What Is Cirrhosis of the Liver?
- Updated on: Aug 7, 2024
- 5 min Read
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
Liver and Liver Cirrhosis – What is liver cirrhosis?
The liver is an important internal organ of the body. It is located in the upper right side of abdomen and below the ribs. Following are the essential functions performed by it:
- Bile production
- Storing sugar and vitamins
- Blood purification
- Blood-clotting proteins
- Detoxification
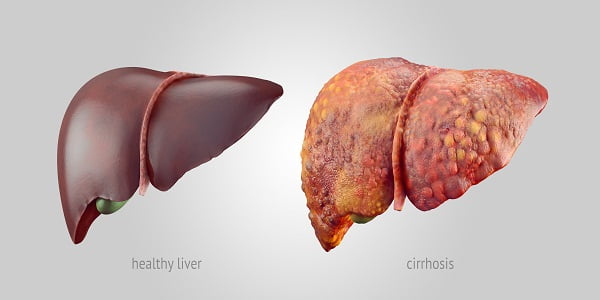
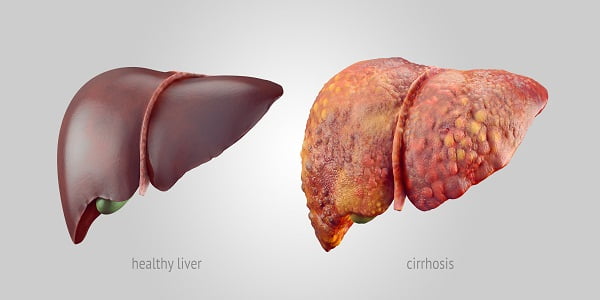
Liver cirrhosis can be described as severe scarring of liver tissue mainly observed at the final stages of chronic liver diseases. It is a leading cause of death in American countries and worldwide.
According to a research, it is more likely to affect men as compared to women.
How does cirrhosis of the liver develop?
Cirrhosis is a progressive disease i.e. it develops slowly over the course of many years. Continuous damage over a long period leads to this condition.
Cirrhosis is the late stage scarring of the liver. It occurs in response to liver damage as our liver has an ability to repair itself after damage.
Certain diseases and conditions injure and kill the healthy liver cells. The inflammation and healing process causes scar tissue formation. The living cells multiply in number to replace dying cells and maintain proper functioning. As the cirrhosis advances, more scar tissue is formed. Ultimately, the functioning of the liver is affected.
The buildup of scarring tissue leads to liver dysfunction and failure. The severity of condition increases with increase in scarred tissue. As the healthy liver tissue is replaced by fibrous scar tissue, clusters of new cells are formed which look like lumps. These lump-like structures are called as regenerative nodules.
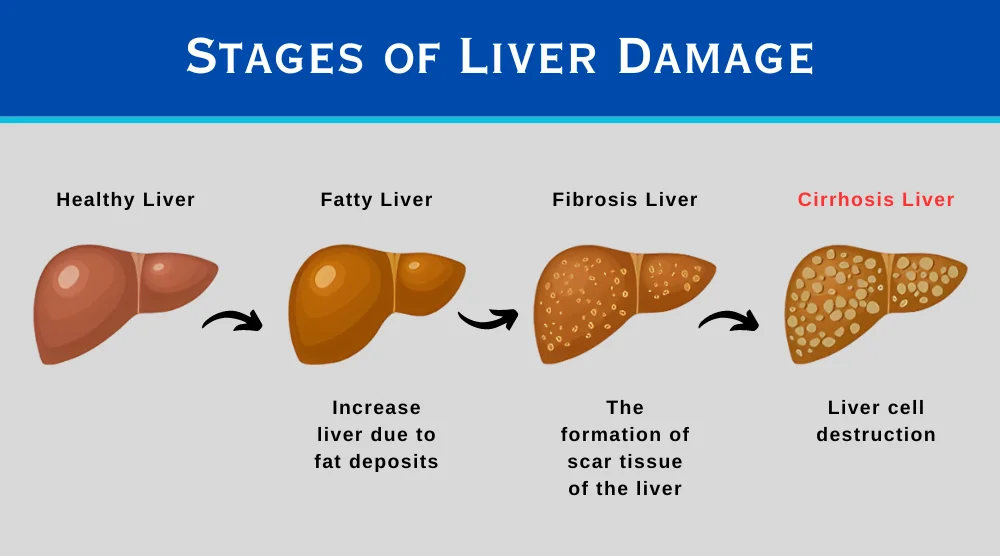
What causes cirrhosis of the liver?
