What Is Urinary Incontinence?
- Updated on: Jan 22, 2024
- 5 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 3, 2019

Definition of Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence refers to a condition of involuntary leakage of urine. It happens when a person loses control over his bladder, thus, resulting in the unintentional passing of urine. In some cases, the bladder empties completely (due to uncontrolled flow), while in other cases, a person may experience only minor leakages.
It is a very embarrassing situation both emotionally and physically, especially when the person experiences it in public. It occurs when the muscles of the bladder that control the flow of urine, relax and contract involuntarily.
Gender-based affects
It is a very common problem that affects millions of people in today’s world. It can be temporary or long-term (chronic). People above 40 are more likely to suffer from this condition. And women are twice as susceptible as men to this body disorder. An estimated study shows that 30 percent of women above 30 are suffering from it while the percentage of men affected is only 1.5-5.
The effects of urinary incontinence are however different at different ages. Both men and women have different risks at different points of time. In childhood, bladder control is seen earlier in girls than boys. And bedwetting is more common in boys at an early age.
However, adult men have full control over their bladder while adult women suffer from urinary incontinence (UI) more likely. This is because adult women undergo a lot of changes in their bodies during pregnancy and delivery. Men suffer from urinary incontinence too but less likely than women. Though it occurs more often with age, it is not an inevitable part of aging.
If a person is suffering from urinary incontinence, he/she should immediately see the doctor. In many cases and with most people, simple positive changes in the lifestyle and proper medication can ease discomfort or stop urinary incontinence.
Types of urinary incontinence
There are many different types of urinary incontinence:
Stress incontinence
What is stress incontinence?
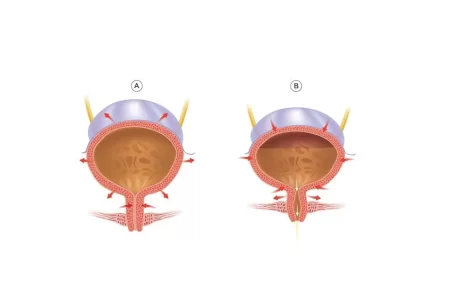
Stress incontinence is the involuntary leakage of the urinary in the presence of a trigger that is generated due to stress. The term “stress” refers to physical pressure rather than mental stress. Stress incontinence occurs because of the poor closure of the bladder. When the muscles that control the urination process are placed under some sudden extra pressure, the person may urinate involuntarily.
What causes stress incontinence?
The following actions may trigger stress incontinence:
- a sudden cough
- sneezing
- laughing
- exercise including cycling
- heavy lifting
Who is affected by stress incontinence?
This most common type of urinary incontinence is seen especially among women. It can occur at any stage of life. The physical change of pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause weakens the pelvic muscles or ligaments that are responsible for bladder support. And so it is more likely to occur at such stages of life in women.
Urge incontinence
What is urge incontinence?
In this type of incontinence, a person suddenly feels an urge to empty his bladder. It occurs due to an overactive bladder. It is also known as reflex incontinence.
It is the second most common type of urinary incontinence. People suffering from urge incontinence suddenly feel an urge to urinate that cannot be delayed or stopped. It is due to a sudden, involuntary contraction of the muscular wall of the bladder.
When the urge to urinate appears, the person cannot hold the urine for longer. He or she has a very short time before the urine is released. The person may urinate more than eight times a day (which is not counted as normal) and twice overnight.
Urge continence occurs more due to mental reflex than physical reflex.
What causes urge incontinence?
The urge to urinate may be caused by:
- change in sitting or standing position
- the sound of running water (for some people)
- damage to the nerves of the bladder, the nervous system, or the muscles themselves makes the muscles of the bladder relax and contract involuntarily
Who is affected by urge incontinence?
This condition occurs twice as frequently in women as in men and increases with age.
Overflow incontinence
What is overflow incontinence?
If a person cannot empty his bladder at a time, he may dribble urine. This happens when a person is suffering from overflow incontinence.
What causes overflow incontinence?
