What Causes Tooth Decay?
- Updated on: Jul 9, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
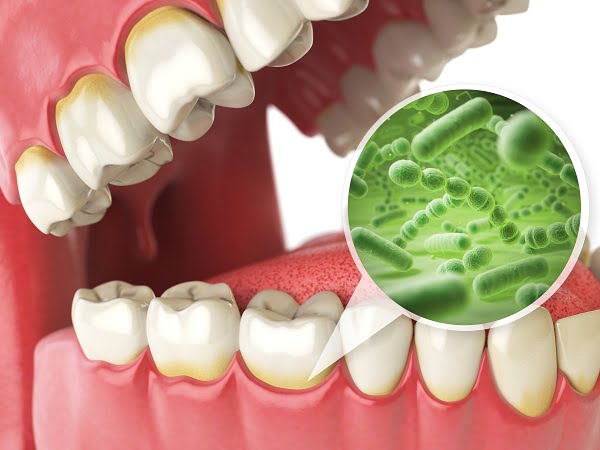
Dental caries or tooth cavity is an oral condition caused by bacteria present in the mouth. These bacteria thrive and grow on the plaque and releases acids which degrade the top enamel of teeth. This condition can lead to the formation of cavities in teeth and sometimes even loss of teeth. Caries is more prevalent in people with low socioeconomic background and people who take a very high amount of sugar in their diet.
Causes of tooth decay
The main reason for tooth decay is biofilm (plaque) deposition on the surface of teeth which matures to form tartar. The plaque functions as a “home” to many bacteria. Dental cavity formation is a slow but continuous process. The process of plaque formation and decay is described in detail below.
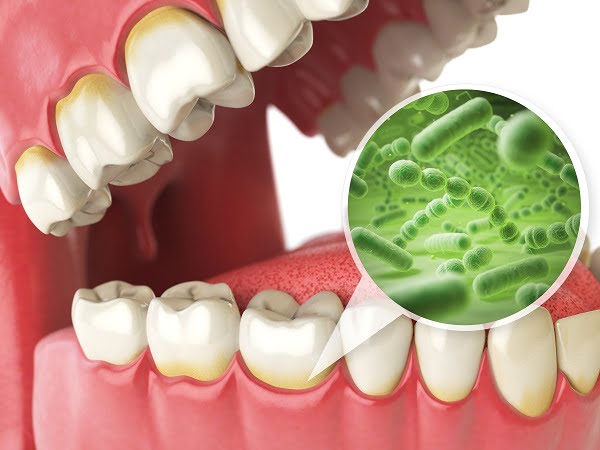
How does tooth decay (dental caries or dental cavities) happen?
- Plaque formation: Plaque, as described earlier, is a clear sticky film that deposits on the surface of teeth. Not cleaning teeth properly and eating lots of sugar can lead to plaque formation. Plaque that stays on teeth gets mineralized to form tartar which forms a shield for bacteria.
- Bacterial attack: Bacteria present in plaque produce acids which erode the hard layer of teeth (enamel). This erosion at first causes small holes on the top layer. This is the first stage of cavity formation. Once enamel gets worn out, the bacteria and acid reach next layer called dentin. The dentin layer being soft is less resistant to acid. In addition, it has tiny tubes that are directly linked with the tooth nerve.
- Teeth Decay: Ultimately, bacteria reaches inner tooth material that has nerves and blood vessels in it. The pulp gets inflamed and irritated due to effects of acid. The nerves are pressed which causes pain and discomfort.
Following are the most commonly involved bacteria in dental caries:
- Streptococcus Sobrinus
- Lactobacillus Acidophilus
- Streptococcus Mutans
- Actinomyces Species
- Nocardia Species
These bacteria are present in dental plaque but the concentration is too low to cause the problem. High concentration of sugar and poor dental hygiene causes the bacteria to increase in number and cause problems.
If left untreated, it can lead to pain, inflammation and tooth loss.
Read about treatment of dental cavities
These strains can be inherited by a child from their mother or caretaker. Depending upon oral hygiene habits and shape of the teeth, people may be differently susceptible to dental caries. The root causes of dental caries are described below.
Oral Hygiene
The main reason for developing dental caries is not taking proper care of your oral hygiene.
The food we eat mixes with saliva to form plaque which gets deposited on the surface of teeth. This plaque works as a breeding ground for the bacteria. Bacteria present in the mouth produce acids that cause damage to teeth’s enamel leading to tooth decay.
Regular brushing prevents deposition of plaque around teeth. Less plaque means low risk of tooth decay. Proper dental care includes brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing. Brushing after every meal is ideal but not very practical for everyone. Brushing daily and using mouthwash maintains mouth cleanliness and control bacterial growth. Also, paying regular visits to the doctor is also of help.
