and mouth. The evaluation continues for the next several visits to see if the process is progressive and to determine the treatment.
Determining the cause
If the dentist finds any sign of bruxism, he will try to find out its cause. It is done by asking questions about your general dental health, personality traits, medications, daily routines, and sleep habits.
To evaluate the severity of bruxism, the dentist may check for:
- Tenderness in the jaw muscles
- Dental abnormalities, such as broken or missing teeth
- Other damage to the teeth, the underlying bone, and inner cheeks (with the help of X-rays)
Referral
If the dentist finds out that bruxism is related to major sleep issues, he or she may recommend a sleep medicine specialist. A sleep medicine specialist will conduct more tests such as a sleep study. This test assesses the number of episodes of teeth grinding and determines any sleep apnea or other sleep disorders.
If the dentist finds out that bruxism is related to anxiety or other psychological issues, he may refer the person to a licensed therapist or counselor.
What are the treatment options for bruxism? How do you relax your jaw?
The treatment of bruxism is done in the following ways:
Dental approaches
Dental approaches refer to certain ways to preserve and improve the condition of the teeth. However these methods can only correct the damage to the teeth. They do not cure the disease. Some dental approaches are listed below:
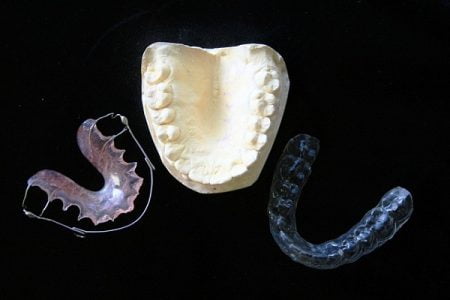
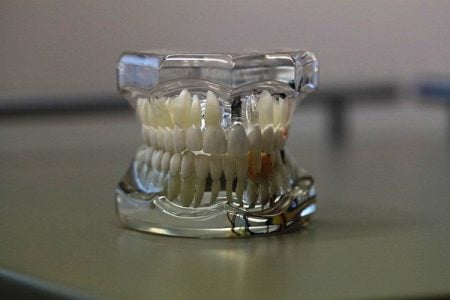
Mouthguards
These devices are designed to keep teeth separated so that the damage caused by clenching and grinding can be prevented. They are made up of hard acrylic or soft materials and they easily fit over the upper and lower teeth.
Dental correction
In severe cases, bruxism may damage the tooth (increased tooth sensitivity or the inability to chew properly). So, the dentist may reshape the chewing surfaces of the teeth or sometimes use crowns to repair the damage.
Lifestyle approaches
Since lifestyle habits lead to bruxism, managing them is one of the solutions to the problem. One or more of these approaches may help relieve the disorder:
Stress or anxiety management
Some learning strategies such as meditation (promotes relaxation) may help to fight the stress that may worsen bruxism. If the bruxism is related to anxiety, a licensed therapist or counselor may help to calm down all these negative factors.
Behavior change
Practicing proper mouth and jaw position is very useful and effective in dealing with bruxism. The dentist can show the best position of the mouth and jaw.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a method that helps to learn how to control muscle activity in the jaw by using monitoring procedures and equipment.
Medications
Medications do not treat bruxism effectively but can be used to control the frequency of the condition. Some of the medications that are normally recommended for patients of bruxism are given below:
Muscle relaxants
The doctor may suggest a muscle relaxant before bedtime, for a short period of time.
Botox injections
Botox is a form of botulinum toxin that may help some people with severe bruxism who don’t respond to other treatments.
Medication for anxiety or stress
Short-term use of antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications is sometimes recommended by doctors to deal with stress or other emotional issues that may be causing your bruxism.
Treating associated disorders
Treatment for associated disorders may include:
Medications
If bruxism occurs as a side effect of a drug, the doctor may decide to change the medication to a different one.
Sleep-related disorders
Sleep-related disorders such as apnea when treated, also have a positive effect on bruxism.
Medical conditions
If the cause of bruxism is an underlying medical condition, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), then such conditions are treated first. Their treatment usually shows some positive results in the improvement of bruxism.
Jaw Exercises
Exercise is effective in many ways. In the case of bruxism also, exercise plays an important role in the treatment. Teeth grinding can be treated by doing jaw exercises daily.
A physical therapist can recommend more specialized exercises that will help relax and strengthen the jaw. The exercises are given below and they are performed three to six times, twice or thrice a day:
- Using a warm, wet washcloth on the jaw
- Place the thumb underneath the chin and open and close the mouth while keeping the thumb in place
- Push the jaw out after keeping the thumb and forefinger on the chin
- Put your tongue on the roof of the mouth and open and close the mouth
- Let the jaw go slack after positioning the finger inside the mouth
What are the preventive measures for bruxism? How do I stop grinding my teeth at night?
Some tips to prevent teeth grinding include:
- Avoid foods and drinks that contain caffeine, such as colas, chocolate, tea, and coffee.
- Avoid alcohol. Alcohol consumption intensifies teeth grinding.
- Do not chew on pencils or pens or anything that is not meant to be eaten.
- Avoid chewing gum as it makes the jaw muscles get more used to clenching and makes the person more likely to grind teeth.
- Train yourself not to clench or grind your teeth. Keep the tip of the tongue between the teeth whenever teeth grinding occurs. This practice trains the jaw muscles to relax.
- Relax your jaw muscles at night by holding a warm washcloth against the cheek.
- Take help from professional counselors to help fight the stress.
- Try stress-reducing techniques like listening to music, taking a warm bath, or exercising. These things can help to relax and reduce the risk of developing bruxism.
- Avoid stimulating substances like coffee, tea, or alcohol in the evening.
- Practice good sleep habits. Always try to sleep at the same time and wake up at the same time daily.
- Take help from the sleeping partner. Ask him or her to be aware of any grinding or clicking sound so that the same can be reported to the dentist or doctor.
- Wear a mouthguard (a dental appliance to stop teeth grinding) at night.
- Schedule regular dental exams. This way the disease can be diagnosed if any signs or symptoms are present.
What are the complications of bruxism?
The complications of bruxism are given below:
Teeth grinding effects
Teeth grinding effects can range from mild disturbance to serious problems (require a dental professional’s attention). Side effects of teeth grinding include:
- Loosening of teeth from the gums
- Losing of teeth
- Fracturing of teeth
- Wearing away of teeth and enamel
- Receding gums
- Aching jaws
- Recurring headaches
- Tooth pain
- Developing jaw joint disorders
Teeth and jaw clenching effects
Teeth clenching and jaw clenching can have an ill effect on the jaw muscles. Some side effects may include:
- Sore and tired jaw muscles from overuse
- Chronic headaches because of the tension in the jaw
TMJ disorders
TMJ stands for the temporomandibular joint. It is found on either side of the jaw and it holds the upper and the lower jaw together and also allows movement. This joint connects the skull with the jawbone. Some of the symptoms of TMJ disorders that may arise because of bruxism are:
- Jaw pain
- Aching muscles
- Inability to move the mouth effectively