How is Urinary Incontinence Diagnosed?
- Updated on: Jun 26, 2024
- 4 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
It is important to determine the type of incontinence and its severity. The symptoms will give a clear idea of the type of incontinence. Your general practitioner will then recommend the treatment procedures accordingly.
Each and every detail of the illness should be told to the doctor. The diagnosis of urinary incontinence proceeds in the following way:
Medical History
The doctor will first ask questions related to the illness in order to get a clear idea about the type of incontinence, severity of the disease and underlying causes. The doctor may ask about the symptoms and the medical history including:
- Whether the patient leaks urine during cough, sneeze or while exerting any other type of physical pressure like during playing sports or cycling
- Whether the patient feels any pain during urination
- Whether the patient needs to go the toilet very frequently during day and/or night
- Whether the patient is at some other medications
- Whether the patient is consuming alcohol, caffeine and in what quantity
- Whether the patient smokes
- Whether the patient is under any stress or depression
Daily Bladder Diary
The doctor may ask the patient to maintain a diary for at least three days, which will record the useful information about the patient’s bladder habits. The dairy may include details like:
- Quantity of fluid intake
- Types of fluid intake
- Frequency of urine passed
- Quantity of urine passed
- Colour and odour of urine
- Episodes of incontinence experienced by patient in a day
- How many times urgency is experienced by the patient
The bladder dairy will provide information about the illness and its severity. Your doctor may ask you to go for further tests.
Tests and Examinations
After analyzing the bladder diary, the doctor may ask the patient to get some tests done. On or more of the following tests may be recommended:
Physical Examination
The health care professional physically examines the urinary system of the patient. This can be done in following ways:
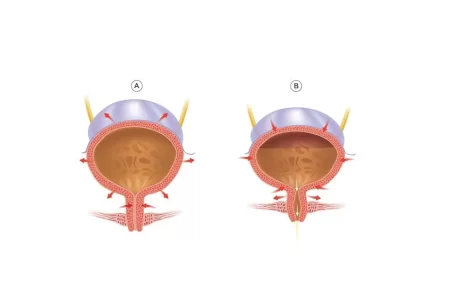
Pelvic exam
It refers to a visual and physical analysis of the pelvic area. The doctor examines the patient with a full bladder and asks him/her to cough. This test is known as cough stress test.
Any leakage means the person is suffering from incontinence. Then the doctor slides a gloved, lubricated finger into the vagina and checks for any prolapsed bladder (bladder that is no longer supported and descends loosely) or other physical problem that may be the cause of incontinence. Then the doctor may ask the patient to squeeze the pelvic floor muscles to determine the strength of the muscles.
Dipstick Test
If the symptoms are caused by urinary tract infection, the doctor may ask the patient to provide a urine sample for bacteria test. A chemically treated stick is dipped into the urine. If the stick changes color, bacteria are considered to be present in your urine. This test also checks the blood and protein levels in the urine.
Residual Urine Test
The test is done to check the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination. It is conducted through an ultrasound scan of the bladder. This test tells about the severity of the incontinence.
Pad Test
Pad test is done to check whether the leaked fluid is urine only. The doctor gives a medication to the patient that changes the color of the urine. If the leaked fluid on the pad changes color, it indicates that the fluid is urine. The pad is weighed before and after its use to check the severity of the urine loss.
Additional Tests
If the causes of incontinence are still not clear, your doctor may ask you for some additional tests. These additional tests are a bit costly. These are described here:
Cystoscopy
An instrument called endoscope is inserted in order to look inside the bladder. The test examines about the abnormalities of the bladder and urethra that may cause incontinence.
Urodynamic tests
These are a series of tests done one after the other in order to analyze the functioning of the bladder and the urethra. These tests:
- analyzes the pressure in the bladder by inserting a catheter (a hollow tube that collects urine from the bladder and leads to a drainage bag) into the urethra.
- analyzes the pressure in the stomach by inserting a catheter into the bottom.
- collects the patient’s urine into a machine that checks the amount and flow of urine.
Blood test
You may be asked to give a sample of blood. The sample is checked in the pathology lab (a lab that diagnoses the disease based on the analysis of blood and urine). The test will show if there is any problem with the kidney or if there is any other chemical imbalance in the body of the patient.
FAQs
Are there specific tests for diagnosing urinary incontinence?
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and may include tests like urinalysis, bladder diary, and urodynamic studies to assess bladder function.
Can medications cause urinary incontinence as a side effect?
Yes, certain medications can contribute to urinary incontinence. It's essential to inform healthcare providers about all medications to determine the cause and explore alternative options.
Is it necessary to see a specialist for urinary incontinence diagnosis?
While a primary care physician can diagnose and manage urinary incontinence, consulting a urologist or urogynecologist may be recommended for a more specialized evaluation.
How long does the diagnostic process for urinary incontinence typically take?
The duration varies, but it usually involves initial assessments and tests that can be completed in a few visits. Timely diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Can imaging tests like MRI or CT scans help diagnose urinary incontinence?
In most cases, imaging tests are not necessary for diagnosing urinary incontinence. However, they may be recommended in specific situations to rule out underlying conditions.