Read what you can do to prevent formation of dental cavities
Sugary Food and Dental caries
Sugary foods are best friends to bacteria. The food we eat has some amount of sugar in it like glucose, fructose and sucrose.
The bacteria present in our mouth converts this sugar into acids by a process called as fermentation. These bacteria convert sugar and starch from the food into acids which dissolve minerals present in the hard enamel (teeth covering) of teeth crown.
The acid also consumes calcium and phosphate from enamel. The weak enamel collapses to form a cavity which advances to degrade teeth. Caries sometimes attacks the root of teeth after the recession of gum line. As the enamel degrades, pits are developed in the tooth.
Taking high sugar accelerates the process of cavity formation. Apart from sugary food, acidic food and drinks also accelerate tooth decay. Food like soda, fish and bread contains some basic amount of acid that can damage teeth. Carbonated beverages such as cold drinks and fruit juices are also acidic in nature. Just like sugary food, it can also degrade enamel.
Deep Tooth Crevices and Enamel Issues
People with enamel issues or people who have deep crevices are very likely to develop this problem. Deep crevices provide space for plaque to deposit which leads to bacterial growth. Dental sealants are used to prevent tooth decay in people with deep crevices.
The location of teeth is also a factor in tooth decay. Dental caries is more commonly seen in back teeth i.e. premolars and molars. These teeth have a lot of grooves and pits in them. Collection of food particles in these grooves lead to plaque formation. These molar and premolars are hard to clean and difficult to reach as compared to front teeth.
Tooth Grinding
Some people have a habit of grinding and clenching their teeth. They do not even realize that they are grinding their teeth.
Tooth grinding normally occurs when the person is asleep or during stressful conditions. It strips of the upper protective enamel layer of the tooth and leads to tooth decay. Often bite guards are suggested for people who grind teeth.
Genes and Age
Just like many other diseases, tooth decay is also hereditary. A person can inherit deep tooth crevices and enamel issues from their family. These people are highly prone to develop tooth caries and decay.
Another reason for the development of tooth caries is the age factor. It becomes more common with growing age. Common medical prescriptions which cause dry mouth like anti-allergic drugs and anti-depressants can also promote tooth decay.
Reduced Saliva flow
In most of the people suffering from dental decay, diseases affecting teeth are not the main cause of cavities. The teeth are made up of mineral which if exposed to the acidic environment will decay. As the enamel gets degraded, dentin and cementum (having lower mineral content) become more susceptible to caries.
Doctors state that saliva neutralizes the acid and help to inhibit plaque growth, thus people with dry mouth are at higher risk of tooth decay.
The person may have a dry mouth because of hereditary or because of some medical condition like diabetes mellitus, Sjögren’s syndrome and sarcoidosis.
Apart from medical conditions, there are certain medicines that promote dryness in the mouth and reduce saliva flow. The medications like methylamphetamine and Tetrahydrocannabinol work as a stimulant to drop down saliva formation in the mouth.
Radiation therapy of head and neck also damages cells in salivary glands which increase the likely chances of getting dental caries.
Fluoride Deficiency
According to researchers, fluoride can prevent and combat tooth decay. Fluoride provides strength to the enamel and makes teeth resistant against acids. The water we drink daily has fluoride in it. Toothpaste, these days, have recommended the level of fluoride in them to protect teeth from infection and cavities.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
People who drink alcohol and chew tobacco are at high risk of developing dental caries. Alcohol contains a high level of sugar in it which accelerates the problem. Its consumption leads to deposition of plaque and bacteria on teeth which cause cavities. Alcohol being dehydrating agent can severely damage teeth as it reduces saliva flow also.
Chewing tobacco and smoking is quite dangerous to teeth and oral health as it causes gingivitis and other periodontal diseases too. As the gum line recedes from tooth base, it exposes tooth roots which get easily demineralized by the acid.
Smokers are also at a very high risk of developing oral diseases and tooth decay. Some tobacco brands contain very high amount of sugar that increases the susceptibility of dental caries.
Other factors
Apart from taking diet high in sugar and consuming alcohol, many other factors can make you prone to dental caries. Some of these factors are listed below:
- Neonatal exposure to lead and cadmium
- Poverty and socio-economic status
Are you at risk of developing dental caries?
Following things make a person more prone to develop dental caries:
- Not taking care of your teeth
- Not seeing doctor regularly for checkups and cleaning
- Eating food high in sugar
- Not getting enough fluoride
- Dry mouth
- Having diabetes or Sjogren’s syndrome
- Anti-depressants and anti-allergens
- Smoking and tobacco chewing
- Heart burn
If you see any of the above-mentioned symptoms very often, you need to see a doctor immediately. He will guide you through treatment. Read about symptoms of tooth decay.