Blood Pressure Measurement: How to Measure Blood Pressure?
- Updated on: Jun 28, 2024
- 4 min Read
By
- Published on Oct 3, 2019
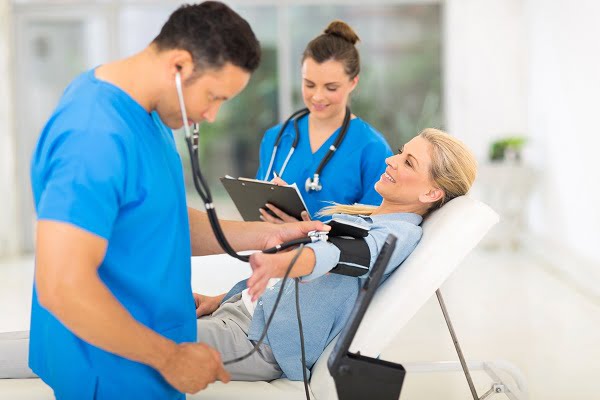
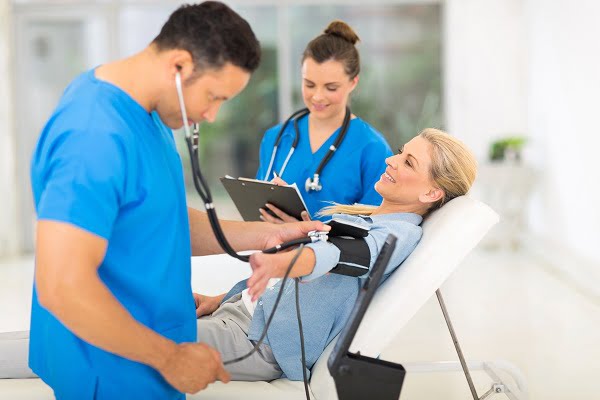


Blood pressure can be measured manually or automatically. Both of the methods are discussed below:
How to measure blood pressure manually: Instruments for measuring the blood pressure
The steps of measuring blood pressure manually are given below:
Choosing the right blood pressure apparatus
The blood pressure instruments needed for measuring the blood pressure are:
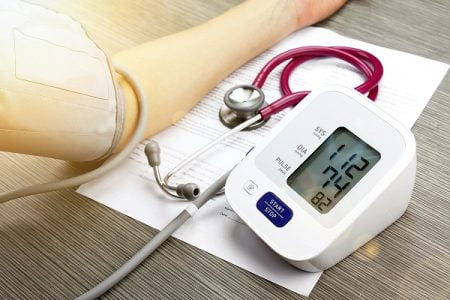
Sphygmomanometer
It is also known as blood pressure meter, blood pressure machine or blood pressure monitor. It is used to measure blood pressure. The blood pressure checker can be an aneroid or mercury column sphygmomanometer or an automated device with a manual inflate mode.
There are a variety of blood pressure monitors that are used these days. Some of them are:
- Upper arm blood pressure monitors – most recommended
- Wrist blood pressure monitors – effective for travelers
- Finger blood pressure monitor
- 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitor
A blood pressure cuff
A blood pressure cuff is used to take blood pressure. The cuff has an inflatable rubber blatter that is fastened to the upper arm of the patient. A pressure meter gives the value of the cuff’s pressure. Blood pressure cuffs are inflated using a small, handheld air pump connected to the cuffs. After the cuff has been inflated, the air pressure can be slowly decreased by an air valve.
A stethoscope
The stethoscope is an instrument that is used to listen to arterial blood flow sounds produced within the body. It consists of a diaphragm, metal and rubber tubing, and earpieces.
More: Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
More: Causes, Risk Factors and symptoms of Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Preparing the patient
In order to measure accurate blood pressure, make sure that the patient is relaxed. Allow the patient to relax for 5-10 minutes before the first reading. The patient should sit upright leveling the upper arm with their heart and feet flat on the floor. Remove clothing from the arm that might interfere with the BP cuff or may constrict blood flow in the arm. Avoid talking with the patient during the reading as it can affect the reading.
Choose the proper BP cuff size
Choosing the correct size of the cuff is very important because most measurement errors occur by using the wrong size cuff. The accurate size of the cuff can be determined as:
- Wrap the cuff around the patient’s arm
- With the help of the INDEX, line check whether the patient’s arm circumference falls within the RANGE area
- If not, choose the appropriate smaller or larger cuff according to the result of the second step
Place the BP cuff on the patient’s arm
Locate the brachial artery of the patient and position the BP cuff in such a way that the ARTERY marker points to the brachial artery. Wrap the BP cuff around the arm.
Position the stethoscope
On the same arm, palpate the arm at the antecubital fossa (crease of the arm). Locate the strongest pulse sounds. Place the stethoscope over the brachial artery at this location.
Inflate the BP cuff
Start pumping the cuff bulb while listening to the pulse sounds. Continue pumping the cuff. A point will reach where no sound will be heard through the stethoscope. This is the point where the pumping should be stopped. At this point, the meter should read 30 to 40 mmHg above the person’s normal BP reading. If this value is unknown, continue again and inflate the cuff to 160 – 180 mmHg. (If pulse sounds are heard right away, inflate to a higher pressure.)
Slowly Deflate the BP cuff
Begin deflating the cuff. The pressure should fall at 2 – 3 mmHg per second. Pressure greater than this may result in an inaccurate measurement.
Listen to the Systolic Reading
The first rhythmic sound heard as blood begins to flow through the artery is called the patient’s systolic pressure. This may resemble a tapping noise at first.
Listen for the Diastolic Reading
Continue to listen to the sound. The sound fades slowly as the BP cuff pressure drops. Diastolic reading is the reading of the gauge reading when the rhythmic sounds stop.
Double Check for Accuracy
In order to be sure about the reading, it is recommended to take the reading with both arms and then calculating the average of the readings. Wait for about five minutes between readings. Typically, blood pressure is higher in the mornings and lower in the evenings.
Precautions while measuring the blood pressure
- Aneroid and digital manometers may require periodic calibration for accurate results.
- Larger cuffs are recommended for obese or heavily muscled subjects.
- Smaller cuffs are recommended for pediatric patients.
- In case of pediatric patients, a lower blood pressure may also sometimes indicate the presence of hypertension.
- Avoid placing the cuff over clothing as it may give inaccurate results.
- Always flex and support the subject’s arm for correct reading.
How to measure blood pressure using the automated blood pressure machine?
Automated blood pressure machine is the easiest to use and they are most helpful to people having hearing impairments. These types of blood pressure cuffs have a digital blood pressure monitor. This automatic blood pressure monitor displays the blood pressure reading on a screen.
Automatic blood pressure machine is recommended for at-home use because of the portable blood pressure monitor. The instructions on how to use the automatic machine are given in a leaflet that comes along with the machine.