Cirrhosis is mainly caused due to long-term exposure to various toxins like alcohol. Virus infection can be another reason for scarring.
In cirrhosis, the scar tissue slowly replaces healthy liver cells. The main reported causes are:
- Excessive use of alcohol
- Viral hepatitis B and C
- Fatty liver disease
The liver can repair itself in case of mild cirrhosis and continue to function properly. However, if the damage is severe, the repair can’t be done.
However, there might be other possibilities.
Read more about causes of cirrhosis of the liver.
People suffering from cirrhosis may also develop jaundice and other complications like fatigue and itching. The damage caused by cirrhosis can’t be reversed. However, early diagnosis and cause can be treated and further damaged can be stopped. The damage is never reversed but can be limited.
Fast facts about Liver Cirrhosis
Following are some quick facts about cirrhosis:
- Cirrhosis is a life-threatening condition. It is the fifth leading cause of death in England and Wales. More than 20,000 people die in the United States each year.
- Liver cirrhosis kills more people than diabetes and road death combined. The number of deaths caused by this disease increases per year.
- People of all ages are prone to this condition. However, people in between the age group of 24 to 44 are more susceptible to this disease.
- Alcoholism and obesity are the leading causes of this condition. In addition, the disease can be genetic.
- A normal healthy liver has a capability to regenerate itself and grow back after damage. However, any injury or condition that prevents it from regenerating can be a warning sign.
- The liver may get inflamed, enlarged and tender during early stages which show that the body is trying to fight off the infection and heal the injury. If the inflammation is continuous, the damage is irreparable.
- The loss of liver function requires immediate medical attention as the condition can be fatal.
- It may be sometimes very hard to self-diagnose liver dysfunction. It is important to see a doctor before it is too late.
- Many people do not show any initial symptoms. As the disease advances, symptoms like weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss and vomiting can be frequently observed.
- Complications may develop along with the liver failure. People suffering from cirrhosis also experience itching because of deposition of bile products in the skin.
- The treatments are generally directed towards halting the progression of the disease. Severe damages can’t be reversed.
- Avoiding alcohol and other drugs along with nutritional therapy can be helpful.
Why does cirrhosis cause problem?
The liver may get injured by a single short-term injury or by a regular injury for a long term. The liver may respond to each injury differently. The liver starts producing strands of scar tissue that surrounds nodules of healing cells.
The loss and dying of liver cells affect the normal functioning of the liver which can create various problems. Some of these can be severe and life-threatening.
Some of the problems are as follows:
Portal hypertension
The regenerative nodules caused due to the repairing of scar tissues can compress the veins within the liver. This causes a rise in blood pressure within the liver. The condition is called as portal hypertension.
This stops the blood flow in the intestines and other abdominal organs. Ultimately, portal hypertension causes bleeding in intestines and accumulation of fluid in the body. High blood pressure occurs in almost all the liver cirrhosis patients.
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Sometimes, portal hypertension causes blood to flow in the veins of the stomach and other abdominal organs. As a result, veins enlarge and form varicose veins. A common symptom of gastrointestinal bleeding is blood in vomiting.
Infection
Cirrhosis makes the person susceptible to many other infections. This is because the injured liver cannot form proteins which are required to fight off any infection.
Fluid retention (ascites)
Portal hypertension is related to several other complications. High blood pressure in the blood vessels of the liver, forcing the fluid to sip out of them. As a result, fluid is pooled in the abdominal cavity.
In some cases, several liters of fluid is retained in the abdomen that causes pain and swelling. Sometimes, the excess of fluid collects in lungs and legs too. Hence, the person may also face difficulty in breathing.
Hepatorenal syndrome
Due to fluid retention in the body and some other unknown reasons, liver failure sometimes leads to malfunctioning of kidneys too. The kidneys try to retain and hold more and more water in them. This results in abnormal functioning of kidneys. Often this condition is a slow process but can cause chronic kidney disease.
Hepatic encephalopathy
One of the main functions of the liver is to get rid of unwanted toxins from the body. Hepatic encephalopathy is a condition caused due to over buildup of toxins in the bloodstream. This is due to the fact that scarred liver is unable to get rid of it. These toxins can cause a patient to behave abnormally.
The patient may lose his/her capability to take care of self and others. Sometimes people can get very sleepy and don’t wake up that easily.
There is no cure for cirrhosis, but removing the cause can slow down the progression of the disease. If the damage is not too severe, the liver can repair itself over time.