Meningitis in Children: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention and Treatment
- Updated on: Jul 13, 2024
- 4 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
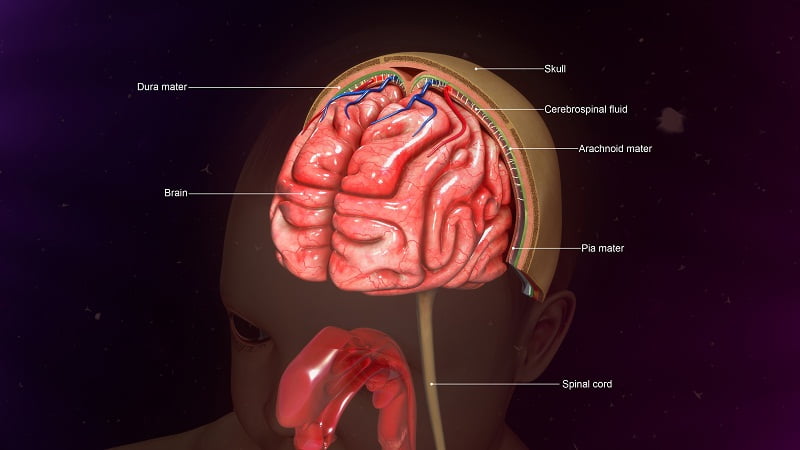
What is meningitis in children?
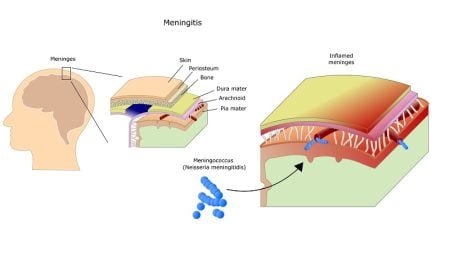
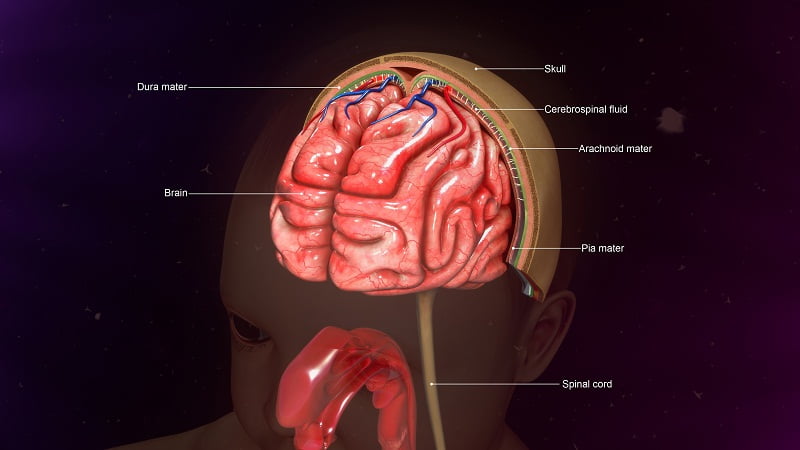
Meningitis is a condition of the brain and spinal cord where an inflammation occurs in the tissues that cover the brain and spinal cord of children. Sometimes, the disease affects the brain only. It is a life-threatening condition but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, a child with meningitis can recover. If left untreated, the disease can progress rapidly and may cause such as:
- permanent brain damage
- neurologic problems
- and finally death
Infants, toddlers and young children are at high risk of meningitis because their immune system is not so strong to fight the disease.
What are the symptoms of meningitis in children?
Meningitis is a deadly disease that can strike very quickly and may kill within hours. A good knowledge of the signs and symptoms may help to understand the disease. Symptoms of meningitis vary by age.