In women, weak bladder muscles, a blocked urethra, a prolapsed pelvic organ, or kidney stones can cause overflow incontinence. It is due to poor bladder contraction or blockage of the urethra.
Who is affected by overflow incontinence?
It is more common in men who are having
- prostate gland problems (an enlarged prostate gland can obstruct the bladder)
- a damaged bladder
- a blocked urethra
The bladder cannot hold as much urine as the body is making causing the overflow, and/or the bladder cannot empty, causing small amounts of urinary leakage. Patients will need to urinate frequently, and they may experience constant dripping of urine from the urethra.
Functional incontinence
What is functional incontinence?
With functional incontinence, the person knows that there is a need to urinate, but cannot make it to the bathroom in time. This may be due to medications or health problems which makes it difficult for the patient to reach the bathroom on time. Functional incontinence is not related to bladder and urethra problems.
What causes functional incontinence?
Generally, functional incontinence is caused by poor eyesight, poor mobility, dementia (brain disease affecting memory and thinking capability), poor dexterity (inability to unbutton pants in time), or unwillingness to go to the bathroom.
It is also a side effect of other diseases like arthritis, and Alzheimer’s.
Who is affected by functional incontinence?
This type of incontinence is more common among elderly people suffering from diseases like arthritis or Alzheimer’s. It is common in nursing homes and old age homes.
Transient incontinence
What is transient incontinence?
It is a temporary form of urinary incontinence that lasts a short time. It is usually caused by medications or a temporary condition.
What causes transient incontinence?
It is caused by a temporary medical condition such as:
- a urinary tract infection (UTI) —It irritates the bladder, and creates a strong urge to urinate
- caffeine or alcohol consumption—it can cause rapid filling of the bladder
- chronic coughing—it can put pressure on the bladder
- constipation—hard stool in the rectum can put pressure on the bladder
- medication—some medications can increase the production of urine such as medicines used to control blood pressure
- restricted mobility
Who is affected by transient incontinence?
People suffering from high blood pressure, diabetes, severe constipation, inflamed bladder, irritated urethra or vagina are more likely to suffer from this type of incontinence.
Mixed incontinence
What is mixed incontinence?
It occurs when a patient experiences both stress and urge incontinence at the same time. It can include leakage of urine initiated by a trigger and a strong, sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate immediately.
What causes mixed incontinence?
The same factors that trigger stress and urge incontinence are involved in mixed incontinence. Weakened pelvic floor muscles, poor connective tissue with activities increase physical pressure in the abdomen (stress incontinence), and abnormal nerve signals trigger inappropriate contractions of the muscles in the bladder wall, creating uncontrollable urges.
Who is affected by mixed incontinence?
Most people who have incontinence have mixed incontinence.
Gross total incontinence
What is gross total incontinence?
When a person completely loses control over his urine, he is suffering from gross total incontinence. In this condition, either the person leaks urine continuously or periodically large amounts of urine in an uncontrollable manner.
What causes gross total incontinence?
Anatomic abnormalities or a severe injury can result in this incontinence.
Who is affected by gross total incontinence?
People who are born with a defect may have an injury to the spinal cord or urinary system or may have a hole (fistula) between the bladder and the vagina.
FAQs
Does urinary incontinence only affect older individuals?
No, urinary incontinence can affect people of all ages. While it's more prevalent in older adults, factors like pregnancy, obesity, and certain medical conditions can contribute to its occurrence at any age.
Can urinary incontinence be prevented through lifestyle changes?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular pelvic floor exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated, can reduce the risk of urinary incontinence.
Is urinary incontinence a permanent condition?
Not necessarily. Many cases of urinary incontinence are treatable or manageable. Seeking timely medical advice and following recommended treatments can significantly improve or resolve symptoms.
Are there different types of urinary incontinence?
Yes, there are various types, including stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and overflow incontinence. Identifying the specific type is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Can certain foods and drinks worsen urinary incontinence symptoms?
Yes, some foods and beverages, such as caffeine and spicy foods, can irritate the bladder and worsen urinary incontinence symptoms. Modifying dietary habits may help manage symptoms.