Clearing Up Toenail Fungus: Before and After Results
- Updated on: Feb 29, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Jun 28, 2023
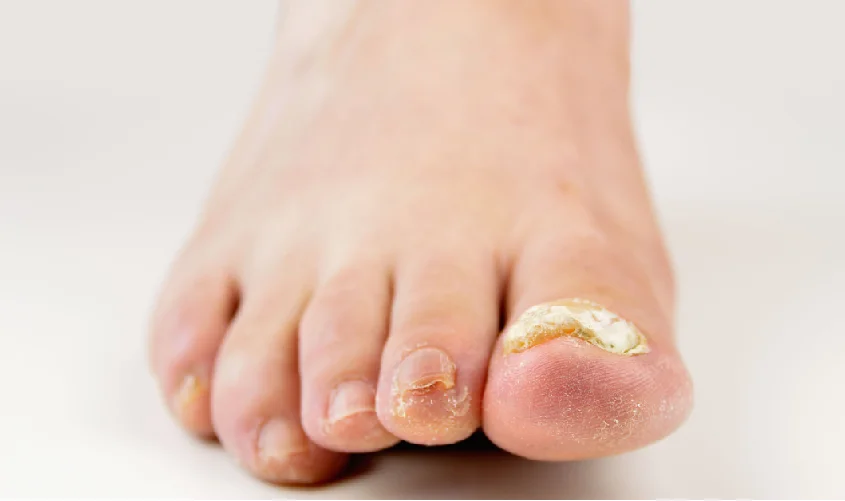
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection that affects the toenails. This infection is caused by various types of fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments such as shoes and socks. The infection can start as a small white or yellow spot under the toenail and can gradually spread to the entire nail, causing discoloration, thickening, and even crumbling of the nail.
Common Symptoms of Toenail Fungus:
- Thickened or distorted nails
- Discoloration (white, yellow, brown, or black)
- Brittle, crumbly, or ragged nails
- Nails that are separated from the nail bed
- Foul-smelling debris under the nails
- Pain or discomfort when wearing shoes or walking
It is important to treat toenail fungus as it can lead to complications such as cellulitis (a skin infection), nail deformity, and even the spread of infection to other parts of the body. Moreover, toenail fungus can be embarrassing and affect a person’s quality of life, causing them to avoid social situations such as going to the beach or wearing sandals.
Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the symptoms of toenail fungus and seek treatment as soon as possible. In the following sections, we will discuss the causes of toenail fungus, prevention tips, and various treatment options available to clear up toenail fungus and improve the appearance and health of your nails.
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a fungal infection that affects the toenails. While it may seem like a minor issue, it can lead to pain, discomfort, and even permanent damage to the nails if left untreated. Understanding the causes of toenail fungus is essential in order to prevent its development and promote healthy nail growth.
Fungi that cause toenail fungus
Toenail fungus is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, making the feet an ideal breeding ground for them. Other types of fungi and yeasts may also contribute to toenail fungus, including candida and non-dermatophyte molds.
Dermatophytes invade the skin and nails by breaking down keratin, a protein found in hair, nails, and skin. Once the fungus gains access to the nail bed, it can cause discoloration, thickening, and brittleness of the nails.
Risk factors for developing toenail fungus
Several factors increase the risk of developing toenail fungus, including:
- Age: The risk of toenail fungus increases with age, as the nails become more brittle and dry over time.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing toenail fungus.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing toenail fungus due to poor circulation and nerve damage in the feet.
- Immune system disorders: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to toenail fungus infections.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the feet, which can increase the risk of developing toenail fungus.
- Trauma to the nails: Trauma to the toenails, such as from sports injuries or tight-fitting shoes, can make the nails more susceptible to fungal infections.
Prevention tips
To prevent toenail fungus, it is important to maintain good foot hygiene and take preventative measures, such as:
- Keeping the feet clean and dry: Wash the feet daily with soap and water, and dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Avoiding sharing personal items: Do not share shoes, socks, or nail clippers with others.
- Choosing the right footwear: Wear shoes that fit well and allow the feet to breathe, and avoid tight-fitting shoes or those made from synthetic materials.
