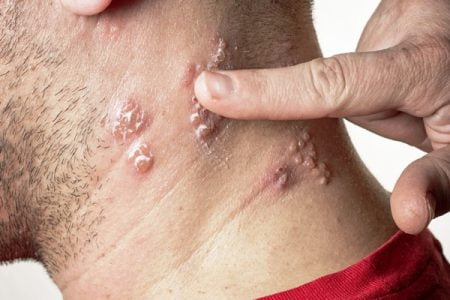
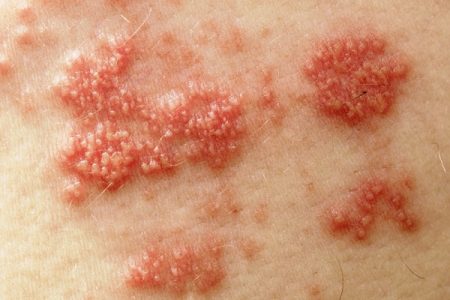
Treatment for Shingles
- Updated on: Jun 12, 2024
- 3 min Read
- Published on Oct 2, 2019

Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is an infection of a nerve and the skin surrounding it.
There is no cure available for shingles, but immediate treatment can help ease an individual’s symptoms until the condition improves. In many cases, shingles gets better within around two to four weeks time. Primary treatment may help reduce the severity of the condition and the further risk of potential complications.
The measures followed for preliminary treatment includes antiviral drugs, pain killers or topical antibiotics.
Secondary treatment includes medications for the complications arising from the herpes zoster virus such as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). Treatments used may include antidepressants, anticonvulsants or opioids.
Prevention measures one needs to take care of for shingles
If an individual gets shingles rash, there are a couple of things one can perform to ease the symptoms. These include:
- keeping the rash clean and dry as much as possible: This reduces the chances of bacterial infection.
- avoiding sharing any kind of clothes such as towels or napkins if shingles rashes persist
- wearing comfortable clothes
- preventing the usage of topical antibiotics or adhesive dressings, which may delay the healing process
- using a dressing that would cover the rashes, so as to prevent the transmission of the virus.
- We need to be isolated from the public only if the rash has oozing fluid and it can’t be covered. In case the rash can be covered by clothing, the risk of passing the infection on to others is low.
Shingles treatment
The following options are available for treating shingles.
Antiviral medication
These medicines are taken to reduce pain, duration as well as complications of the shingles. These are best to reduce severe pain observed initially when the rashes appear.
Commonly prescribed antiviral medicines include acyclovir (zovirax), valaciclovir (valtrex) and famciclovir (Famvir). The course of these medicines can last for a week. These antivirals prevent the future multiplication of virus, if not kill the same.
Who needs to take antivirals?
People who have symptoms of shingles and who are above the age of 50 years are prescribed antivirals. Others who are prescribed the same include:
- individuals who have been infected with the virus on the eyes
- people with weak immune system
- people experiencing moderate to severe pain
- people possessing a moderate to severe rash
- Pregnant woman must consult a doctor before taking these medicines in order to determine if any risk is involved.
- Children are avoided giving antivirals as they develop only mild symptoms of shingles and pose a minimum threat of developing complications.
Pain relief medicines
Many pain relief medicines are available over the counter or prescribed by doctors to help minimize the pain. These are mentioned below:
Over-the-counter available pain drugs
Acetaminophen or ibuprofen are the most commonly available over the counter medicines for pain relief. Acetaminophen is used to treat mild to moderate pains. Whereas ibuprofen is a non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) which aids to decrease inflammation, pain or fever.
Paracetamol is another easily available pain reliever and is available without a prescription.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs act by reducing the inflammation or swelling and also relieve fever and pain by blocking enzymes and proteins made by the body. Ibuprofen is an example of the same.
Opioids
These are drugs that relieve pain by acting on the nervous system. Codeine and morphine are few examples of opioids. These are available by prescription only.
Antidepressants
These drugs are primarily used to treat depression, but have also shown relief to nerve pain. Antidepressants most often used to treat shingles pain are tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). Few examples of these drugs are amitriptyline, desipramine, and nortriptyline.
Topical antibiotics
These are used to inhibit the bacterial infections in the rashes and can be applied directly to the skin.
Topical anesthetics
These are used to numb the surface of a body part and act as a local anesthetic. Benzocaine is an example of topical anesthetics available over-the-counter that can be applied directly to the skin for pain relief.
Lidocaine patches, such as Lidoderm, are got by prescription only, and can be worn on one’s skin. Lidocaine gel such as xylocaine is a medicine that an individual can rub into the skin directly to get relief.
Topical creams
Topical creams having the component capsaicin are used in the treatment for shingles. Capsaicin is obtained from chili peppers. Capsaicin cream (Zostrix) and Qutenza (which is a skin patch) are advised for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia.
Burning sensation, stinging, and skin redness are few side effects seen with capsaicin and should be used with care. These provide long lasting pain relief.
Anticonvulsants
These are medications used for seizures but are also useful in relieving nerve pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are the most commonly prescribed anticonvulsants for shingles pain.
Steroid injections
These are used in patients to treat the pain of postherpetic neuralgia, where above treatments are unable to reduce pain.
Natural Remedies
There are many natural remedies available to reduce pain and irritations, but no cure for shingles as such is available through them. Some of these include healing baths, cool compress, skin paste, home-made lotions, and diet improvement.