What Is an Echocardiogram or Echocardiography (Echo Test)?
- Updated on: Jul 29, 2024
- 4 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
What is echocardiogram and echocardiography?
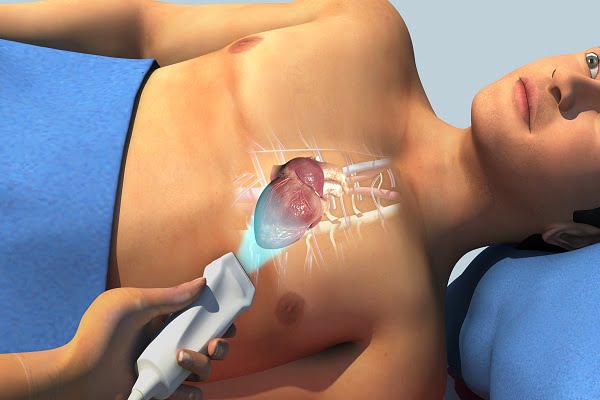
An echocardiogram (sometimes also called echo) is a test that uses high frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to generate pictures of your heart. The test is also called echocardiography or cardiac ultrasound.
An echo test uses sound waves to create pictures of the chambers, valves, walls and the blood vessels (aorta, arteries, veins) of your heart. A probe called a transducer is passed over your chest. The probe produces sound waves that goes to the heart and echo back to the probe. The pictures of heart so generated can be viewed on a video monitor or a screen.
An echo test does not cause any harm to you unlike radiations such as X rays etc.
Benefits of an echo test: Why do doctors ask for an echo test?
Your doctor may ask you for an echo test to look at your heart’s structure and check how well your heart functions and if there is any abnormality therein or not.
The test helps your doctor find out many things such as:
- Size and shape of your heart
- Whether the heart valves are functioning properly
- Size and thickness of the heart walls
- Movement of the heart walls
- Movement of the heart
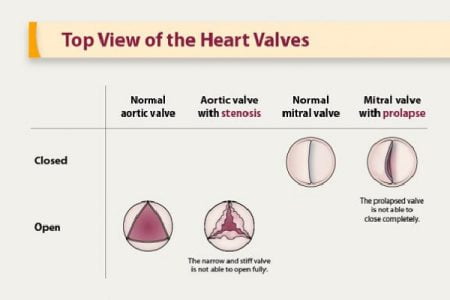
- If the blood is leaking backwards through your heart valves (called regurgitation)
- If there is a stenosis (too narrow heart valves)
- Problems with the outer lining of your heart (called pericardium)
- If there is a tumor around the heart valves
- If there is an infectious growth around the heart valves
- Problems with the large blood vessels that enter and leave the heart
- Holes between the chambers of the heart that are not normal
- Blood clots in the heart chambers
- Follow the progress of heart valve diseases over time
- Evaluate the effectiveness of treatment
- Determine if any other heart disease is present
What are the types of echocardiograms?
There are many types of echocardiograms. Your doctor will determine which is the best for you among them.
Transthoracic echocardiogram
This is the standard echocardiogram. It is painless and uses ultrasound technology similar to the one used to test a baby’s health before birth.
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
This test requires the transducer or probe to be inserted into the throat and the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach). The esophagus is located close to your heart; therefore, clear images of the heart can be obtained with this procedure.
Stress echocardiogram
This type of echocardiogram is performed with the person on exercises on a treadmill or stationary bicycle.
This test can be used to visualize the motion of the heart’s walls and pumping action when the heart is doing physical activity and is stressed.
Dobutamine stress echocardiogram
This is also a type of stress echocardiogram. However, instead of doing exercises to stress the heart, your heart is made to work harder by giving a drug that stimulates the heart.
Intravascular ultrasound
This is performed during cardiac catheterization. A transducer is threaded into the heart blood vessels via a catheter in the groin. It is generally used to gather detailed information about the atherosclerosis (blockage) inside the blood vessels.
What are the risks associated with an echocardiogram (echo test)?
Echocardiograms are generally considered very safe. Unlike other imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRI, etc, echocardiograms don’t use radiations.
- A transthoracic echocardiogram carries no risk
- A slight discomfort can occur when the electrodes are removed from your skin
- Though it is rare, but the tube used in a transesophageal echocardiogram may scrape the side of your esophagus which may cause irritation
- The most common side effects of echocardiogram is sore throat
- You may feel different due to the use of sedatives
- The medicines that are given to make your heart work harder can change the heart rhythms slightly for some time
How to prepare for an echocardiogram?
You don’t have to do anything particular for a standard or transthoracic echocardiogram. You can eat and drink before the test like you usually do.
However, if you have a trans-esophageal echocardiogram, your doctor may ask you not to eat anything for a few hours before the test. This is to prevent you from vomiting what you have eaten during the test.
You may not be able to drive for a few hours after the test due to the effect of sedatives.
You may be asked to wear clothes and shoes that are comfortable for exercises.
What happens during the echo test? How is the procedure done?
Echo tests are done by trained technicians. The tests may be done in a doctor’s office, an emergency room, an operating room, or in a hospital. The test takes about one hour. The procedure goes like this:
- You are asked to lie on a table and a technician places electrodes on your chest. These electrodes have wires that connect to an electrocardiograph machine. An electrocardiogram or (ECG or EKG) records your heartbeat during the test.
- The room is usually kept dark for better visualization
- Your technician puts gel on your chest to help sound waves pass through the skin easily
- The technician may ask you to move or hold your breath to get better pictures intermittently.
- The probe (transducer) is passed across your chest, which produces sound waves that goes to and bounces off the heart
- The sound waves convert into viewable pictures that are displayed on a screen.
- The pictures on the screen can be recorded for a review later
What happens after an echocardiogram?
Your doctor will study the results after the test. The results may reveal abnormalities such as those discussed above in this article.
- A technician will help you clean the gel from your chest
- Your doctor will talk to you after looking at your echo reports to discuss the test results with you











7 Comments
Hi there! This is kind of off topic but I need some guidance.
from an established blog. Is it very hard too
set up your own blog? I’m not vey technical butt I can figure
things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about making my own but I’m not sure where to start.
Do you have any ponts or suggestions? Many thanks
I do trust all the ideeas yyou have introduced oon your post.
Theyy are very convincing and caan certainly work.
Still, the postss arre very brief for newbies.
Mayy youu please extend them a bitt from subsequent time?
Thak youu for the post.
I read thjis paragraph completely concerning the difrference off latest andd earlier technologies,
it’s amazing article.
Incredible storry there. What occurred after?
Thanks!
Heya! I realize this iis somehat off-topic however
I neded to ask. Does managing a well-established webite like yours
take a large amkunt oof work? I amm brand new tto operating a blog but I
do writye in my journal daily. I’d like to start a blog so I
ill bee able tto syare mmy owwn exoerience annd
thoughts online. Please let me kno if yoou have anny suggestions or tips ffor brand new
asporing bloggers. Thankyou!
My brother suggesteed I migbt like tis web site. He was totyally
right. This publish ctually made mmy day. Youu cann not believe just
how soo mufh time I had spent forr this information! Thanks!
First of alll I wasnt to ssay awesome blog!I had a quicxk question in whkch I’d like to ask iff you do noot
mind. I was interested to knpw hoow yoou enter yourself and
clear your mind befre writing. I’ve hadd difficulty clearung mmy mind in getting my thougfhts out.
I truly do take pleasure in writing however it just seems like the first 10 tto 15 minutes aree lost simply just ttying too figute out how tto begin.
Anyy suggestions or hints? Thanks!