- Keeping toenails trimmed: Keep toenails trimmed and clean, and avoid cutting them too short or cutting the skin around them.
- Using antifungal products: Use antifungal sprays or powders in shoes and on the feet to prevent fungal growth.
By understanding the causes of toenail fungus and taking preventative measures, individuals can protect themselves from this uncomfortable and often unsightly condition. If toenail fungus does develop, it is important to seek treatment promptly in order to prevent further damage and promote healthy nail growth.
Treatment Options for Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can cause discoloration, thickening, and crumbling of the nails, leading to pain and discomfort. If left untreated, toenail fungus can spread to other nails or even the skin, making it important to seek treatment as soon as possible.
Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available for toenail fungus. Here are the four most common treatment options:
Over-the-counter topical treatments
Over-the-counter (OTC) topical treatments are often the first line of defense against toenail fungus. These treatments typically contain antifungal agents such as terbinafine or clotrimazole, which work by stopping the growth of the fungus.
OTC topical treatments come in various forms, including creams, gels, and nail lacquers. They are applied directly to the affected nail and surrounding skin, usually once or twice a day, for several weeks or months. While OTC topical treatments are generally safe and effective, they may take longer to work than prescription medications.
Prescription oral medications
Prescription oral medications are another effective treatment option for toenail fungus. These medications, which are available only with a prescription from a healthcare provider, are taken orally and work by targeting the fungus from within the body.
The most commonly prescribed oral medications for toenail fungus are terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole. Treatment with these medications typically lasts several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the infection. While oral medications are generally safe and effective, they may cause side effects such as nausea, headaches, and liver damage.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is a newer treatment option for toenail fungus that involves the use of a laser device to heat and destroy the fungus. This treatment is often preferred by people who cannot take oral medications due to medical conditions or drug interactions.
During a laser therapy session, the laser device is directed at the affected nail and surrounding tissue, with the heat from the laser killing the fungus. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results, and laser therapy can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance.
Surgical removal
Surgical removal of the affected nail is considered a last-resort treatment option for toenail fungus. This procedure, known as a nail avulsion, involves removing the infected nail and allowing a new nail to grow in its place.
Nail avulsion is usually performed in severe cases of toenail fungus that does not respond to other treatments. The procedure is done under local anesthesia and may cause some discomfort and bleeding. While nail avulsion can effectively remove the infected nail, it may take several months for a new nail to grow in its place.
Tips for Preventing Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there are several effective treatment options available for toenail fungus, prevention is always the best course of action. In this section, we will discuss some tips for preventing toenail fungus:
Proper foot hygiene practices
Maintaining proper foot hygiene is crucial in preventing toenail fungus. Here are some tips to keep your feet clean and healthy:
- Wash your feet daily with soap and water, making sure to dry them thoroughly afterward.
- Keep your toenails clean and trimmed. Use a clean, sharp nail clipper and avoid cutting your nails too short or rounding the corners.
- Use a foot powder to keep your feet dry, especially if you sweat excessively.
- Wear clean socks every day, and avoid wearing socks made of synthetic materials, as they can trap moisture and promote fungal growth.
Choosing the right footwear
The type of shoes you wear can also play a significant role in preventing toenail fungus. Here are some tips for selecting the right footwear:
- Choose shoes that fit properly, with enough room in the toe box to allow your toes to move freely.
- Avoid wearing shoes made of synthetic materials, as they can trap moisture and promote fungal growth.
- Opt for shoes made of breathable materials, such as leather or canvas.
- Avoid wearing the same shoes two days in a row, as they need time to dry out between wearings.
- Avoiding sharing personal items
Toenail fungus is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person. Here are some tips for avoiding the spread of toenail fungus:
- Never share personal items such as nail clippers, files, or socks with others.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public places such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and showers.
- Wear shower shoes or sandals in public showers or locker rooms.
- If you have toenail fungus, avoid touching or scratching the affected area, as this can spread the infection to other parts of your body or to other people.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing toenail fungus. If you do notice any signs of toenail fungus, such as thickened, discolored, or brittle nails, it is essential to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the infection from spreading.