Symptoms of meningitis in newborn babies and infants
Newborns and children under 12 months of age are unable to communicate specific discomfort. Also at this age, the signs of meningitis can be very subtle and difficult to detect. Important signs of illness that should alert parents include:
- Fussiness, discomfort and irritability
- Abnormal drowsiness
- Poor feeding
- Temperature too high or too low
- Frequent vomiting
- Rash
- Sudden seizures
- Jaundice (a yellowish tint to the skin)
- Stiffness of the body and neck
- A high-pitched cry
- Bulging fontanelle (soft spot on head)
Symptoms of meningitis in toddlers and young children
Toddlers and young children are most vulnerable to meningitis. Symptoms that may appear are:
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Decreased appetite
- Excessive crankiness (extreme cranky periods)
- Excessive sleepiness (impossible to arouse)
- Seizures along with a fever
- Rash
Symptoms of meningitis in older children
Older children with meningitis typically show the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Headache
- Confusion
- Stiff neck
- Back pain
- Upper respiratory tract infection before the meningitis
- Seizures
- Pressure on the brain
- Nerve damage
- Objection to bright lights
What Causes meningitis in children?
Causes of meningitis in newborn babies and infants
Meningitis in infants may be caused due to an infection of the bloodstream (known as sepsis). The underlying bacteria usually responsible for this infection are acquired from the birth canal (mostly include group B streptococci, Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes).
Causes of meningitis in toddlers and young children
The infection in young children is usually caused by contact with respiratory secretions (such as saliva or mucus from the nose). These secretions contain causative bacteria which include Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae type B.
What are the risk factors for meningitis in children? Who is likely to get it?
The bacteria that cause meningitis are normally found in the mouths and throats of healthy children. When such bacteria get into the bloodstream, a child gets the disease.
Certain groups of children are more likely to get the illness. These include the following:
- Newborn babies, especially under two months of age as their immune systems are not well developed. The bacteria can get into the bloodstream very easily.
- Children with recurrent sinus infections.
- Children with recent serious head injuries and skull fractures.
- Children with recent brain surgery.
What are the treatment options for meningitis in children?
Antibiotics
A high dose of antibiotics is given intravenously as soon as the disease is suspected. Very sick children receive antibiotics even before the diagnosis. After the proper diagnosis is made, the antibiotics can be changed, if needed, based on the type of bacteria causing meningitis.
During initial days of treatment, the child may not be able to eat or drink, so intravenous fluids are given to provide the medicine and nutrition he needs. Intravenous antibiotics are given for seven to twenty-one days, depending on the age of the child and the bacteria causing the infection.
How can meningitis in children be prevented?
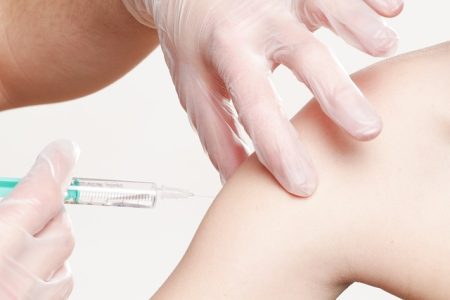
Vaccination
Routine vaccinations can prevent many cases of meningitis. Some types of bacterial meningitis can be prevented with vaccines such as:
Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b) Vaccine
This vaccine decreases the change of infection with Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) bacteria, which is the main cause of bacterial meningitis among young children. The vaccine is given by injection to children:
- At two months
- At four months
- At six months
- Between twelve and fifteen months
Pneumococcal Vaccine
This vaccine is helpful in fighting meningitis infections caused by the pneumococcus bacteria. Along with meningitis, this vaccine also fights bacteremia (an infection of the bloodstream) and pneumonia effectively.
This vaccination is given by injection to children:
- At two months of age
- At four months
- At six months
- Between twelve and fifteen months of age
- Between two and five years of age (to children who are at high risk because of abnormally functioning immune systems, sickle cell disease, kidney problems, and chronic conditions)
Meningococcal Vaccine
This vaccination is recommended for older children (eleven to twelve years of age), or teenagers (fifteen years old).
Chemoprophylaxis
Doctors usually give antibiotics to children who have been in close contact with someone who has meningitis. Ideally, it is given within 24 hours to:
- Children who go to child care centers (and someone is affected by meningitis at the care center)
- Children who are directly exposed to the infected child’s saliva (such as using same utensils or towels)
- Children who are not immunized or partially immunized
- Children with a weak immune system